티스토리 뷰
Paper/TTS
[Paper 리뷰] DMOSpeech: Direct Metric Optimization via Distilled Diffusion Model in Zero-Shot Speech Synthesis
feVeRin 2025. 12. 22. 13:44반응형
DMOSpeech: Direct Metric Optimization via Distilled Diffusion Model in Zero-Shot Speech Synthesis
- Diffusion model은 iterative denoising process로 인해 computationally intensive 함
- DMOSpeech
- Distilled diffusion-based model을 활용하여 teacher 보다 더 빠른 추론 속도를 달성
- Connectionist Temporal Classification, Speaker Verification loss에 대한 end-to-end optimization을 지원
- 논문 (ICML 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- SpeechX, MaskGCT와 같은 large-scale Text-to-Speech (TTS) model은 우수한 합성 성능을 보이고 있음
- 이때 consistent quality와 speaker similarity를 보장하려면 relevant perceptual metric을 optimize 해야 함
- BUT, NaturalSpeech2, YourTTS와 같은 기존 TTS model은 non-differentiable component로 인해 end-to-end optimization의 한계가 있음 - 특히 최근의 end-to-end TTS model은 iterative sampling을 활용하므로 direct optimization을 적용하기 어려움
- 대표적으로 F5-TTS는 iterative sampling을 위해 16 step이 필요하므로 gradient instability가 존재함
- 추가적으로 diffusion process의 direct optimization은 low noise-level에서만 intelligible speech를 생성할 수 있으므로 higher noise level의 perceptual metric에는 uninstructive 함
- 이때 consistent quality와 speaker similarity를 보장하려면 relevant perceptual metric을 optimize 해야 함
-> 그래서 TTS model의 end-to-end direct metric optimization을 위한 DMOSpeech를 제안
- DMOSpeech
- Distribution Matching Distillation을 활용해 end-to-end diffusion TTS model의 sampling step을 절감
- Noise input에서 speech output으로의 direct graident pathway를 구성
- 이를 기반으로 Speaker Verification (SV) loss와 Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) loss를 활용해 speaker similarity와 Word Error Rate를 directly optimize
< Overall of DMOSpeech >
- Distribution Matching Distillation과 SV, CTC loss의 direct metric optimization을 활용한 end-to-end TTS model
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 성능을 달성
2. Method
- Preliminary: End-to-End Latent Speech Diffusion
- DMOSpeech는 DiTTo-TTS의 end-to-end latent speech diffusion framework를 기반으로 함
- 먼저 audio length $T$, latent AutoEncoder $\mathcal{E}$에 대해 raw audio waveform $\mathbf{y}\in\mathbb{R}^{1\times T}$는 latent representation $\mathbf{x}_{0}=\mathcal{E}(\mathbf{y})$로 encoding 됨
- Latent AutoEncoder는 DAC를 기반으로 Residual Vector Quantization을 Variational AutoEncoder loss로 replace 하여 얻어짐 - Ground-truth latent distribution을 $p_{data}$라고 하자
