티스토리 뷰
Paper/TTS
[Paper 리뷰] HierSpeech++: Bridging the Gap Between Semantic and Acoustic Representation of Speech by Hierarchical Variational Inference for Zero-Shot Speech Synthesis
feVeRin 2025. 10. 18. 06:17반응형
HierSpeech++: Bridging the Gap Between Semantic and Acoustic Representation of Speech by Hierarchical Variational Inference for Zero-Shot Speech Synthesis
- Zero-shot speech synthesis는 inference speed와 robustness의 한계가 있음
- HierSpeech++
- Hierarchical synthesis framework를 활용하여 naturalness를 향상
- Text representation과 prosody prompt를 기반으로 self-supervised/$F0$ representation을 생성하는 Text-to-Vec framework를 도입하고 16kHz에서 48kHz로의 super-resolution framework를 적용
- 논문 (TNNLS 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- 최근 zero-shot speech synthesis를 위해 Large Language Model (LLM)이 활용되고 있음
- BUT, 해당 LLM-based speech model은 다음의 한계점을 가짐:
- Autoregressive manner로 인해 inference speed가 느리고 repeating, skipping, mispronunciation과 같은 robustness의 문제가 있음
- Pre-trained Neural Audio Codec (NAC)와 discrete speech unit에 의존적임
- 기존 end-to-end (E2E) framework 보다 낮은 합성 품질을 보이는 경우가 있음
- Training을 위해 large-scale dataset이 필요함
- 앞선 LLM framework 외에도 DiffVC, DDDM-VC, Diff-HierVC와 같은 diffusion-based voice conversion (VC) model을 고려할 수 있음
- BUT, diffusion model은 iterative generation으로 인해 inference speed가 느리고, noisy data에 vulnerable 하다는 한계점이 있음 - 한편으로 E2E Text-to-Speech (TTS) framework를 활용하면 더 나은 speech quality와 더 빠른 inference speed를 달성할 수 있음
- 대표적으로 VITS, HierSpeech는 Variational AutoEncoder (VAE) 활용하여 pipeline을 구성함
- BUT, 해당 LLM-based speech model은 다음의 한계점을 가짐:

-> 그래서 fast/strong zero-shot speech synthesis를 위해 E2E framework를 도입한 HierSpeech++를 제안
- HierSpeech++
- Self-supervised speech representation을 semantic representation으로 사용해 semantic/acoustic representation 간의 gap을 bridging
- Hierarchical speech synthesizer, Text-to-Vec (TTV), Speech Super-Resolution (SpeechSR)로 구성된 hierarchical E2E framework를 구성
< Overall of HierSpeech++ >
- Hierarchical E2E framework를 활용한 zero-shot TTS model
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 성능을 달성
2. Method
