티스토리 뷰
Paper/TTS
[Paper 리뷰] ARCHI-TTS: A Flow-Matching-Based Text-to-Speech Model with Self-Supervised Semantic Aligner and Accelerated Inference
feVeRin 2026. 2. 13. 12:47반응형
ARCHI-TTS: A Flow-Matching-Based Text-to-Speech Model with Self-Supervised Semantic Aligner and Accelerated Inference
- Diffusion-based non-autoregressive Text-to-Speech model은 text-speech alignment와 high computational overhead의 문제점이 있음
- ARCHI-TTS
- Text, audio 간의 robust temporal, semantic consistency를 보장하는 dedicated semantic aligner를 도입
- Denoising step에서 encoder feature를 reuse 하여 추론 속도를 향상
- 논문 (ICASSP 2026) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Zero-shot Text-to-Speech (TTS) model은 autoregressive (AR), non-autoregressive (NAR) model로 나눌 수 있음
- 특히 F5-TTS와 같은 NAR model은 parallel synthesis를 기반으로 AR model의 성능을 크게 개선함
- BUT, Flow Matching 기반의 NAR model은 여전히 다음의 한계점이 존재함:
- Text-Speech alignment modeling
- 대표적으로 NaturalSpeech3, VoiceBox는 phoneme-level duration과 같은 explicit guidance에 의존하고 Matcha-TTS는 monotonic alignment search와 같은 auxiliary predictor에 의존함 - Iterative denoising으로 인한 computational intensity
- 특히 E1-TTS와 같은 distillation strategy는 training을 복잡하게 만든다는 단점이 있음
- Text-Speech alignment modeling
-> 그래서 Flow Matching TTS model의 앞선 한계점들을 개선한 ARCHI-TTS를 제안
- ARCHI-TTS
- Text-Speech alignment modeling을 위해 flexible length의 self-supervised text-aligned semantic representation을 생성하는 semantic aligner를 도입
- Condition encoder output을 multiple denoising step에 걸쳐 resue 하여 iterative denoising step을 절감
< Overall of ARCHI-TTS >
- Semantic aligner와 condition encoder reusing을 활용한 fast, high-quality Flow Matching TTS model
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 성능을 달성
2. Method
- ARCHI-TTS는 text input과 short audio prompt를 condition으로 fully non-autoregressive speech synthesis를 수행함
- 구조적으로 Semantic Aligner는 text embedding과 해당 speech representation 간의 alignment를 생성하고 Diffusion Transformer (DiT) block으로 구성된 Flow Matching Decoder는 synthesis를 수행함
- Semantic Aligner
- 논문은 text의 semantic content와 speech의 temporal structure를 explicitly learning 하기 위해 Transformer encoder를 기반으로 한 Semantic Aligner를 도입함
- 이때 aligner는 2가지 input sequence를 처리함:
- Text Sequence
- Character token sequence로 represent 된 input text $y$를 embedding으로 encoding 하고, 해당 embedding을 ConvNeXtV2 block에 전달하여 rich semantic feature를 얻음 - Speech-Length Sequence
- Target speech의 temporal duration을 represent 하기 위해 learnable mask embedding $m$을 speech latent length $N$ 만큼 replicate 하여 masked sequence를 생성함
- Text Sequence
- 이후 각 sequence에는 learnable start-of-sequence token이 prepend 되어 Transformer로 전달됨:
(Eq. 1) $ z=\texttt{Transformer}(e_{st},y,e_{sm},\underset{N\,\text{times}}{\underbrace{m,...,m}})$
- $e_{st}, e_{sm}$ : 각각 start-of-sequence, mask sequence를 represent 하는 learnable special token - Replicated mask embedding은 uniform temporal canvas로 사용되어 초기에는 target speech의 duration 만을 encoding 함
- 이후 semantic aligner는 Transformer block을 통해 text feature의 semantic representation을 aggregate 하고 temporal canvas와 align 함
- 이를 통해 simple duration marker sequence를 contextually-aware semantic feature의 rich sequence로 convert 하고 text token length에 대한 speech audio length dependency를 remove 할 수 있음
- 이때 aligner는 2가지 input sequence를 처리함:

- Compressed Speech Latent Representation
- 논문은 Variational AutoEncoder (VAE)의 highly compressed, low-token-rate latent representation을 활용하여 기존 intermediate acoustic representation인 mel-spectrogram의 high temporal redundancy 문제를 해결함
- 여기서 VAE는 KL-divergence를 사용하여 latent space를 regularzie 하는 neural audio comressor로 사용됨
- 즉, VAE는 encoder, decoder 역할을 동시에 수행하여 representation, synthesis stage를 unify 할 수 있음 - 결과적으로 논문은 24kHz speech signal을 12.5Hz token rate의 continuous latent sequence로 encoding 하도록 VAE를 training 함
- 여기서 VAE는 KL-divergence를 사용하여 latent space를 regularzie 하는 neural audio comressor로 사용됨
- Condition Encoder with Flow Matching
- Speech decoder는 다양한 input에 condition 된 VAE latent representation을 생성함
- 이를 위해 논문은 Conditional Flow Matching (CFM) framework를 채택함:
- CFM은 simple prior distribution $p_{0}$를 true data distribution $q$와 match 하는 target data distribution $p_{1}$으로 transform 하는 flow $\phi_{t}$를 생성하는 time-dependent vector field $v_{t}(x_{t};\theta)$를 학습함
- Optimal transport path를 따라 noise sample $x_{0}\sim p_{0}$와 data sample $x_{1}\sim q$ 간의 trajectory는 linear interpolation $x_{t}=(1-t)x_{0}+tx_{1}$으로 정의됨
- $t\in [0,1]$
- 여기서 conditional vector field $v_{t}$를 parameterize 하기 위해, 논문은 DiT를 encoder-decoder architecture에 도입함
- 한편으로 model은 다음과 같은 rich input set으로 condition 됨:
- Speech content를 guide 하기 위해 semantic aligner로부터 전달되는 semantic feature $z$
- Coarse-grained speaker timbre를 control 하기 위해 speech length에 맞춰 replicate 된 global embedding인 speaker embedding $s$
- Fine-grained speaker timbre를 preserve 하기 위해 사용되는 target speech latent의 masked segment인 audio prompt $x_{ref}$
- 이는 $x_{ref}=(1-n)\odot x_{1}$과 같이 random start position을 가지는 binary mask $n$을 ground-truth latent에 적용하여 얻어짐
- Condition encoder는 conditioned hidden state $h_{t}$를 생성하여 velocity decoder가 flow velocity $v_{t}$를 predict 하기 위한 rich contextual information을 제공함
- CFM loss는 optimal transport path의 ground-truth/predicted velocity 간의 match를 유도함:
(Eq. 2) $\mathcal{L}_{CFM}=\mathbb{E}_{t,q(x_{1}),p_{0}(x_{0})}\left[ \left|\left| v_{t}\left(x_{t},x_{ref},z,s;\theta\right)-\hat{v}_{t}\right|\right|^{2}\right]$ - Hidden repesentation과 input text 간의 semantic alignment를 향상하기 위해 논문은 Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) framework 기반의 auxiliary text alignment loss를 도입함:
(Eq. 3) $\mathcal{L}_{CTC}=-\log p_{CTC}\left(y|\Phi_{i}\left(v_{t}\left( x_{t},x_{ref},z,s;\theta\right)\right)\right)$
- $\Phi_{i}$ : condition encoder의 $i$-th DiT block의 intermediate hidden representation
- 이를 위해 논문은 Conditional Flow Matching (CFM) framework를 채택함:
- Velocity Decoder
- Velocity decoder는 denoising process의 각 step $t$에서 velocity vector field $v_{t}$를 predict 함
- 구조적으로는 DiT block과 predicted velocity를 output 하는 final projection layer로 구성되고, noisy speech latent $x_{t}$, condition encoder의 conditioned hidden state $h$를 input으로 사용함
- 이때 $h$를 $x_{t}$에 simply concatenate 하지 않고 $h$를 global condition으로 inject 함