- Diffusion process는 noise schedule을 따라 continuous time $t\in[0,1]$에 대해 $\mathbf{x}_{0}\sim p_{data}$에 noise를 add 함
- 이때 noise schedule은 signal, noise를 control 하는 $\alpha_{t},\sigma_{t}$로 구성된 Shifted Cosine Noise Schedule을 사용함
- Training 시 model은 latent representation에 add 된 noise를 remove 하는 방법을 학습함
- Latent variable $\mathbf{x}_{0}$와 noise $\epsilon\sim \mathcal{N}(0,I)$가 주어지면, time step $t$의 noisy latent $\mathbf{x}_{t}$는 $\mathbf{x}_{t}=\alpha_{t}\mathbf{x}_{0}+\sigma_{t}\epsilon$과 같이 얻어짐
- 여기서 논문은 binary prompt mask $\mathbf{m}$을 사용하여 prompt에 해당하는 region에서 original value를 preserve 함 - 그러면 element-wise multiplication $\odot$에 대해 noisy latent $\mathbf{x}_{t}$는 $\mathbf{x}_{t}\leftarrow \mathbf{x}_{t}\odot (1-\mathbf{m})+\mathbf{x}_{0}\odot \mathbf{m}$과 같이 adjust 됨
- Binary mask $\mathbf{m}$은 $\mathbf{x}_{0}$ length의 $0\%$에서 $50\%$를 mask 하도록 random sample 됨 - 이후 reparameterized velocity $\mathbf{v}=\alpha_{t}\epsilon-\sigma_{t}\mathbf{x}_{0}$를 정의할 수 있고, ProDiff와 같이 training objective로 사용할 수 있음
- Latent variable $\mathbf{x}_{0}$와 noise $\epsilon\sim \mathcal{N}(0,I)$가 주어지면, time step $t$의 noisy latent $\mathbf{x}_{t}$는 $\mathbf{x}_{t}=\alpha_{t}\mathbf{x}_{0}+\sigma_{t}\epsilon$과 같이 얻어짐
- 결과적으로 논문은 text embedding $\mathbf{c}$, prompt mask $\mathbf{m}$, time step $t$에 condition 된 noisy latent $\mathbf{x}$가 주어지면 $\phi$로 parameterize 된 diffusion Transformer model $f_{\phi}$를 training 하여 $\mathbf{v}$를 predict 함:
(Eq. 1) $\mathcal{L}_{diff}(f_{\phi};p_{data}) =\mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{x}_{0}\sim p_{data}, t\sim \mathcal{U}(0,1), \epsilon\sim \mathcal{N}(0,I)}\left[ \left|\left| \mathbf{v}-f_{\phi}\left( \mathbf{x}_{t};\mathbf{c},\mathbf{m},t\right)\right|\right|_{2}\right] $ - 추론 시 model은 target speech의 total duration $L$에 대해, fixed size $[d,L]$을 가진 noise $\mathbf{z}\sim \mathcal{N}(0,I)$를 사용함
- $L$은 target text의 phoneme 수에 speaking rate를 multiply 하여 얻어짐
- 먼저 audio length $T$, latent AutoEncoder $\mathcal{E}$에 대해 raw audio waveform $\mathbf{y}\in\mathbb{R}^{1\times T}$는 latent representation $\mathbf{x}_{0}=\mathcal{E}(\mathbf{y})$로 encoding 됨
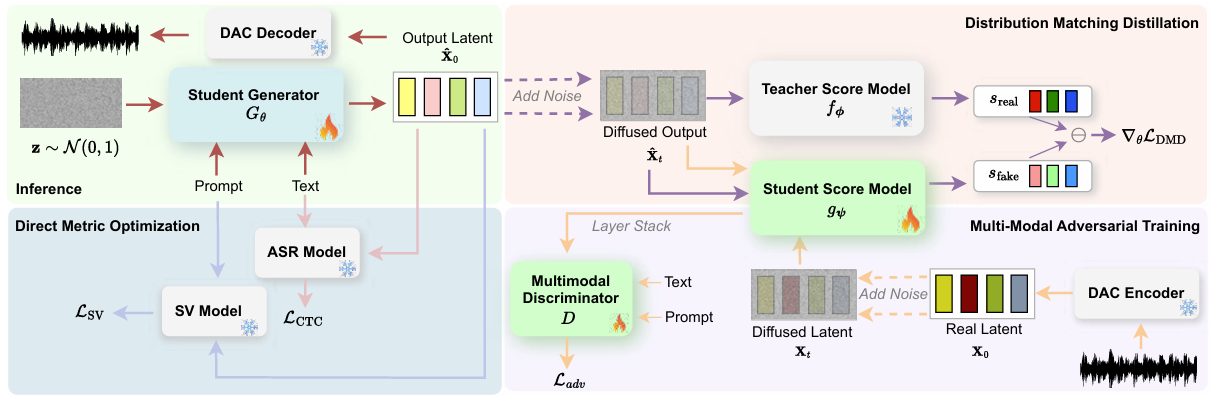
- Improved Distribution Matching Distillation
- 논문은 Distribution Matching Distillation (DMD2)를 사용해 teacher model을 distill 하여 fast sampling과 direct metric optimization을 지원함