- HierSpeech++는 high-quality zero-shot speech synthesis를 위해 Hierarchical Speech Synthesizer, Text-to-Vec (TTV), Speech Super-Resolution (SpeechSR)로 구성된 hierarchical framework를 활용함
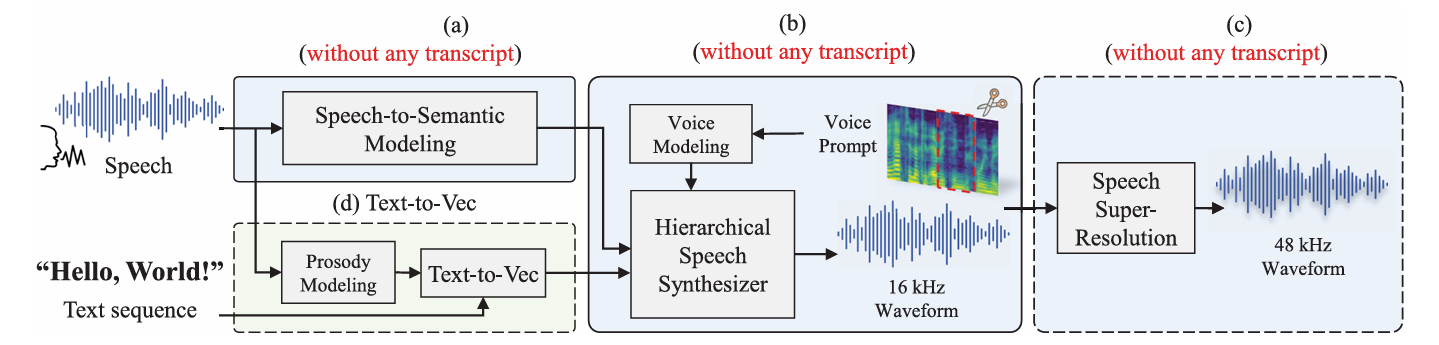
- Speech Representations
- 논문은 4kHz 이하의 human voice frequency band range를 고려하여 16kHz downsampled audio를 사용함
- 이후 better perceptual quality를 위해 SpeechSR를 사용하여 audio를 16kHz에서 48kHz로 upsampling 함
- Acoustic/Semantic representation의 경우 50Hz의 low-resolution representation을 사용함
- Acoustic Representation
- 논문은 waveform에 STFT를 적용하여 얻어진 mel-spectrogram을 intermediate acoustic feature로 고려함
- 이때 acoustic feature는 pronunciation/context와 같은 semantic information 외에도 timbre/intonation/recording environment와 같은 voice information도 포함함
- 따라서 이러한 rich representation을 text로부터 directly infer 하면 one-to-many mapping 문제가 발생하고, mispronunciation/oversmoothed speech로 이어짐
- 이를 해결하기 위해 논문은 HierSpeech를 따라 text/acoustic feature 간의 gap을 bridging 하는 Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) representation을 semantic representation으로 채택함
- Semantic Representation
- 논문은 waveform으로부터 continuous semantic representation을 추출하기 위해 Wav2Vec 2.0을 도입함
- 해당 SSL model의 middle layer는 linguistic information을 포함하고 있기 때문
- Style Representation
- Prosody, voice style을 위해 2가지 global style representation을 사용함
- Prosody representation의 경우 reference prosody prompt의 mel-spectrogram에서 global prosody representation을 추출하여 사용함
- 이는 TTV model을 conditioning 하는 데 사용됨 - Voice style representation은 reference voice prompt로부터 mel-spectrogram을 추출하여 얻어지고, hierarchical speech synthesizer를 conditioning 하는 데 사용함
- Prosody representation의 경우 reference prosody prompt의 mel-spectrogram에서 global prosody representation을 추출하여 사용함
- 이때 acoustic/semantic modeling은 disentangle 되어 있으므로 prosody/voice style을 separately transfer 할 수 있고, HierSpeech++는 각각의 characteristic을 reflect 하도록 training 됨
- Prosody, voice style을 위해 2가지 global style representation을 사용함
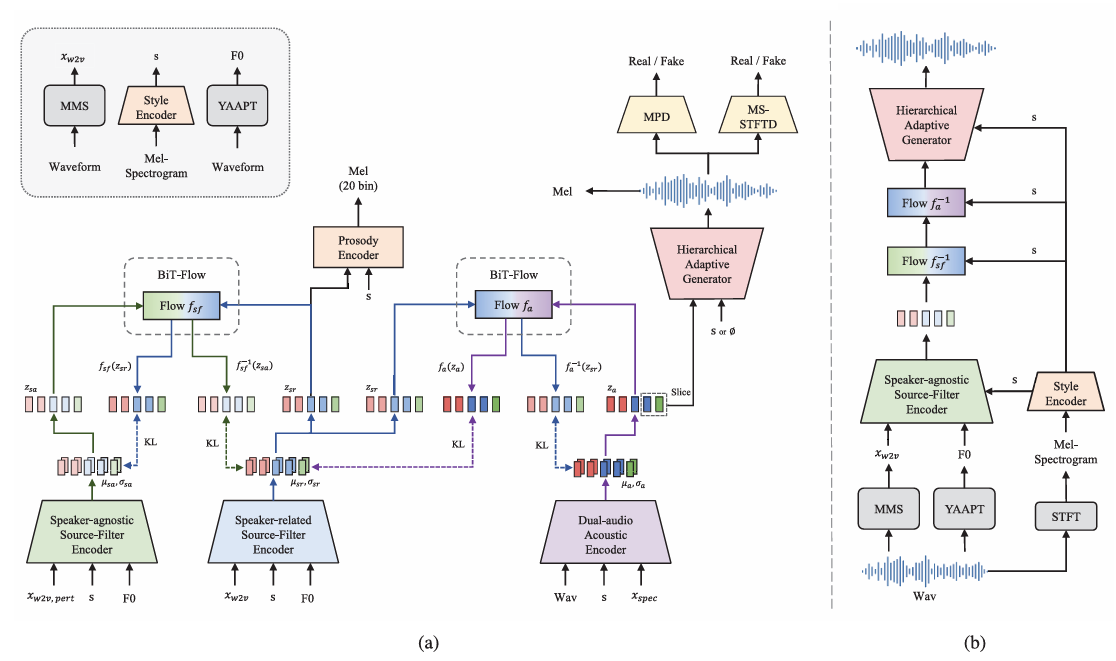
- Hierarchical Speech Synthesizer
- HierSpeech++는 backbone speech synthesizer로 hierarchical speech synthesizer를 사용함
- 해당 module은 speaker ID, text transcript와 같은 label 없이 speech data 만으로 training 됨 - Dual-Audio Acoustic Encoder
