티스토리 뷰
Paper/TTS
[Paper 리뷰] PITS: Variational Pitch Inference without Fundamental Frequency for End-to-End Pitch-Controllable TTS
feVeRin 2025. 6. 6. 10:08반응형
PITS: Variational Pitch Inference without Fundamental Frequency for End-to-End Pitch-Controllable TTS
- Pitch-controllable text-to-seech는 fundamental frequency를 directly modeling 하는 것에 의존함
- PITS
- Variational inference를 사용하여 pitch를 modeling 하는 end-to-end model
- VITS를 기반으로 Yingram encoder, Yingram decoder, adversarial training을 incorporate
- 논문 (ICML 2023) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Text-to-Speech (TTS)는 주어진 text input에서 human-like speech waveform을 합성하는 것을 목표로 함
- 특히 TTS는 one-to-many mapping에 해당하므로 duration, pitch 등을 효과적으로 modeling 해야 함
- 대표적으로 FastSpeech2는 pitch information을 제공하기 위해 frame-level에서 fundamental frequency $f_{0}$를 predict 하는 pitch predictor를 활용함
- FastPitch의 경우 character-level pitch prediction을 사용하고 FastPitchFormant는 source-filter theory를 활용함
- BUT, 해당 방식은 pitch prediction이 deterministic하고 ground-truth $f_{0}$를 directly modeling 하므로 low pitch variance를 가짐
- Normalizing flow를 활용하는 VarianceFlow 역시 $f_{0}$를 directly modeling함
- FastPitch의 경우 character-level pitch prediction을 사용하고 FastPitchFormant는 source-filter theory를 활용함
- VITS의 경우 conditional Variational AutoEncoder (cVAE)와 normalizing flow를 사용한 end-to-end (E2E) model을 활용하여 one-to-many nature를 modeling 함
- 이때 VISinger, Period VITS와 같이 VITS에 pitch predictor를 적용할 수 있지만, external annotated duration label과 pitch contour가 필요하므로 synthesis diversity가 제한됨 - 한편으로 pitch information에 해당하는 $f_{0}$는 linguistic information에 entangle 되어 있음
- HuBERT, Wav2Vec 2.0 등을 활용해 disentangle 하면 더 나은 controllability를 달성할 수 있음
- 특히 NANSY의 경우 $f_{0}$를 대체하는 Yingram을 통해 $f_{0}$-based model의 성능을 개선함
-> 그래서 external $f_{0}$ extractor에 대한 의존성을 제거한 pitch-controllable TTS model인 PITS를 제안
- PITS
- $f_{0}$를 directly modeling 하지 않고, cVAE와 normalizing flow를 사용하여 Yingram에 대한 pitch information을 modeling
- 추가적으로 pitch controllability를 향상하기 위해 Yingram reconstruction loss, Yingram decoding loss, adversarial pitch-shifted loss를 도입
< Overall of PITS >
- VITS를 기반으로 한 pitch-controllable end-to-end TTS model
- 결과적으로 기존보다 뛰어난 pitch controllability를 달성
2. Method
- PITS는 pitch-controllable model을 구성하기 위해 VITS를 기반으로 Yingram encoder, Yingram decoder, Q-VAE를 도입함
