티스토리 뷰
Paper/Neural Codec
[Paper 리뷰] LSCodec: Low-Bitrate and Speaker-Decoupled Discrete Speech Codec
feVeRin 2025. 7. 11. 13:13반응형
LSCodec: Low-Bitrate and Speaker-Decoupled Discrete Speech Codec
- Discrete speech token은 high bitrate, redundant timbre information으로 인한 한계를 가짐
- LSCodec
- Speaker perturbation을 활용한 multi-stage unsupervised training framework를 채택
- Continuous information bottleneck을 설정한 다음, discrete speaker-decoupled space를 생성하는 vector quantization을 수행하고, discrete token vocoder를 통해 acoustic detail을 refine
- 논문 (INTERSPEECH 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- VALL-E, UniAudio, VQTTS 등에서 discrete speech token은 language model (LM)의 input으로 사용됨
- 특히 speech token의 bitrate는 quantizer 수 $Q$, frame rate $F$, 각 quantizer의 vocabulary size $V$에 따라 $Q\times F\times \lceil \log_{2} V\rceil \text{bps}$로 결정됨
- $F$가 작으면 speech, text modality 간의 length mismatch를 mitigate할 수 있음
- $Q,V$가 작으면, speech LM은 simpler training objective를 가질 수 있음
- 추가적으로 discrete speech token은 다음과 같이 분류됨:
- EnCodec, DAC와 같은 acoustic codec은 vector quantization (VQ) module을 통해 audio를 perfectly reconstruct 하는 것을 목표로 함
- BUT, acoustic token에서는 timbre가 여러 timestep에 걸쳐 repeatedly encode됨 - VQ-Wav2Vec, HuBERT, Wav2Vec 2.0, WavLM과 같은 semantic token은 self-supervised learning (SSL)에서 derive 되어 content information을 반영함
- BUT, semantic token은 paralinguistic information을 discard 할 수 있음
- EnCodec, DAC와 같은 acoustic codec은 vector quantization (VQ) module을 통해 audio를 perfectly reconstruct 하는 것을 목표로 함
- 이때 speech token의 bitrate를 lowering 하면서 동시에 speaker information을 remove 하기는 어려움
- 특히 speech token의 bitrate는 quantizer 수 $Q$, frame rate $F$, 각 quantizer의 vocabulary size $V$에 따라 $Q\times F\times \lceil \log_{2} V\rceil \text{bps}$로 결정됨
-> 그래서 speaker decoupling을 수행하면서 low-bitrate speech token을 얻을 수 있는 LSCodec을 제안
- LSCodec
- Speaker disentanglement와 temporal compression을 위해 3-stage process로 Speech Variational AutoEncoder (VAE)를 training
- Explicit timbre removal을 위해 stretching-based perturbation을 도입
< Overall of LSCodec >
- Speaker decoupling을 만족하면서 single-codebook low-bitrate speech token을 생성하는 codec model
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 성능을 달성
2. Method
- Speaker Perturbation
- Discrete speech token과 speaker information을 explicitly disentangle 하기 위해서는 tokenization 이전에 speaker timbre를 appropriate modification 해야 함
- 이를 위해 논문은 pitch, timbre change만 가지는 time-aligned perturbed speech를 생성하는 time stretching approach를 도입함
- Coefficient $\beta$가 주어지면, 해당 perturbation process는 먼저 utterance의 total duration을 $\times \beta$로 scaling 하는 rate-based speed-up effect를 적용함
- 이를 통해 pitch, formant position을 변경하여 timbre를 altering 할 수 있음 - 이후 WSOLA algorithm을 통해 utterance를 original duration으로 re-stretch 하는 pitch-preserving tempo effect를 적용함
- 이를 통해 content, pitch variation을 retain 하면서 global pitch position과 timbre feature를 change 함
- Coefficient $\beta$가 주어지면, 해당 perturbation process는 먼저 utterance의 total duration을 $\times \beta$로 scaling 하는 rate-based speed-up effect를 적용함
- 결과적으로 speech를 reconstruct 하기 위해서는 perturbed segment가 아닌 additional input에서 timbre를 학습해야 하고, reconstruction process의 information bottleneck으로 인해 speaker는 explicitly disentangle 됨
- Training 시에는 각 utterance에 대해 $1$을 중심으로 한 interval 내에서 $\beta$가 independently sampling 되어 randomized variation을 제공함
- 이를 위해 논문은 pitch, timbre change만 가지는 time-aligned perturbed speech를 생성하는 time stretching approach를 도입함

- Training Stage 1: Speech VAE
- LSCodec의 first stage에서는 continuous space에서의 Speech VAE를 training 함
- 먼저 utterance waveform이 주어지면, 논문은 reference prompt와 content segment로 randomly cut 함
- Content segment $x$는 random $\beta$와 함께 perturbation algorithm에 전달되고, CNN encoder는 time-domain에서 signal을 compress 한 다음, 각 frame $t$에 대해 isotropic Gaussian posterior $\mathcal{N}(\mu_{t},\sigma_{t}^{2})$을 output 함
- Frame rate는 CNN stride를 통해 control 됨 - 이후 sampled posterior는 Conformer-based decoder에 feed 됨