- 기존 방식들은 mel-spectrogram을 linear spectrogram으로 replace 하여 KL-divergence를 minimize 하도록 AutoEncoder를 training 함
- BUT, 해당 방식은 zero-shot task에서 perceptual quality를 저하시킴 - 따라서 논문은 linear spectrogram 대신 comprehensive, richer acoustic representation을 capture 할 수 있는 dual-audio acoustic encoder를 도입함
- 이를 위해 raw waveform audio로부터 information을 distilling 하는 waveform encoder를 추가하고 linear spectrogram과 해당 representation을 concatenate 함
- 이후 해당 concatenated representation을 project 하여 acoustic representation을 얻음
- 기존 방식들은 mel-spectrogram을 linear spectrogram으로 replace 하여 KL-divergence를 minimize 하도록 AutoEncoder를 training 함
- Source-Filter Multipath Semantic Encoder
- 논문은 speaker-related/speaker-agnostic semantic representation을 위해 multi-path SSL representation을 채택하고, 이때 각 representation은 hierarchical style adaptation을 위한 prior로 사용됨
- Linguistic information은 Wav2Vec 2.0의 middle layer에서 semantic representation을 추출하여 얻어짐
- Fundamental frequency $F0$는 enhanced prior와 disentanglement를 위해 사용됨
- Speaker-agnostic semantic representation은 SSL representation에 speech perturbation을 적용하여 speaker-related information을 remove 해 얻어짐
- Speaker-related smeantic representation의 경우 speech perturbation이 적용되지 않음
- 논문은 speaker-related/speaker-agnostic semantic representation을 위해 multi-path SSL representation을 채택하고, 이때 각 representation은 hierarchical style adaptation을 위한 prior로 사용됨
- Hierarchical Variational AutoEncoder
- HierSpeech++는 text encoder를 linguistic restorer로 replace 한 HierSpeech structure를 기반으로 함
- 먼저 conditional information $c$에 대한 perturbed linguistic representation $x_{w2v, pert}$를 얻음
- 추가적으로 un-perturbed original waveform의 self-supervised representation의 enhanced linguistic representation을 얻음 - 이후 추출된 acoustic representation으로부터 raw waveform을 생성함
- 이때 acoustic과 multi-path linguistic representation을 connect 하기 위해 hierarchical variational inference를 사용함
- 먼저 conditional information $c$에 대한 perturbed linguistic representation $x_{w2v, pert}$를 얻음
- 특히 perturbed linguistic representation과 hierarchical VAE를 사용하면 VC task를 수행할 수 있음
- NANSY를 따라 speech perturbation을 위해 formant shifting, pitch normalization, random frequency shaping을 적용하면,