- Background on Distribution Matching Distillation
- DMD는 student generator $G_{\theta}$를 training하여 forward diffusion process 이후의 data distribution $p_{data}$와 match 하는 distribution의 sample을 생성하는 것을 목표로 함
- 이때 objective는 time $t\in[0,1]$에 대해 diffused student generator output $p_{\theta,t}$와 diffused real data $p_{data,t}$ 간의 Kullback-Liebler (KL) divergence를 minimize 함:
(Eq. 2) $ D_{KL}\left(p_{\theta,t}||p_{data,t}\right)=\mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{x}\sim p_{\theta,t}}\left[ \log\left(\frac{p_{\theta,t}(\mathbf{x})}{p_{data,t}(\mathbf{x})}\right)\right]= -\mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{x}\sim p_{\theta,t}}\left[\log \left(p_{data,t}(\mathbf{x})\right)-\log \left(p_{\theta,t}(\mathbf{x})\right)\right]$ - 그러면 DMD loss는 $\mathcal{L}_{DMD}=\mathbb{E}_{t\sim\mathcal{U}(0,1)}\left[D_{KL}\left(p_{\theta,t}||p_{data,t}\right)\right]$와 같음
- DMD는 $G_{\theta}$를 gradient descent를 통해 학습하므로, formulation은 generator parameter $\theta$에 대해 얻어짐
- 이때 해당 formulation은:
(Eq. 3) $\nabla_{\theta}\mathcal{L}_{DMD}=-\mathbb{E}_{t,\mathbf{x}_{t},\mathbf{z}}\left[\omega_{t}\alpha_{t}\left(s_{real}(\mathbf{x}_{t},t) -s_{\theta}(\mathbf{x}_{t},t)\right)\frac{dG}{d\theta}\right]$
- $\mathbf{x}_{t}$ : $\mathbf{z}\sim\mathcal{N}(0,I)$에 대한 generator output $\mathbf{x}_{0}=G_{\theta}(\mathbf{z})$의 diffused version
- $s_{real}(\mathbf{x}_{t},t),s_{\theta}(\mathbf{x}_{t},t)$ : 각각 diffused data distribution, student output distribution의 score function에 대한 neural network approximation
- $\omega_{t}$ : weighting factor
- TTS task에서 generator $G_{\theta}$는 input text $\mathbf{c}$와 speaker prompt에 condition 된 latent speech representation $\mathbf{x}_{0}$를 생성함
- Teacher diffusion model $f_{\phi}$는 real data distribution에 대한 score function $s_{real}$로 사용됨 - 추가적으로 논문은 distilled generator output distribution $p_{\theta}$의 score를 approximate 하기 위해 다른 diffusion model $g_{\psi}$를 (Eq. 1)을 따라 training 함
- 여기서 score는 다음과 같이 estimate 됨:
(Eq. 4) $s(\mathbf{x}_{t},t,\hat{\mathbf{x}}_{0})=-\frac{\mathbf{x}_{t}-\alpha_{t}\hat{\mathbf{x}}_{0}}{\sigma^{2}_{t}}$ - $\hat{\mathbf{x}}_{0}$는 diffusion model $h$의 $\mathbf{x}_{0}$에 대한 estimation으로써:
(Eq. 5) $\hat{\mathbf{x}}_{0}=\frac{\mathbf{x}_{t}-\sigma_{t}h\left(\mathbf{x}_{t};\mathbf{c},\mathbf{m},t\right)}{\alpha_{t}}$