- Yingram Encoder
- Pitch information을 포함한 harmonics modeling을 위해 additional posterior encoder인 Yingram encode를 도입함
- 이때 PITS는 NASNY를 따라 STFT encoder와 Yingram encoder를 각각 linguistic, pitch information을 encoding 하는 데 사용함
- Yingram encoder는 STFT encoder와 동일한 structure를 가지는 대신, 80-input/output channel을 가짐 - Pitch controllability를 위해 논문은 Yingram encoder에서 latent variable을 crop 함
- 특히 TTS는 voice conversion과 달리 추론 시에 Yingram을 calculate 하기 위한 source speech에 access 할 수 없으므로, channel dimension에서 latent variable의 middle ($16$th-$65$th channel)을 crop 함
- 이는 NANSY에서 Yingram의 middle-frequency bin을 crop 하는 것과 같음 - Yingram encoder에서 latent variable $z_{yin}$을 default scope ($16$th-$65$th channel)로 crop 하여 $z_{crop}$을 얻음
- Scope-shift는 $[-15,15]$의 uniform distribution에서 randomly sample 된 integer $s$에 따라 결정됨
- Scope-shifted latent variable $z_{crop}^{shift}$는 $(s+16)$th-$(s+65)$th channel을 crop 하여 얻어짐 - Yingram encoder에서 cropped latent variable은 STFT encoder의 latent variable과 concatenate 되고, concatenated latent variable은 이후 decoder에 전달됨
- Scope-shift는 $[-15,15]$의 uniform distribution에서 randomly sample 된 integer $s$에 따라 결정됨
- Flow와 Monotonic Alignment Search (MAS)를 위해, 논문은 Yingram encoder와 STFT encoder의 variational latent variable을 concatenate 하여 normalizing flow에 전달함
- ELBO/Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence는 concatenation 없이 기존 VITS를 따름 - 한편으로 Yingram encoder는 source sample에서 pitch information을 추출하여 VC task에 적용될 수 있음
- [Algorithm 1] 참고
- 이때 PITS는 NASNY를 따라 STFT encoder와 Yingram encoder를 각각 linguistic, pitch information을 encoding 하는 데 사용함

- Yingram Decoder
- Latent variable의 scope를 shifting 하여 pitch-controllability를 달성하기 위해서는 channel direction에서 Yingram encoder가 translation equivariant 해야 함
- 따라서 해당 translation equivariance를 enforce 하기 위해, 논문은 Yingram decoder를 활용하여 shifted latent variable로부터 shifted scope의 Yingram을 reconstruct 함
- 즉, Yingram decoder는 $(s+16)$th에서 $(s+65)$th channel의 Yingram을 scope-shifted latent variable $z_{crop}^{shift}$로부터 reconstruct 함 - 해당 reconstruction을 measure 하기 위해 $L1$ norm이 사용되고, 이때 Yingram decoding loss $\mathcal{L}_{yd}$는:
(Eq. 1) $ \mathcal{L}_{yd}=\lambda_{yin}\mathbb{E}\left[\left|\left| Y_{crop}^{shift}-\text{Dec}_{yin}\left(z_{crop}^{shift}\right)\right|\right|_{1}\right]$
