티스토리 뷰
Paper/TTS
[Paper 리뷰] LiveSpeech: Low-Latency Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech via Autoregressive Modeling of Audio Discrete Codes
feVeRin 2025. 5. 29. 17:28반응형
LiveSpeech: Low-Latency Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech via Autoregressive Modeling of Audio Discrete Codes
- Neural audio codec을 통해 zero-shot text-to-speech가 가능하지만 low-latency scenario에서 활용하기 어려움
- LiveSpeech
- 각 frame의 codebook contribution을 고려한 adaptive codebook loss를 도입
- Codebook을 grouping 하고 해당 group에 대한 parallel processing을 수행
- 논문 (INTERSPEECH 2024) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- NaturalSpeech2와 같은 Zero-shot Text-to-Speech (TTS)는 speaker-specific model adaptation 없이도 any voice와 유사한 speech를 생성할 수 있음
- 특히 VALL-E는 tokenized audio와 language model을 활용하여 high-quality audio를 생성함
- BUT, real-time, low-latency setting에서는 high inference time으로 인해 사용하기 어려움
- 특히 audio의 high bandwidth nature로 인해 single audio frame은 multiple code로 represent 되고, 해당 code는 sequentially dependent 하므로 sequential Transformer step으로 predict 되어야 함
- 한편으로 MusicGen과 같이 delayed generation pattern을 사용하여 generation을 가속할 수도 있음
- BUT, human speech의 subtle variation을 반영하기 위해서는 많은 codebook이 필요하므로, low-latency TTS task에는 적합하지 않음
-> 그래서 low-latency zero-shot TTS를 위한 LiveSpeech를 제안
- LiveSpeech
- Model capacity를 codebook 전반에 redistribute 하기 위해 loss weighing mechanism을 도입
- Codebook group을 parallel modeling 하여 step capability를 향상
< Overall of LiveSpeech >
- Streaming manner로 low-latency inference를 수행할 수 있는 fully autoregressive Transformer architecture
- 결과적으로 기존보다 빠른 latency와 합성 성능을 달성
2. Background
- Audio Compression with Residual Vector Quantization
- Language model을 audio domain에 적용하기 위해서는 encoder, quantizer, decoder로 구성된 audio tokenization component가 필요함
- 먼저 Encoder는 audio를 $T$ time step의 latent speech representation $\mathbf{z}_{1},\mathbf{z}_{2},...,\mathbf{z}_{T}$로 변환함
- 이후 quantizer는 해당 representation을 recursively quantize 하여 각 $\mathbf{z}_{i}$에 대해 $Q$ code $ \mathbf{c}_{i}=\left[c_{i}^{(1)},c_{i}^{(2)},...,c_{i}^{(Q)}\right]\in\mathcal{C}^{Q}$를 생성함
- $\mathcal{C}$ : codebook index set - 결과적으로 first few code는 audio content를 represent 하고 later code는 fine-grained detail을 represent 함
- 이때 early codebook을 high-level, later codebook을 low-level이라고 함
- 먼저 Encoder는 audio를 $T$ time step의 latent speech representation $\mathbf{z}_{1},\mathbf{z}_{2},...,\mathbf{z}_{T}$로 변환함
- Audio Generation via Discrete Tokens
- Residual Vector Quantization (RVQ) code를 sequentially predict 하면 high inference time을 가짐
- MusicGen은 $Q$ code를 함께 predict 하여 context size를 reduce 할 수 있음