- $\hat{\mathbf{x}}_{0}^{real}$의 경우 $h=f_{\phi}$이고, $\hat{\mathbf{x}}_{0}^{fake}$의 경우 $h=g_{\psi}$
- $s_{real}(\mathbf{x}_{t},t)=s(\mathbf{x}_{t},t,\hat{\mathbf{x}}_{0}^{real})$, $s_{\theta}(\mathbf{x}_{t},t)=s(\mathbf{x}_{t},t,\hat{\mathbf{x}}_{0}^{fake})$ - $G_{\theta},g_{\psi}$의 parameter는 teacher diffusion model parameter $\phi$로부터 initialize 됨
- 여기서 score는 다음과 같이 estimate 됨:
- DMD2 for Speech Synthesis
- One-step student model은 teacher model이 생성하는 acoustic detail을 capture 할 computational capacity가 부족하므로 noticeable artifact가 발생할 수 있음
- 따라서 논문은 DMD2를 채택하여 student generator $G_{\theta}$를 noise level $t$에 conditioning 함 - DMD2의 해당 conditioning을 통해 model은 pre-defined time step $t\in\{t_{1},...,t_{N}\}$에 대해 noisy counterpart $\mathbf{x}_{t}$로부터 clean latent speech representation $\mathbf{x}_{0}$을 estimate 할 수 있음
- 먼저 time step $t_{n}$에 대해 student model은 estimate $\hat{\mathbf{x}}_{0}^{n}=G_{\theta}[\mathbf{x}_{t_{n}};\mathbf{c},\mathbf{m},t_{n}]$을 생성하고
- 이를 re-noise 하여 next time step의 input $\mathbf{x}_{t_{n+1}}$을 얻음:
(Eq. 6) $\mathbf{x}_{t_{n+1}}=\alpha_{t_{n+1}}\hat{\mathbf{x}}_{0}^{n}+\sigma_{t_{n+1}}\epsilon,\,\,\, \epsilon \sim\mathcal{N}(0,I)$
- 해당 process는 decreasing noise level $\sigma_{t_{n+1}}<\sigma_{t_{n}}$에서 $\mathbf{x}_{0}$의 progressively less noisy version을 생성함 - 특히 논문은 4-step model을 위해 teacher의 full-range $t\in[0,1]$에 mapping 된 schedule $\{1.0,0.75, 0.50, 0.25\}$를 사용함
- 추가적으로 training 중에 one-step inference를 simulate 하여 training/inference mismatch를 minimize 함
- 이때 ground-truth의 noisy version $\mathbf{x}_{t_{n}}=\alpha_{t_{n}}\mathbf{x}_{0}+\sigma_{t_{n}}\epsilon$을 input으로 사용하지 않고, noise level $\sigma_{n-1}>\sigma_{n}$에서 noisy ground-truth $\mathbf{x}_{t_{n-1}}$에 대한 student prediction의 noisy version $\alpha_{t_{n}}G_{\theta}(\mathbf{x}_{t_{n-1}};\mathbf{c},\mathbf{m},t_{n-1})+\sigma_{t_{n}}\epsilon$을 사용함
- Student model의 성능을 향상하기 위해 Adversarial Training을 추가적으로 도입함
- 이때 generated speech는 text의 semantic content와 prompt speaker style을 strictly adhere 해야 함
- 이를 위해 논문은 adversarial discriminator를 conditional multimodal discriminator로 modify 함 - Discriminator $D$는 Conformer에 기반해 student score network $g_{\psi}$의 모든 Transformer layer의 stacked feature와 text embedding $\mathbf{c}$, prompt mask $\mathbf{m}$, noise level $t$를 input으로 사용함