- $Y$ : original Yingram, $Y_{crop}$ : default scope의 cropped Yingram, $Y_{crop}^{shift}$ : scope-shift의 cropped Yingram
- $\text{Dec}_{yin}$ : Yingram decoder, $\lambda_{yin}=45$ : yin reconstruction loss multiplier
- 따라서 해당 translation equivariance를 enforce 하기 위해, 논문은 Yingram decoder를 활용하여 shifted latent variable로부터 shifted scope의 Yingram을 reconstruct 함
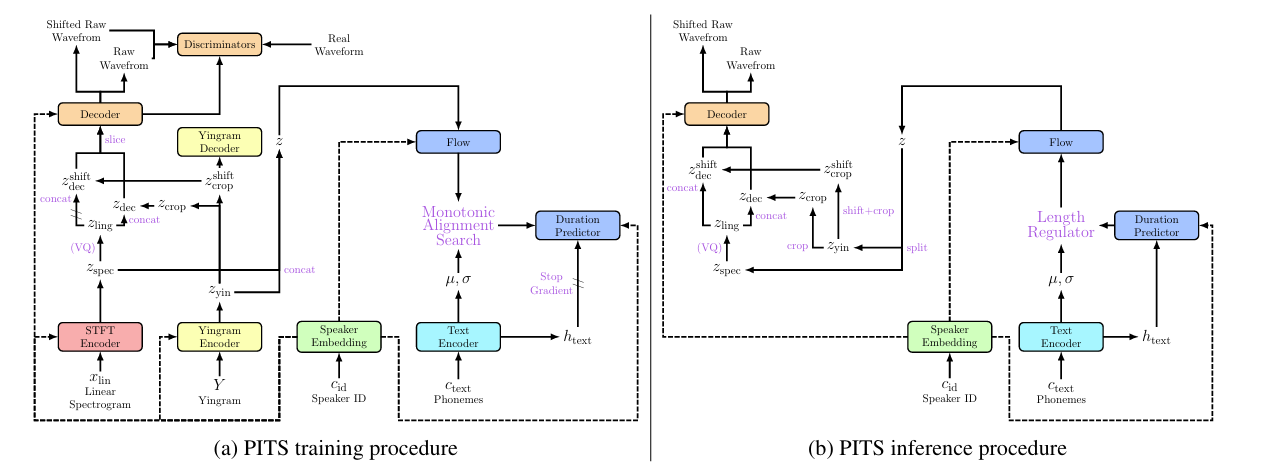
- Q-VAE
- STFT encoder output $z_{spec}$을 disentangle 하기 위해 Q-VAE를 도입함
- STFT encoder의 latent variable을 quantize 하면 linguistic feature와 pitch information을 effectively separate 할 수 있기 때문
- 따라서 VQ extractor와 vocoder training을 포함한 multiple stage 구성을 제거하기 위해 Q-VAE를 VITS training scheme에 적용하여 STFT encoder의 latent variable output $z_{spec}$을 quantize 함
- 즉, VQ extractor는 waveform decoder, flow, text encoder, duration predictor와 함께 training 됨 - PITS의 scheme은 normal VQ-VAE와 다르므로, Q-VAE를 적용할 때 codebook loss $\mathcal{L}_{vq}$와 commit loss $\mathcal{L}_{commit}$이 diverge 할 수 있음
- $z_{spec}$이 flow, codebook으로부터 multiple gradient를 취하기 때문
- 이때 diverging loss를 방지하기 위해 codebook으로부터 $z_{crop}^{shift}$의 gradient를 $1/\lambda_{mel}$로 scale 함
- $\lambda_{mel}=45$ : mel-spectrogram reconstruction loss에 대한 multiplier - 추가적으로 HuBERT, Wav2Vec 2.0의 quantization module과 같이 size 160의 2개의 codebook을 활용함
- Pitch-Shifted Waveform Synthesis
- Yingram encoder의 cropped latent variable $z_{crop},z_{crop}^{shift}$는 quantization 적용 여부에 따라 STFT encoder의 latent variable $z_{vq}, z_{spec}$과 concatenate 되어 $z_{dec},z_{dec}^{shift}$를 구성한 다음 decoder에 input 됨
- Scope-shifted variable이 있는 경우, $z_{crop}^{shift}$는 pitch information을 disentangle 하기 위해 gradient stop을 적용한 다음 $z_{ling}$과 concatenate 됨
- 여기서 brevity를 위해 $z_{vq},z_{spec}$을 $z_{ling}$으로 replace 함 - Stable pitch-controllable model을 위해, PITS는 training 중에 pitch-shifted waveform을 synthesis 함
- Default synthesized raw waveform은 mel-spectrogram loss와 reconstruction loss를 minimize 하도록 training 되고, pitch-shifted waveform은 Yingram reconstruction loss와 adversarial pitch-shifted loss를 활용함 - 먼저 pitch-shifted speech의 ground-truth mel-spectrogram이 존재하지 않으므로, normal synthesized signal과 pitch-shifted signal 모두에 Yingram reconstruction loss를 적용함
- 이때 Yingram은 autocorrelation-based algorithm이므로 differentiable 하지만, pitch-shifted speech의 ideal Yingram은 linguistic information으로 인해 perfectly translation equivariant 하지 않음