- Hierarchical speech synthesizer의 optimization objective는 다음과 같이 얻어짐:
(Eq. 1) $ \log p_{\theta}(x)\geq \mathbb{E}_{q_{\phi}(z|x)}\left[\underset{\text{Reconstruction}}{\underbrace{\log p_{\theta_{d}}(x|z_{d})}}- \underset{\text{Acoustic KL}}{\underbrace{\log \frac{q_{\phi_{a}}(z_{a}|x)}{p_{\theta_{a}}(z_{a}|z_{sr})}}}- \underset{\text{Linguistic KL}}{\underbrace{\log\frac{q_{\phi_{sr}}(z_{sr}|x_{w2v},F_{0}) }{p_{\theta_{sr}} (z_{sr}|x_{w2v,pert},F_{0})}}}\right]$
- $q_{\phi_{a}}(z_{a}|x), q_{\phi_{sr}}(z_{sr}|x_{w2v},F_{0})$ : 각각 input waveform, linguistic feature에 대한 approximate posterior
- $q_{\phi_{a}}(z_{a}|x)$는 raw waveform $x$로부터 acoustic latent variable을 encode 하고 $q_{\phi_{sr}}(z_{sr}|x_{w2v},F_{0})$는 semantic latent variable을 infer 함
- Semantic latent variable $z_{sr}$에 대한 prior distribution은 perturbed linguistic feature와 pitch를 condition으로 하는 $p_{\theta}(z_{sr}|x_{w2v,pert},F_{0})$에 의해 주어짐
- Acoustic prior $p_{\theta_{a}}(z_{a}|z_{sr})$은 semantic latent $z_{sr}$이 주어졌을 때 $z_{a}$에 대한 conditional distribution을 define 하여 hierarchical generation을 지원함
- $p_{\theta_{d}}(x|z_{a})$는 Hierarchical Adaptive Generator로 parameterize 된 likelihood function으로 acoustic latent $z_{a}$로부터 waveform $x$를 reconstruct 함
- HierSpeech++는 text encoder를 linguistic restorer로 replace 한 HierSpeech structure를 기반으로 함
- Hierarchical Adaptive Generator
- Semantic-to-Waveform generation을 위해 source generator $G_{s}$, waveform generator $G_{w}$로 구성된 Hierarchical Adaptive Generator (HAG)를 도입함
- 먼저 acoustic representation $z_{a}$, style representation $s$를 포함한 generated representation가 $G_{s}$에 전달되면 $G_{s}$는 refined pitch representation $p_{h}$를 생성함
- 이때 auxiliary $F0$ predictor는 $p_{h}$에 $F0$ information을 enforce 함:
(Eq. 2) $\mathcal{L}_{pitch}=||p_{x}-G_{s}(z_{a},s)||_{1}$
- $p_{x}$ : ground-truth $F0$ - 이후 $G_{w}$는 $z_{a}, p_{h}, s$로부터 audio를 hierarchically synthesize 하고, STFT를 사용하여 ground-truth와 generated mel-spectrogram 간의 reconstruction loss를 계산함:
(Eq. 3) $\mathcal{L}_{STFT} =|| \psi(x)-\psi(G_{w}(z_{a},p_{h},s))||_{1}$
- $\psi$ : mel-filter
- 이때 auxiliary $F0$ predictor는 $p_{h}$에 $F0$ information을 enforce 함:
- 추가적으로 better peceptual audio quality를 위해 adversarial learning을 적용하면:
(Eq. 4) $ \mathcal{L}_{adv}(D)=\mathbb{E}_{(x,z_{a})}\left[\left( D(x)-1\right)^{2}+D\left( G(z_{a},s)\right)^{2}\right]$
(Eq. 5) $\mathcal{L}_{adv}(\phi_{a},\theta_{d})=\mathbb{E}_{(z_{a})}\left[\left(D (G(z_{a},s))-1\right)^{2}\right]$
- HiFi-GAN의 Multi-Period Discriminator와 EnCodec의 Multi-Scale STFT Discriminator (MS-STFTD)를 사용
- Bidirectional Transformer Flow
- Normalizing flow를 활용해 prior distribution의 expressiveness를 향상하고 posterior/prior distribution을 bridge 하여 audio quality를 개선할 수 있음
- BUT, 해당 framework는 training-inference 문제와 speaker adaptation의 한계를 가짐 - 따라서 HierSpeech++는 Bidirectional Transformer Flow (BiT-Flow)를 도입함
- 먼저 NaturalSpeech를 따라 bidirectional normalizing flow를 구성함
- 이후 latent representation의 large context를 capture 하기 위해 WaveNet-based adaptive network를 convolutional feed-forward-based Transformer network로 replace 함
- 이때 VITS2와 달리 Transformer block에 AdaLN-Zero와 dropout을 적용함
- Training 시 audio sequence는 slice 되고 Transformer에는 positional embedding이 사용되지 않음
- Normalizing flow를 활용해 prior distribution의 expressiveness를 향상하고 posterior/prior distribution을 bridge 하여 audio quality를 개선할 수 있음
- Prosody Distillation
- 논문은 speaker-related source-filter encoder에서 linguistic representation $z_{sr}$을 향상하기 위해 prosody distillation을 도입함
- 먼저 $z_{sr}$은 prosody information을 포함하는 mel-spectrogram의 first 20-bin을 reconstruct 하기 위해 prosody decoder로 전달됨
- 이때 voice style representation을 conditioning 하여 $z_{sr}$이 speaker-related prosody를 학습하도록 함
- 이는 ground-truth와 reconstructed mel-spectrogram의 20-bin 간의 $l1$ distance를 minimize 하는 prosody loss $\mathcal{L}_{prosody}$를 사용하여 training 됨
- Unconditional Generation
- Progressive speaker adaptation을 위해 hierarchical adaptive generator는 unconditional generation을 지원함
- Unconditional generation을 사용하면 acoustic representation이 speaker characteristic을 adopt 하므로, entire model의 speaker adaptation을 향상할 수 있음 - 이를 위해 HierSpeech++에서는 training 중에 $10\%$ probability로 voice style representation $s$를 null style embedding $\varnothing$으로 replace 함
