티스토리 뷰
Paper/TTS
[Paper 리뷰] ZipVoice: Fast and High-Quality Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech with Flow Matching
feVeRin 2025. 12. 11. 13:17반응형
ZipVoice: Fast and High-Quality Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech with Flow Matching
- 기존의 large-scale text-to-speech model은 massive parameter로 인해 추론 속도가 느림
- ZipVoice
- Zipformer-based vector field estimator, text encoder를 도입하고 average upsampling-based initial speech-text alignment를 활용
- 추가적으로 sampling step을 줄이기 위해 flow distillation method를 도입
- 논문 (ASRU 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
-> 그래서 compact size, fast inference를 지원하는 zero-shot TTS model인 ZipVoice를 제안
- ZipVoice
- Zipformer-based backbone을 채택하여 model capacity를 확보
- Sub-optimal speech-text alignment로 인한 speech intelligibility 문제를 해결하기 위해 Average Upsampling strategy를 적용
- 추가적으로 Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG)의 additional inference pass를 mitigate 하기 위해 Flow Distillation method를 도입
< Overall of ZipVoice >
- Zipformer architecture를 기반으로 한 compact zero-shot TTS model
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 성능을 달성
2. Method
- Preliminary: Flow-Matching
- ZipVoice는 Conditional Flow Matching (CFM)을 기반으로 함
- CFM은 standard Gaussian distribution과 같은 simple initial distribution $p_{0}$를 real data distribution $q$에 approximate 한 complex data distribution $p_{1}$으로 transform 하는 방법을 학습함
- 이때 CFM model은 time-dependent vector field $v_{t}(x_{t};\theta),\,\, t\in [0,1]$로 parameterize 되고, 해당 model을 통해 $p_{0}$를 $p_{1}$으로 transition 하는 flow $\phi_{t}$를 construct 할 수 있음
- Optimal transport $\phi_{t}(x)=(1-t)x_{0}+tx_{1}$ 하에서 CFM loss는 다음과 같이 얻어짐:
(Eq. 1) $ \mathcal{L}_{CFM}=\mathbb{E}_{t,q(x_{1}),p_{0}(x_{0})}\left|\left| v_{t}(x_{t};\theta)-(x_{1}-x_{0})\right|\right|^{2}$
- $x_{t}=(1-t)x_{0}+tx_{1}$, $x_{0}$ : Gaussian noise, $x_{1}$ : data sample
- Sample 생성은 Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE)를 solve 하여 수행됨
- 대표적으로 Euler solver는 initial sample $x_{0}\sim p_{0}$에서 시작하여 sample을 target distribution $p_{1}$를 향해 iteratively update 함
- 즉, discrete time sequence $0=t_{0}<...<t_{k}<...<t_{K}=1$에 대해 Eulere solver는 각 step $k$에서 sample을 다음과 같이 udpate 함:
(Eq. 2) $x_{t_{k+1}}=x_{t_{k}}+(t_{k+1}-t_{k})\cdot v_{t_{k}}(x_{t_{k}};\theta)$
- 이는 $x_{0}$를 $x_{1}\sim p_{1}$으로 iteratively transform 함
- $K$ : Number of Function Evaluation (NFE) - 추가적으로 generation quality를 향상하기 위해 Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG)를 활용할 수 있음:
(Eq. 3) $\tilde{v}_{t}(x_{t},c,\omega;\theta)=(1+\omega)v_{t}(x_{t},c;\theta)-\omega v_{t}(x_{t},\emptyset;\theta)$