- 이때 각 step이 $Q$ code를 predict 하도록 codebook을 shifting 하는 방식을 사용함 - $\mathbf{C}'=[\mathbf{c}'_{1},...,\mathbf{c}'_{T'}]$을 $\mathbf{C}$로부터 얻어진 shifted code, $T'=T+Q-1$을 shifted code sequence length라고 하자
- Invalid code position에 대해 padding value를 가정하면 $\mathbf{c}'_{i}=\left[c_{i}^{(1)},...,c_{i-(Q-1)}^{(Q)}\right]$를 얻을 수 있음
- 여기서 $\mathbf{C}'$은 $\mathbf{C}$ 대신 Transformer로 modeling 됨 - 그러면 $\mathbf{C}$의 $i$-th audio frame은 $\mathbf{C}'$의 $(i+Q-1)$-th step에서 fully generate 됨
- 이는 discrete code distribution을 modeling 하기 위한 inexact autoregressive decomposition을 제공함
- Invalid code position에 대해 padding value를 가정하면 $\mathbf{c}'_{i}=\left[c_{i}^{(1)},...,c_{i-(Q-1)}^{(Q)}\right]$를 얻을 수 있음
- 결과적으로 해당 delayed generation pattern을 사용하는 경우, limited model capacity로 인해 아래 표와 같이 content accuracy와 voice quality 간에 trade-off가 발생함
- MusicGen은 $Q$ code를 함께 predict 하여 context size를 reduce 할 수 있음

3. Method
- 먼저 편의를 위해 각 Transformer step에 대한 input token $[c'_{1},...,c'_{T'}]$을 $[c_{1},...,c_{T}]$라고 하자
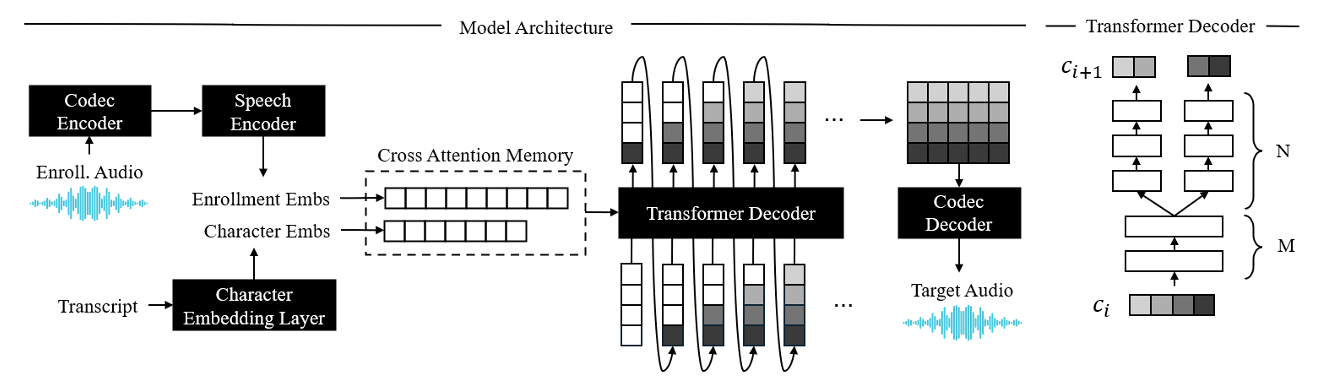
- Model Architecture
- 논문은 GPT-style autoregressive language model과 architecture를 share 함
- 구조적으로는 audio codec, speech encoder, text embedding layer, Transformer decoder를 가짐
- Speech encoder는 encoder-decoder Transformer를 기반으로 variable-length enrollment speech를 사용해 non-autoregressive manner로 fixed-length feature sequence를 생성함
- Transformer decoder는 각 time step에서 $Q$ codebook의 $Q$ code를 처리함
- Decoder는 모든 code embedding의 summation $\mathbf{x}_{t}=\sum_{q=1}^{Q}\text{Emb}_{q}\left(c_{t}^{(q)}\right)$을 취한 다음, vector output으로부터 모든 code를 $\mathbf{p}_{t}^{(q)}=\text{Softmax}\left(\text{Proj}_{q}(\mathbf{o}_{t})\right)$와 같이 predict 함
- $\text{Emb}_{q},\text{Proj}_{q}$ : $q$-th codebook의 embedding, projection layer
- $\mathbf{x}_{t},\mathbf{o}_{t}$ : Transformer step $t$의 input, output
- $\mathbf{p}^{(q)}_{t}$ : step $t$에서 $q$-th code의 softmax probability distribution
- Input, target code는 MusicGen과 같이 delayed generation을 위해 shift 됨
- 구조적으로는 audio codec, speech encoder, text embedding layer, Transformer decoder를 가짐
- Adaptive Codebook Weights
- Content accuracy-Voice quality trade-off를 해결하기 위해 논문은 training 중에 각 codebook에 대한 capacity를 redistribute 하는 adaptive codebook weighing을 도입함
- 즉, high-level code가 final constructed frame에 더 많이 contribute 하고 speech content를 guide 하므로 early training stage에서 high-level code를 prioritize 함
- High-level codebook의 accuracy가 향상되면 correctly predict 하기 어려운 lower-level code에 focus 할 수 있음 - 이를 위해 논문은 model을 frame-level로 fine-tuning 하는 mechanism을 도입하여 same frame 내에서 higher-level code가 얼마나 잘 predict 되는지에 따라 loss의 각 term에 weight를 assign 함