- 추론 시에는 conditional generation을 위해 target voice style representation 만이 사용됨
- Progressive speaker adaptation을 위해 hierarchical adaptive generator는 unconditional generation을 지원함

- Text-to-Vec
- 논문은 text sequence로부터 semantic representation과 $F0$를 생성하는 Text-to-Vec (TTV) model을 도입함
- 먼저 VITS를 따라 VAE, Montreal Alignment Search (MAS)를 사용하여 text, speech를 internally align 함
- 이때 posterior encoder input을 linear spectrogram에서 SSL representation으로 replace 하고 TTV output으로부터 동일한 SSL representation을 reconstruct 함
- $F0$는 SSL representation의 $4\times $ larger resolution으로 predict 됨
- Text sequence, prosody prompt는 data의 self-supervised speech representation을 생성하기 위한 conditional information으로 사용됨
- 특히 prosody conditional text representation은 prior information으로 사용되고, prosody style representation은 full-length input speech에서 추출되어 global style embedding으로 사용됨
- 이때 SSL reprsentation이 가진 semantic information으로 인해 voice style과 irrelevant 하게 TTV framework에서 prosody style를 transfer 할 수 있음
- 추가적으로 semantic representation의 linguistic capacity를 향상하기 위해 latent representation을 phoneme encoder에 fed 하고 Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) loss를 minimize 함
- Prosody adaptation을 위해서는 AdaLN-Zero가 포함된 Transformer-based normalizing flow가 사용됨
- 먼저 VITS를 따라 VAE, Montreal Alignment Search (MAS)를 사용하여 text, speech를 internally align 함

- Speech Super-Resolution
- Speech Super-Resolution (SpeechSR)은 16kHz에서 48kHz로 low-resolution speech waveform을 high-resolution speech waveform으로 upsampling 함
- 이를 위해 논문은 low-pass filter, periodic activation Snake function으로 구성된 BigVGAN의 Anti-aliased Multi-periodicity Composition (AMP) block을 채택함
- 이때 transposed convolution은 Nearest Neighbor (NN) upsampler로 replace 됨 - 추가적으로 hierarchical speech synthesizer를 따라 MPD, MS-STFTD를 적용하고 각 subband의 feature를 reflect 하기 위해 DWT-based subband Discriminator (DWTD)를 도입함
- 기존 Fre-GAN2과 달리 논문에서는 discriminator를 각 sub-audio $[0,12], [12,24], [24, 36], [36,48]\text{kHz}$의 subband discriminator로 decompose 하여 reconstruction quality를 향상함
- 이를 위해 논문은 low-pass filter, periodic activation Snake function으로 구성된 BigVGAN의 Anti-aliased Multi-periodicity Composition (AMP) block을 채택함

- Model Architecture