- CFG는 training 중에 certain probability로 condition을 drop 하고 추론 시에는 conditional/unconditional prediction을 linear interpolate 함
- $c, \emptyset$ : 각각 condition, zero condition, $\omega$ : CFG strength
- CFM은 standard Gaussian distribution과 같은 simple initial distribution $p_{0}$를 real data distribution $q$에 approximate 한 complex data distribution $p_{1}$으로 transform 하는 방법을 학습함
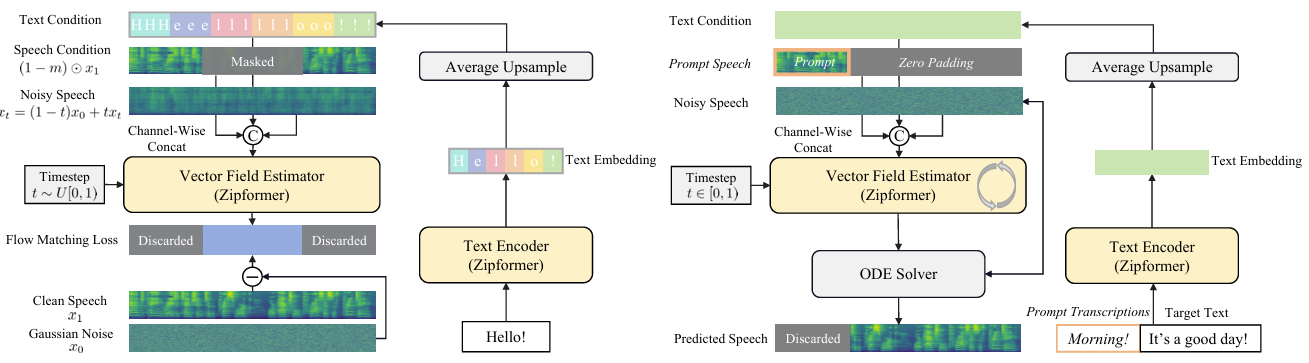
- Overview
- ZipVoice는 Zipformer를 backbone으로 사용하는 text encoder, vector field estimator로 구성됨
- 먼저 text sequence는 $i$-th token $y_{i}$, token length $N$에 대해 $y=(y_{1},y_{2},...,y_{N})$과 같이 text token으로 tokenize 됨
- 이후 text token은 text encoder에 전달되어 text feature $\hat{y}\in\mathbb{R}^{F\times N}$으로 transform 됨
- $F$ : text feature dimension - 대응하는 speech feature는 $x_{1}\in\mathbb{R}^{D\times T}$로 얻어지고, text feature에 Average Upsampling을 적용하여 text condition $z\in \mathbb{R}^{F\times T}$를 얻음
- $D$ : feature dimension, $T$ : feature length
- 이후 text token은 text encoder에 전달되어 text feature $\hat{y}\in\mathbb{R}^{F\times N}$으로 transform 됨
- 논문은 zero-shot TTS를 위해 VoiceBox를 따라 speech infilling task를 도입함
- 먼저 binary temporal mask $m\in \{0,1\}^{D\times T}$가 speech feature $x_{1}\in \mathbb{R}^{D\times T}$에 적용됨
- $1$ : masked position - 그러면 model은 speech condition $(1-m)\odot x_{1}$, interpolated noisy speech feature $x_{t}=(1-t)x_{0}+tx_{1}$, text condition $z$에 대해 $m\odot x_{1}$을 reconstruct 하도록 training 됨
- 해당 input은 same length를 가지고 vector field estimator를 위해 feature dimension으로 concatenate 됨 - 결과적으로 (Eq. 1)의 CFM loss는 다음과 같이 reformulate 됨:
(Eq. 4) $ \mathcal{L}_{CFM\text{-}TTS}=\mathbb{E}_{t,q(x_{1}),p_{0}(x_{0})}\left|\left| \left( v_{t}(x_{t},z,(1-m)\odot x_{1};\theta)-(x_{1}-x_{0})\right)\odot m\right|\right|^{2}$
- $m$ : loss masking
- 먼저 binary temporal mask $m\in \{0,1\}^{D\times T}$가 speech feature $x_{1}\in \mathbb{R}^{D\times T}$에 적용됨
- ZipVoice는 (Eq. 4)의 flow matching loss로 training 되고 flow distillation을 통해 further fine-tuning 됨
- Training 이후에는 ODE solver를 사용하여 speech feature를 생성하고 vocoder를 통해 waveform으로 변환함
- 먼저 text sequence는 $i$-th token $y_{i}$, token length $N$에 대해 $y=(y_{1},y_{2},...,y_{N})$과 같이 text token으로 tokenize 됨
- ZipVoice Architecture with Zipformer Backbone
- ZipVoice는 Zipformer-based text encoder와 Zipformer-based vector field esitmator로 구성됨
- 특히 vector field estimator에서 Zipformer architecture는 다음의 장점을 가짐:
- Feature representation을 위한 U-Net architecture는 diffusion에서 effective inductive bias를 제공함
- CNN은 fine-grained local feature pattern을 capture 하여 Transformer의 long-range global dependency modeling을 complement 함
- Zipformer는 attention weight를 reusing 하므로 parameter-efficient 함