- 따라서 논문은 cropped Yingram에 대해 negative exponential을 적용함 - 그러면 Yingram reconstruction loss $\mathcal{L}_{yin}$은:
(Eq. 2) $\mathcal{L}_{yin}=\lambda_{yin}\mathbb{E}\left[\left|\left| e^{(-Y_{crop})}-e^{(-\mathcal{Y}_{crop}(G(z_{dec})))}\right|\right|_{1}+ \left|\left| e^{(-Y_{crop}^{shift})}-e^{(-\mathcal{Y}_{crop}(G(z_{dec}^{shift})))}\right|\right|_{1}\right]$
- $\mathcal{Y}_{crop}$ : Yingram crop function, $G$ : waveform decoder
- 이때 Yingram은 autocorrelation-based algorithm이므로 differentiable 하지만, pitch-shifted speech의 ideal Yingram은 linguistic information으로 인해 perfectly translation equivariant 하지 않음
- 한편으로 $\mathcal{L}_{yin}$만 사용하여 training 된 model은 pitch-shifted speech의 quality가 낮음
- 따라서 논문은 pitch-shifted synthesized speech를 discriminator에 제공하여 pitch-shifted speech에 대한 adversarial feedback을 제공함
- 이때 HiFi-GAN, MelGAN을 따라 pitch-shifted waveform을 original real waveform과 pairing 하고 least-square loss $\mathcal{L}_{adv}^{shift}(G)$와 feature matching loss $\mathcal{L}_{fm}^{shift}(G)$를 적용함
- Discriminator의 경우, Avocodo의 CoMBD, SBD를 채택함
- Scope-shifted variable이 있는 경우, $z_{crop}^{shift}$는 pitch information을 disentangle 하기 위해 gradient stop을 적용한 다음 $z_{ling}$과 concatenate 됨
- Total Loss
- 결과적으로 얻어지는 total loss는:
(Eq. 3) $\mathcal{L}_{total}=\mathcal{L}_{mel}+\mathcal{L}_{KL}+\mathcal{L}_{dur}+\mathcal{L}_{adv}(G)+\mathcal{L}_{fm}(G)+\mathcal{L}_{yin}$
$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,+\left(\mathcal{L}_{adv}^{shift}(G)+\mathcal{L}_{fm}^{shift}(G)\right)+(\mathcal{L}_{yd})+(\mathcal{L}_{vq}+\mathcal{L}_{commit})$
- $\mathcal{L}_{mel},\mathcal{L}_{KL}, \mathcal{L}_{adv},\mathcal{L}_{fm}$ : VITS의 loss 구성을 따름
- $(\,\,)$ 안의 loss term은 model architecture search 시 ommit 될 수 있음
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : VCTK
- Comparisons : VITS, FastSpeech2
- Results
- 전체적으로 PITS의 성능이 가장 뛰어남
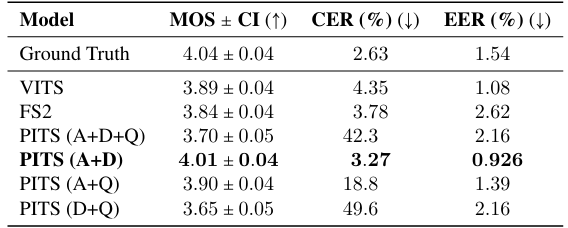
- Adversarial loss (A), Yingram decoding loss (D), Q-VAE loss (Q)에 대해, A+D의 조합은 pitch-shifted speech synthesis에 대한 성능 저하가 나타나지 않음

- Pitch contour 측면에서 PITS는 high controllability를 보임
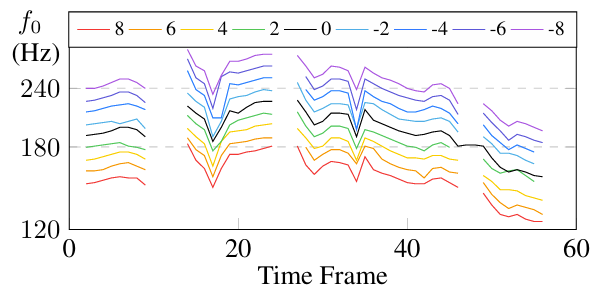
- 실제로 동일한 text에 대해, PITS는 variational Yingram decoder를 활용하여 다양한 pitch를 반영할 수 있음

반응형
'Paper > TTS' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