- Hierarchical Speech Synthesizer
- Dual-audio acoustic encoder는 wav encoder와 spec encoder로 구성됨
- Wav encoder는 BigVGAN의 AMP block과 downsampling block으로 구성되어 spectrogram과 Wav2Vec representation 간의 temporal sequence를 mapping 함
- Downsampling rate는 $[8,5,4,2]$, kernel size는 $[17,10,8,4]$, hidden size는 $[16,32,64,128,192]$로 설정 - Spec encoder는 192 hidden size의 16-layer non-causal WaveNet으로 구성됨
- Wav encoder는 BigVGAN의 AMP block과 downsampling block으로 구성되어 spectrogram과 Wav2Vec representation 간의 temporal sequence를 mapping 함
- HAG는 source generator와 wavevform generator로 구성됨
- 이때 inducitve bias와 anti-aliasing을 위해 AMP block으로 Multi Receptive-field Fusion (MRF)를 replace 함
- Source generator는 256 initial channel과 $[2,2]$ upsampling rate를 가지고, waveform generator는 512 initial channel과 $[4,5,4,2,2]$의 upsampling rate를 가짐
- Discriminator는 $[2,3,5,7,11]$ period의 MPD와 $[2048,1024,512,256,128]$ window size의 Multi-Scale STFT-based Discriminator (MS-STFTD)를 사용함
- Source-Filter encoder의 source/filter/adaptive encoder는 8-layer non-causal WaveNet으로 구성됨
- Hidden size는 192로 설정 - BiT-Flow는 previous Convolutional network (preConv), 3개의 Transformer block, post Convolutional network (postConv)로 구성됨
- Transformer block은 adjacent information을 encoding 하기 위해 5 kernel size의 convolution을 사용하고 voice style adaptation을 위해 AdaLN-Zero가 적용됨
- Hidden size는 192, filter size는 768, attention head는 2개가 사용됨
- Dropout rate는 0.1로 설정
- Style encoder는 linear projection이 있는 2개의 spectral encoder와 1D convolution을 가지는 2개의 temporal encoder, multi-head self-attention으로 구성됨
- Dual-audio acoustic encoder는 wav encoder와 spec encoder로 구성됨
- Text-to-Vec
- TTV content encoder는 256 hidden size, 5 kernel size를 가진 16-layer non-causal WaveNet으로 구성되고, Content decoder는 512 hidden size, 5 kernel size를 가진 8-layer non-causal WaveNet으로 구성됨
- Text encoder는 256 hidden size, 9 kernel size, 1024 filter size를 가진 3개의 unconditional/prosody-conditional Transformer로 구성됨
- Dropout rate는 0.2로 설정 - T-Flow는 preConv, 3개의 Transformer block, postConv로 구성된 4개의 residual coupling layer로 구성됨
- Transformer block은 adjacent information encoding을 위해 5 kernel size의 convolutional network를 사용하고 better prosody style adaptation을 위해 AdaLN-Zero가 적용됨