- 최근의 E2-TTS, F5-TTS와 같은 flow matching TTS는 text embedding을 vector field esitmator에 directly input 하여 dedicated text encoder를 omit 함
- 이와 달리 ZipVoice는 Zipformer-based text encoder를 통해 intelligibility를 향상할 수 있음
- 특히 vector field estimator에서 Zipformer architecture는 다음의 장점을 가짐:
- Speech-Text Alignment with Average Upsampling
- NAR-TTS model은 training 시 Monotonic Alignment Search와 같은 speech-text alignment와 추론을 위한 duration prediction model이 필요함
- 해당 alignment는 training을 복잡하게 하고 inaccurate duration estimation으로 인해 naturalness를 저하시킴
- 따라서 논문은 sentence 내에서 각 token이 identical duration을 가진다는 assumption을 기반으로 parameter-free Average Upsampling strategy를 도입함
- 먼저 $N$ text token, $T$ speech feature frame에 대해 각 text token의 duration은:
(Eq. 5) $d=\left\lfloor \frac{T}{N}\right \rfloor$
- $\lfloor \cdot \rfloor$ : floor operation
- Practically valid assumption $T\geq N$ 하에서 minimum token duration은 $1$과 같음 - 이후 각 text embedding은 $d$번 repeat 되고 text feature length는 $N$에서 $d\cdot N$으로 expand 됨
- 만약 $T>d\cdot N$이면 expanded text feature는 $T-d\cdot N$ filler embedding으로 further pad 됨 - Final text feature $z\in \mathbb{R}^{F\times T}$는 vector field estimator의 text condition으로 사용됨
- 먼저 $N$ text token, $T$ speech feature frame에 대해 각 text token의 duration은:
- Speedup ZipVoice with Flow Distillation
- ZipVoice에 Flow Distillation method를 적용하여 faster-variant인 ZipVoice-Distill을 얻을 수 있음
- 이를 위해 논문은 teacher model의 2-step inference를 사용하여 teacher vector field를 구성하고, student model의 prediction을 해당 vector field에 regress 함
- 먼저 pre-trained TTS model $\theta^{T}$가 teacher로 주어지면 student model $\theta^{S}$를 $\theta^{T}$의 parameter로 initialize 함
- 이때 논문은 student model이 CFG strength에 condition 되도록 설정함
- CFG strength $\omega$는 Fourier embedding과 linear layer를 통과한 다음 model에 integrate 됨 - Time-step $t$와 input noisy speech $x_{t}$에 대해, teacher model을 사용하여 middle time-step $t_{mid}$와 destination time-step $t_{dest}$에 reach 하는 2-step process를 고려할 수 있음:
(Eq. 6) $x_{t_{mid}}=\Phi(x_{t},t,t_{mid},c,\omega;\theta^{T})$
$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, x_{t_{dest}}=\Phi(x_{t_{mid}},t_{mid},t_{dest},c,\omega;\theta^{T})$ - 여기서 one-step ODE solver $\Phi$는 다음과 같이 정의됨:
(Eq. 7) $ \Phi(x_{t},t,t_{mid},c,\omega;\theta^{T})=x_{t}+(t_{mid}-t)\tilde{v}_{t}(x_{t},c,\omega;\theta^{T})$
- $\tilde{v}_{t}(x_{t},c,\omega;\theta^{T})$ : (Eq. 3)과 같이 CFG를 사용해 얻어지는 prediction
- 2가지 step size $t_{mid}-t$와 $t_{dest}-t_{mid}$는 $[0,\Delta t_{\max}]$에서 uniformly sample 되고, $\omega$ 역시 $[\omega_{\min},\omega_{\max}]$에서 uniformly sample 됨 - 그러면 teacher vector field는 다음과 같이 얻어짐:
(Eq. 8) $v^{T}=\frac{x_{t_{dest}}-x_{t}}{t_{dest}-t}$ - 결과적으로 얻어지는 flow distillation loss는:
(Eq. 9) $\mathcal{L}_{FD}=\mathbb{E}_{t,q(x_{1}),p_{0}(x_{0})}\left|\left| \left(v_{t}(x_{t},\hat{e},(1-m)\odot x_{1};\theta)-v^{T}\right)\odot m\right|\right|^{2}$
- Teacher prediction은 (Eq. 6)에서 CFG를 통해 얻어지므로, flow distillation 후에는 student model input으로 CFG strength $\omega$를 전달하여 각 step에서 model evaluation 없이 CFG 효과를 얻을 수 있음
- 이때 논문은 student model이 CFG strength에 condition 되도록 설정함
- Fixed teacher model $\theta^{T}$를 통해 flow distillation을 수행한 다음, latest student model $\theta^{S}$를 사용해 second distillation phase를 수행할 수 있음
- 이를 위해 (Eq. 10)과 같이 update 되는 Exponential Moving Average (EMA)-version student model $\tilde{\theta}$가 teacher vector field로 사용됨:
(Eq. 10) $\tilde{\theta}^{S}=(1-\beta)\theta^{S}+\beta\tilde{\theta}$
- $\beta$ : EMA decay factor - Continuously evolving student model에서 derive 된 해당 teacher vector field는 second distillation phase가 student의 성능을 iteratively refine 하도록 함
- 이를 위해 (Eq. 10)과 같이 update 되는 Exponential Moving Average (EMA)-version student model $\tilde{\theta}$가 teacher vector field로 사용됨:
- Inference Strategy
- Zero-shot TTS를 위해서는 synthesis text $y^{synthesis}$ 외에도 audio prompt $s^{prompt}$와 transcription $c^{prompt}$가 필요함
- Synthesized audio의 sentence duration은 prompt transcription과 synthesis text 간의 token length ratio를 기반으로 estimate 됨:
(Eq. 11) $ T^{synthesis}=T^{prompt}\cdot \frac{|y^{synthesis}|}{|y^{prompt}|}$
- $T^{prompt}$ : prompt audio의 sentence duration - Text encoder input은 tokenized text token $y^{synthesis}, y^{prompt}$를 concatenate 하여 얻어지고, 이후 text condition은 average upsampled text feature로 구성됨
- Audio condition은 audio prompt를 length $T^{prompt}+T^{synthesis}$에 pad 하여 얻어짐
- Initial noisy speech는 standard Gaussian distribution에서 sample 되고 ODE solver를 통해 synthesized speech가 sample 됨
- 논문은 speaker similarity, intelligibility 간의 trade-off를 만족하기 위해 time-dependent CFG strategy를 활용함
- Early NFE에서는 unconditional prediction을 위해 text condition만 drop 하고 later step에서는 text, audio condition을 모두 drop 함
- Synthesized audio의 sentence duration은 prompt transcription과 synthesis text 간의 token length ratio를 기반으로 estimate 됨:
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : Emilia, LibriTTS
- Comparisons : CosyVoice, CosyVoice2, MaskGCT, E2-TTS, F5-TTS, Spark-TTS
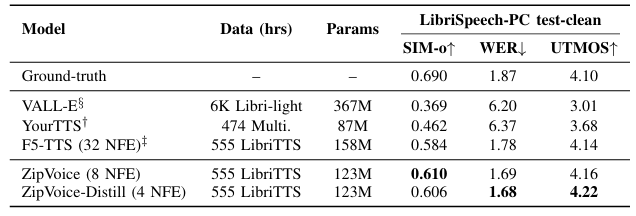
- Results
- 전체적으로 ZipVoice는 우수한 성능을 달성함

- Inference speed 측면에서도 빠른 속도를 보임

- Zero-Shot TTS 측면에서도 우수한 성능을 달성함
- Ablation Study
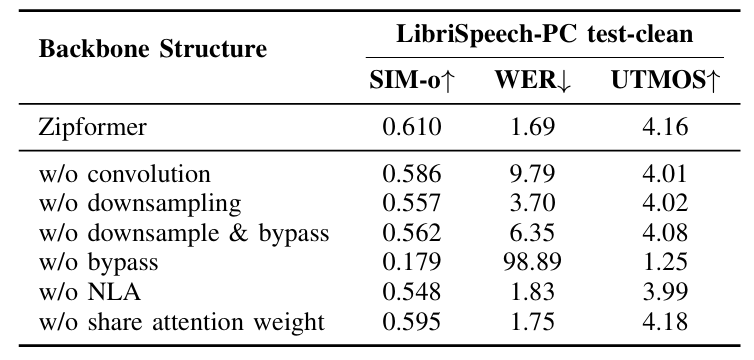
- 각 component는 성능 향상에 유효함

- Zipformer backbone에서 각 component를 제거하면 성능 저하가 발생함
- Distillation Methods
- 논문의 flow distillation을 활용하면 더 나은 성능을 달성할 수 있음

반응형
'Paper > TTS' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