- 즉, $h$는 sinusoidal timestep embedding에 add 되고 해당 combined embedding이 각 DiT block에 전달됨
- 추가적으로 convergence와 synthesis quality를 향상하기 위해 velocity direction loss $\mathcal{L}_{DIR}$을 도입하고 logit-normal timestep sampling을 적용함
- Direction loss는 cosine-similarity를 사용하여 correct flow orientation을 보장하고, logit-normal sampling은 start/end point에 대한 training에 focus 하도록 유도함 - 결과적으로 final training objective는:
(Eq. 4) $\mathcal{L}=\mathcal{L}_{CFM}+\mathcal{L}_{DIR}+\eta\cdot \mathcal{L}_{CTC}$
- $\eta$ : hyperparameter
- 구조적으로는 DiT block과 predicted velocity를 output 하는 final projection layer로 구성되고, noisy speech latent $x_{t}$, condition encoder의 conditioned hidden state $h$를 input으로 사용함
- Zero-Shot TTS
- Zero-shot synthesis는 reference audio $x_{ref}$, reference transcription $y_{ref}$, speaker embedding $s_{ref}$를 condition으로 사용하여 target text $y_{gen}$에 대한 speech audio를 생성함
- 이때 output VAE latent sequence duration은 reference audio의 token-per-frame rate를 preserve 하여 estimate 되므로 prosodic consistency를 보장할 수 있음
- Reference audio에 대한 $T_{ref}$ latent frame, referece/target transcription에 대한 $L_{ref}, L_{gen}$ text token이 주어지면, target duration은 $d=\lfloor L_{gen}\cdot (T_{ref}/L_{ref})\rfloor$와 같이 얻어짐
- 이후 semantic conditioning을 위해 reference, target transcription $y_{ref}$, $y_{gen}$을 concatenate 하여 unified context를 얻고, Semantic Aligner를 통해 single semantic feature vector $z_{ref\cdot gen}$을 추출하여 synthesis를 guide 함
- 최종적으로 condition encoder, velocity decoder를 통해 final VAE latent representation을 얻기 위해 Euler solver를 적용하고, VAE decoder를 통해 speech audio로 transform 함
- Sampling
- Sample generation은 learned velocity field에 대해 ODE를 solve 하여 수행됨
- 논문은 quality를 향상하기 위해 Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG)를 도입하고, 추론 시 guided velocity는 conditional에서 unconditional prediction으로 extrapolate 하여 얻어짐:
(Eq. 5) $ \tilde{v}_{t}(x_{t},c,\omega;\theta)=(1+\omega)v_{t}(x_{t},c;\theta)-\omega v_{t}(x_{t},\emptyset;\theta)$
- $c, \emptyset$ : condition, zero (unconditional) condition, $\omega$ : CFG strength - 추론 시 intermediate conditioned hidden state $h_{t}$는 adjacent $t$에 걸쳐 share 되어 sampling을 가속함
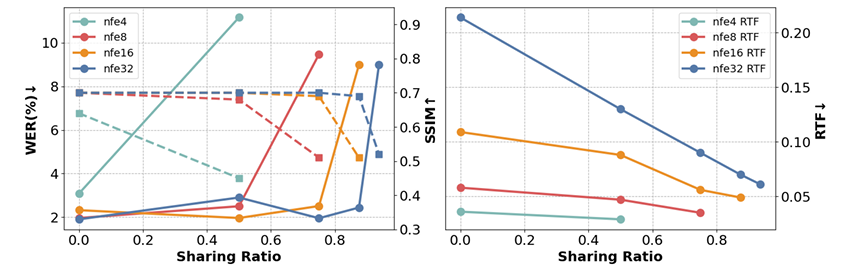
- 이때 $N$ NFE step과 $K$ sharing step이 주어지면 sharing ratio는 $1-K/N$과 같이 얻을 수 있음 - 결과적으로 논문은 해당 mechanism을 기반으로 previous timestep에서 store 된 encoder output을 reuse 함으로써 expansive encoder component를 bypass 함
- 논문은 quality를 향상하기 위해 Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG)를 도입하고, 추론 시 guided velocity는 conditional에서 unconditional prediction으로 extrapolate 하여 얻어짐:
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : Emilia, LibriHeavy, LibriTTS
- Comparisons : CosyVoice, MaskGCT, E2-TTS, F5-TTS, DiTAR, FireRedTTS
- Results
- 전체적으로 ARCHI-TTS의 성능이 가장 우수함

- Seed-TTS dataset에 대해서도 높은 성능을 달성함

- MOS 측면에서도 우수한 성능을 보임

- 각 component는 성능 향상에 유효함

- High sharing ratio는 추론 속도를 크게 가속할 수 있음
반응형
'Paper > TTS' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