- T-Flow의 4개 attention head는 256 hidden size, 1024 filter size를 가짐
- Dropout rate는 0.1을 사용함
- Pitch predictor는 HAG와 동일한 structure를 가진 source generator를 사용함
- SpeechSR
- SpeechSR은 upsampling layer 없이 32 initial channel을 가진 single AMP block으로 구성됨
- 이때 hidden representation을 upsampling 하기 위해 NN upsampler를 사용함 - Discriminator의 경우 $[2,3,5,7,11]$ period를 가진 MPD와 $[4096, 2048, 1024,512,256,128]$ window size에 대한 MS-STFTD를 사용함
- 추가적으로 4개의 subband discriminator를 포함한 DWTD도 사용됨
- SpeechSR은 upsampling layer 없이 32 initial channel을 가진 single AMP block으로 구성됨

3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : LibriTTS, Multi-Speaker Speech Synthesis (MSSS), EXPRESSO, NIKL
- Comparisons
- Zero-Shot VC : AutoVC, VoiceMixer, DiffVC, Diff-HierVC, DDDM-VC, YourTTS
- Zero-Shot TTS : Seed-TTS, FireRedTTS, MaskGCT, E2-TTS, F5-TTS, CosyVoice2
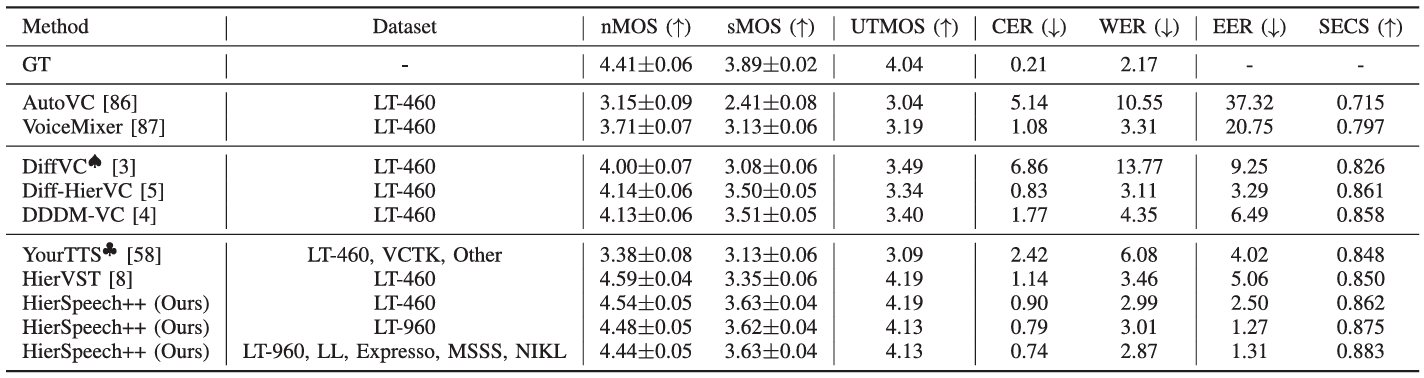
- Results
- HierSpeech++는 가장 우수한 zero-shot VC 성능을 달성함
- Zero-Shot TTS에서도 HierSpeech++가 가장 뛰어남
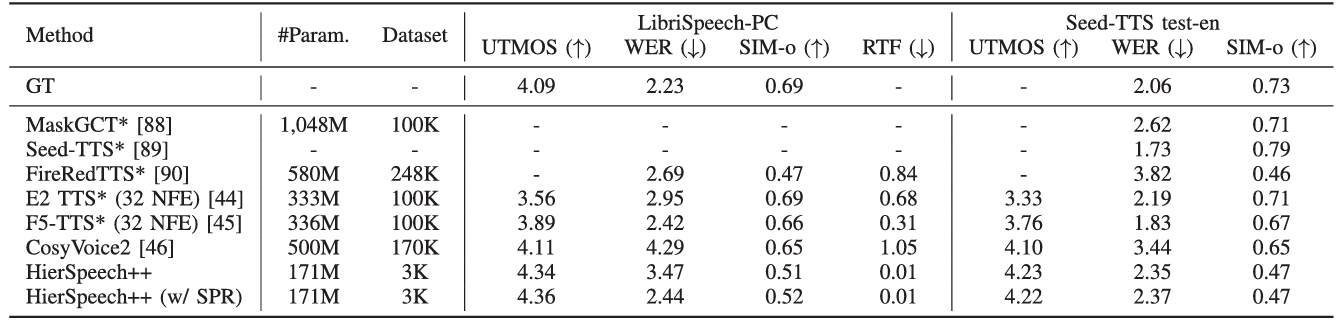
- Short prompt의 경우에도 robust 한 성능을 보임

- Unseen speaker에 대해서도 뛰어난 합성 품질을 달성함

- Noisy prompt에 대해서도 우수한 성능을 보임

- Ablation Study
- 각 component를 제거하는 경우 성능 저하가 발생함
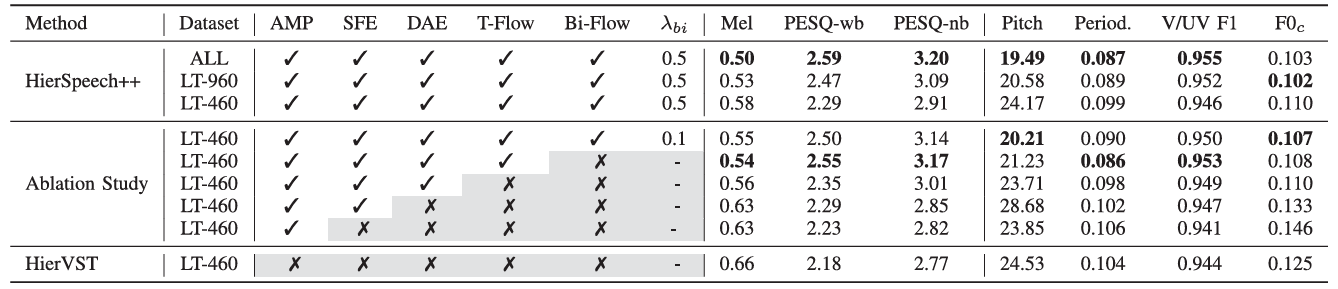
- Resynthesis task에 대해서도 각 component는 유효함

- VC task에서도 유사한 결과를 보임

- Temperature Parameter
- $T_{ttv}$가 증가하면 target prosody에 대한 intonation, pronunciation과 같은 prosody가 향상됨
- $T_{h}$가 증가하면 voice style similarity가 향상됨

- Speech Super-Resolution
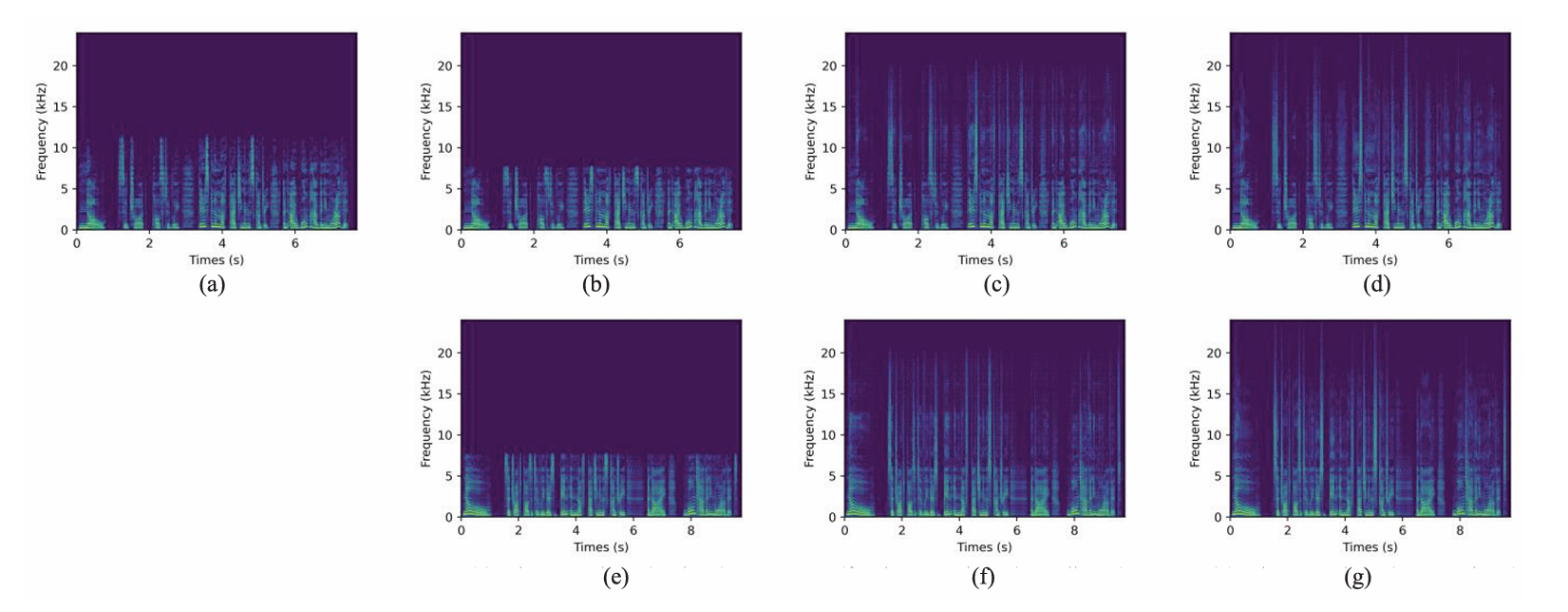
- HierSpeech++의 SpeechSR은 기존 model 보다 뛰어난 성능을 가짐
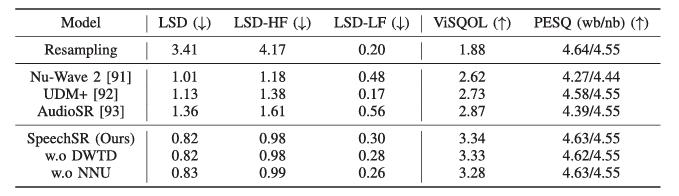
- ABX test 측면에서도 SpeechSR이 가장 선호됨
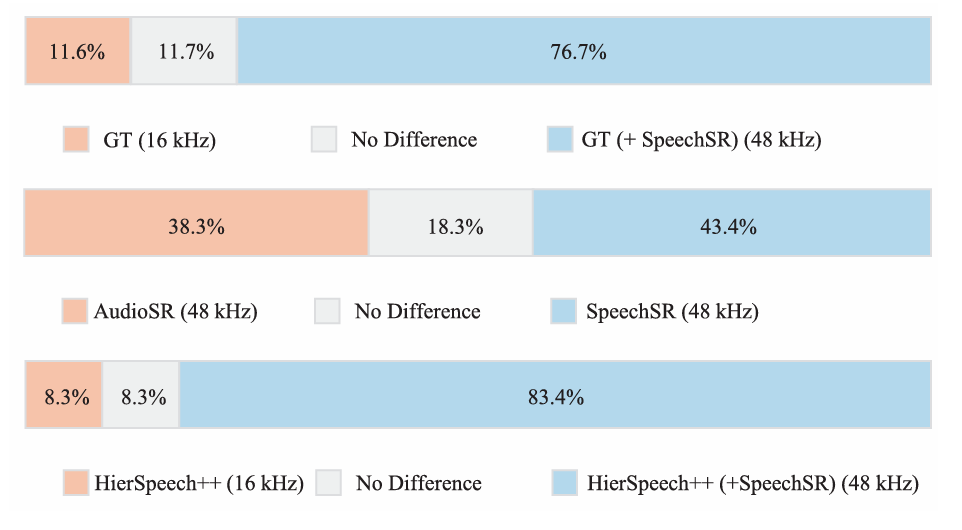
- Mel-Spectrogram 측면에서도 ground-truth (GT)와 큰 차이를 보이지 않음
- (a) 24kHz GT, (b) 16kHz GT, (c) AudioSR, (d) SpeechSR, (e) 16kHz HierSpeech++, (f) AudioSR+HierSpeech++, (g) SpeechSR+HierSpeech++
- Prosody/Voice Style Control
- 동일한 style prompt를 사용하더라도 다양한 pitch contour를 가질 수 있음

- Prosody, voice style을 모두 separately control 할 수도 있음

반응형
'Paper > TTS' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글