- 이때 discriminator는 LSGAN loss로 training 됨:
(Eq. 7) $\mathcal{L}_{adv}(G_{\theta};D)=\mathbb{E}_{t,\hat{\mathbf{x}}_{t}\sim p_{\theta,t},\mathbf{m}}\left[ \left(D(\hat{\mathbf{x}}_{t};\mathcal{C})-1\right)^{2}\right]$
(Eq. 8) $\mathcal{L}_{adv}(D;G_{\theta})=\mathbb{E}_{t}\left[\mathbb{E}_{\hat{\mathbf{x}}_{t}\sim p_{\theta,t},\mathbf{m}}\left[ \left(D(\hat{\mathbf{x}}_{t};\mathcal{C})\right)^{2}\right]\right]+ \mathbb{E}_{t}\left[\mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{x}_{t}\sim p_{data,t},\mathbf{m}}\left[\left(D(\mathbf{x}_{t};\mathcal{C})-1\right)^{2}\right]\right]$
- $\mathcal{C}=\{\mathbf{c},\mathbf{m},t\}$ : conditional input
- $\hat{\mathbf{x}}_{t}=\alpha_{t}G_{\theta}(\mathbf{z};\mathcal{C})+\sigma_{t}\epsilon$ : time step $t$, $\mathbf{z}\sim\mathcal{N}(0,I)$의 student-generated speech $G_{\theta}(\mathbf{z};\mathcal{C})$에 대한 noisy version
- 이때 generated speech는 text의 semantic content와 prompt speaker style을 strictly adhere 해야 함
- One-step student model은 teacher model이 생성하는 acoustic detail을 capture 할 computational capacity가 부족하므로 noticeable artifact가 발생할 수 있음
- Direct Metric Optimization
- 논문은 zero-shot speech synthesis model을 evaluate 하기 위해 사용되는 speaker embedding cosine similarity (SIM)과 Word Error Rate (WER)을 directly optimize 함
- 먼저 WER을 개선하기 위해 Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) loss를 도입하여 input text를 synthesized speech와 character-level로 align 함:
(Eq. 9) $ \mathcal{L}_{CTC}=\mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{x}_{fake}\sim p_{\theta},\mathbf{c}}\left[-\log p(\mathbf{c}|C(\mathbf{x}_{fake}))\right]$
- $\mathbf{x}_{fake}$ : student-generated speech, $\mathbf{c}$ : text transcript, $C(\cdot)$ : pre-trained CTC-based ASR model - 이후 synthesized speech가 target speaker identity와 match 하도록 Speaker Verification (SV) loss를 도입함:
(Eq. 10) $\mathcal{L}_{SV}=\mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{x}_{real}\sim p_{data},\mathbf{x}_{fake}\sim p_{\theta},\mathbf{m}}\left[1-\frac{\mathbf{e}_{real}\cdot\mathbf{e}_{fake}}{\left|\left| \mathbf{e}_{real}\right|\right|\,\left|\left| \mathbf{e}_{fake}\right|\right|}\right]$
- $S$ : latent의 pre-trained speaker verification model
- $\mathbf{e}_{real}=S(\mathbf{x}_{real}), \mathbf{e}_{fake}=S(\mathbf{x}_{fake})$ : 각각 prompt, student-generated speech의 speaker embedding