- 먼저 $\tilde{p}_{t}^{(q)}=\mathbb{p}_{t}^{(q)}\left[c_{t}^{(q)}\right]$를 code $c_{t}^{(q)}$를 correctly predict 하기 위한 softmax probability value라고 하자
- 그러면 weighted loss는:
(Eq. 1) $\mathcal{L}=\frac{1}{TQ}\sum_{q=1}^{Q}\sum_{t=1}^{T}\bar{w}_{t}^{(q)}\mathcal{L}_{CE}\left(\mathbf{p}_{t}^{(q)},c_{t}^{(q)}\right) $
- $\bar{w}_{t}^{(1)}=1,\bar{w}_{t}^{(q>1)}=\prod_{q'<q}\left(\tilde{p}_{t}^{(q')}\right)^{\lambda} $ : $c_{t}^{(q)}$ predict loss와 관련된 weight
- $\lambda\geq 0$ : lower level codebook을 얻는데 필요한 decay rate를 control 하는 hyperparameter
- $\bar{w}$ : $w$의 gradient backpropagation을 allow 하지 않음을 의미 - 해당 loss는 beggining에서 high-level code에 focus 하도록 encourage 하고 training이 진행됨에 따라 lower-level code에 대한 focus를 shift 함
- $\lambda=0$일 때 모든 codebook loss term은 same weight를 할당받음
- $\lambda>0$일 때 각 time step $t$에서 codebook weight는 strictly decrease 하고, decreasing rate는 same frame 내에서 previous code를 correctly predict 할 probability에 따라 달라짐
- 해당 weighing은 각 audio frame에서 predict 된 모든 code에 대해 recursively apply 되고, target speech의 각 audio frame에 대해 differently apply 됨
- 한편으로 low-level code에 대한 weight vanish를 방지하기 위해 threshold $p_{\max}$를 도입하고, code $\tilde{\mathbf{p}}_{t}^{(q)}$를 correctly predict 할 probability가 $p_{\max}$보다 크면 $q$-th code를 ignore 함
- Same frame에 있는 remaining code의 weight는 largest weight가 $1$이 되도록 scale 되어 easy prediction을 ignore 할 수 있도록 함
- 즉, high-level code가 final constructed frame에 더 많이 contribute 하고 speech content를 guide 하므로 early training stage에서 high-level code를 prioritize 함
- Parallel Codebook Group Heads
- Transformer는 모든 codebook 내에서 code를 single step으로 predict 해야 함
- 따라서 논문은 각 step의 modeling capacity를 향상하기 위해 $Q$ code를 $G$ group으로 grouping 한 다음, 각 group에서 own hidden representation과 함께 parallel decoding step에서 code를 predict 함
- 한편으로 code를 grouping 하면 각 group이 memory의 서로 다른 part에 attend 할 수 있음
- e.g.) Low-level code는 recent time step에서 생성된 code로부터 더 많은 benefit을 얻을 수 있음 - $L$을 Transformer layer 수라고 하자
- 먼저 모든 codebook group에 대해 $M$ shared layer를 keep 한 다음, 각 group을 independently process 하기 위해 $N=L-M$ layer를 사용함
- Transition layer에서는 group-specific projection layer를 사용하여 layer output $\mathbf{o}_{t,M}$을 $G$ next layer input으로 $\mathbf{h}_{t,M+1}^{g}=\text{GProj}_{g}(\mathbf{o}_{t,M})$과 같이 split 함
- $g$ : group index - Last layer에서는 $q$-th codebook에 대한 group $\gamma(q)$의 output으로부터 각 code $c_{t}^{(q)}$의 probability $\mathbf{p}^{(q)}_{t}=\text{Softmax}\left(\text{Proj}_{q}\left( \mathbf{o}_{t,L}^{\gamma(q)}\right)\right)$를 얻음
4. Experiments
- Settings
- Results
- 전체적으로 LiveSpeech의 성능이 가장 우수함

반응형
'Paper > TTS' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