- 먼저 WER을 개선하기 위해 Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) loss를 도입하여 input text를 synthesized speech와 character-level로 align 함:
- Training Objectives and Stability
- $G_{\theta}$에 대한 overall training objective는
- DMD와 adversarial loss를 SV, CTC loss와 함께 combine 하여 얻어짐:
(Eq. 11) $\min_{\theta}\mathcal{L}_{DMD}+\lambda_{adv}\mathcal{L}_{adv}(G_{\theta};D)+ \lambda_{SV}\mathcal{L}_{SV}+\lambda_{CTC}\mathcal{L}_{CTC}$ - $g_{\psi}, D$에 대한 training objective는:
(Eq. 12) $\min_{\psi}\mathcal{L}_{diff}(g_{\psi};p_{\theta}),\,\,\, \min_{D}\mathcal{L}_{adv}(D;G_{\theta})$ - 논문은 student generator $G_{\theta}$, student score estimator $g_{\psi}$, discriminator $D$를 서로 다른 rate로 update 하는 Altering Training Strategy를 사용함
- 즉, $G_{\theta}$를 한번 update 할 때마다 $g_{\psi}$를 5번 update 함
- 이를 통해 score estimator $g_{\psi}$가 generator distribution $p_{\theta}$의 dynamic change에 quickly adapt 할 수 있도록 함 - $D$의 경우 $G_{\theta}$와 동일한 rate로 update 함
- 즉, $G_{\theta}$를 한번 update 할 때마다 $g_{\psi}$를 5번 update 함
- $G_{\theta}, g_{\psi}$는 teacher parameter $\phi$로부터 initialize 되므로 learning rate를 teacher model의 final learning rate에 가깝게 설정하여 catastrophic forgetting과 training collapse를 방지함
- 특히 teacher model은 cosine annealing warmup scheduler를 통해 training 되므로, $G_{\theta}, g_{\psi}$에 high learning rate를 적용하면 pre-trained knowledge와 deviate 할 수 있음 - Balancing term의 경우 $\lambda_{adv}=10^{-3}$으로 설정함
- First 5000, 10000 iteration의 경우 $\lambda_{CTC}=0,\lambda_{SV}=0$으로 설정하고 이후에는 $\lambda_{CTC}=1, \lambda_{SV}=1$로 설정함
- DMD와 adversarial loss를 SV, CTC loss와 함께 combine 하여 얻어짐:
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : LibriLight
- Comparisons : StyleTTS, NaturalSpeech3, DiTTo-TTS, VoiceCraft, CLaM-TTS, XTTS
- Results
- 전체적으로 DMOSpeech의 성능이 가장 우수함

- Non-E2E model에 대해서도 DMOSpeech가 더 나은 성능을 보임

- RTF 측면에서도 DMOSpeech가 가장 빠름

- Emilia dataset에 대해서도 우수한 성능을 달성함

- Ablation Study
- 각 component는 성능 향상에 유효함
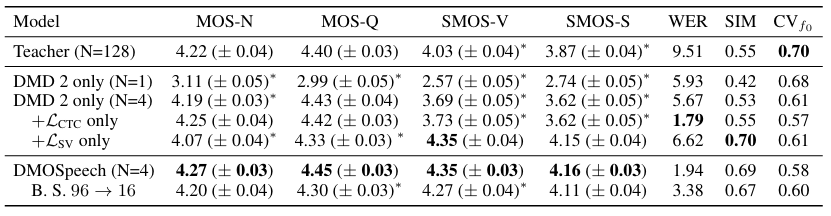
- Effects of Distribution Matching Distillation
- Speaker Verification loss를 도입하면 mode shrinkage를 방지할 수 있음

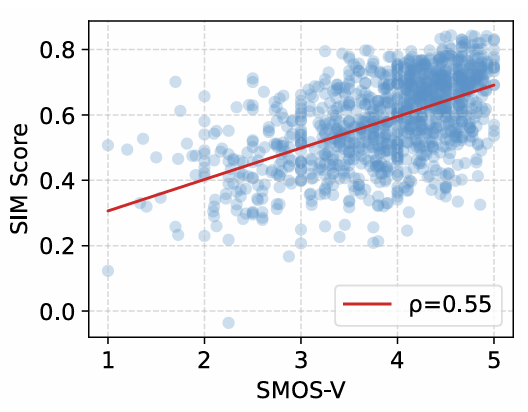
- Effect of Direct Metric Optimization
- DMO에 사용된 각 metric은 subjective rating에 대해 높은 correlation을 보임
반응형
'Paper > TTS' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