- Content segment $x$는 random $\beta$와 함께 perturbation algorithm에 전달되고, CNN encoder는 time-domain에서 signal을 compress 한 다음, 각 frame $t$에 대해 isotropic Gaussian posterior $\mathcal{N}(\mu_{t},\sigma_{t}^{2})$을 output 함
- 한편으로 논문은 AutoVC와 같이 information bottleneck을 형성하기 위해, decoder에 sufficient timbre information을 제공함
- 특히 prompt segment에서 decoder로 timbre를 feed 하기 위해 position-agnostic cross-attention을 사용함
- 추가적으로 discriminative timbre feature를 제공하기 위해 WavLM을 사용하여 reference prompt의 hidden embedding을 추출함
- 결과적으로 reference, content segment가 서로 다르고, cross-attention은 position-agnostic 하므로 reference prompt는 timbre information만 제공할 수 있음 - Decoder에 sufficient timbre와 perturbed input이 제공되면, VAE를 통해 형성된 information bottleneck은 posterior와 timbre를 naturally disentangle 할 수 있음
- 여기서 WavLM embedding은 decoder input 이전에 CNN prompt prenet에 feed 됨
- Decoder는 original unperturbed content segment에서 mel-spectrogram과 SSL semantic token의 2가지 feature를 predict 함
- 즉, VAE model은 acoustic mel-feature로 regress 하고 fixed vocabulary size에서 SSL semantic token을 classify 하는 multi-task learning을 수행함
- 이때 ground-truth SSL token은 WavLM과 $k$-means clustering을 통해 추출됨 - Mel-spectrogram prediction은 bottleneck feature의 reconstruction ability를 보장함
- Semantic token은 compact discrete space에서 rich content information을 retain 하므로, SSL token prediction은 bottleneck feature가 sufficient content를 encode 하도록 guide 할 수 있음
- 한편으로 prosody information은 discrete WavLM token에서 largely damage 되므로 논문은 mel-prediction task를 keeping 하여 prosody가 bottleneck에 encode 되지 않도록 함
- 즉, VAE model은 acoustic mel-feature로 regress 하고 fixed vocabulary size에서 SSL semantic token을 classify 하는 multi-task learning을 수행함
- 결과적으로 training loss는 KL loss $\mathcal{L}_{KL}$와 predicted mel-feature의 $L1$ loss $\mathcal{L}_{recon}$, predicted SSL index의 cross-entropy loss $\mathcal{L}_{idx}$로 구성됨:
(Eq. 1) $ \mathcal{L}_{KL}=\frac{1}{T}\sum_{t=1}^{T}D_{KL}\left(\mathcal{N} (\mu_{t},\sigma_{t}^{2})|| \mathcal{N}(0,1)\right)$
- 각 loss term에는 $\gamma_{KL},\gamma_{recon}, \gamma_{idx}$가 weight 됨 - Speech VAE의 information bottleneck을 통해 speaker timbre는 continuous space에서 partially remove 됨
- 먼저 utterance waveform이 주어지면, 논문은 reference prompt와 content segment로 randomly cut 함
- Training Stage 2: Speech VQ-VAE
- Second stage에서는 desired LSCodec token을 얻기 위해 trained VAE에 codebook size $V$의 VQ layer를 inject 함
- 먼저 training data의 일부를 사용하여 VAE에서 Gaussian mean $\mu$를 추출하고 codebook을 initialize 하기 위해 $V$-centroid $k$-means clustering을 수행함
- VQ-VAE architecture는 first stage와 동일한 대신, training 이전에 encoder, decoder, prompt prenet parameter를 resume 함
- 그러면 VQ layer는 encoder output을 $V$ candidate 중에서 smallest Euclidean distance를 가지는 codebook entry로 quantize 함
- 여기서 gradient backpropagation을 위해 Straight-Through estimator가 적용됨 - 이후 quantized token은 codebook vector에 mapping 되어 decoder에 전달됨
- VQ layer의 codebook은 Exponential Moving Average (EMA)로 update 됨
- Training criterion은 Stage 1을 inherit 하되, VQ layer에서 KL loss를 commitment loss $\mathcal{L}_{cmt}$로 replace 함
- 여기서 previous Gaussian variance의 dimension은 disable 되고 loss $\mathcal{L}_{cmt}$는 $\gamma_{cmt}$로 weight 됨 - 결과적으로 해당 VQ layer와 resumed parameter를 활용해, VQ-VAE는 Stage 1의 insufficiently speaker-decoupled continuous space를 기반으로 한 discrete space를 construct 함
- Information bottleneck은 timbre가 encode 되는 것을 further restrict 함
- 먼저 training data의 일부를 사용하여 VAE에서 Gaussian mean $\mu$를 추출하고 codebook을 initialize 하기 위해 $V$-centroid $k$-means clustering을 수행함
- Training Stage 3: Vocoder CTX-Vec2Wav$^{\alpha}$
- Predicted mel-spectrogram에서 waveform을 synthesize 하면 audio quality가 저하될 수 있으므로, 논문은 Vocos와 같이 discrete token을 기반으로 한 specialized vocoder를 additionally training 함
- 이때 LSCodec token은 timbre를 decently remove 하므로 strong timbre controllability를 가진 CTX-Vec2Wav를 vocoder로 채택함
- 특히 이전 stage에 맞춰, timbre feature로 reference prompt의 mel-spectrogram이 아닌 WavLM output을 사용하는 CTX-Vec2Wav$^{\alpha}$를 구성함 - 결과적으로 해당 vocoder를 통해 acoustic detail을 refine 하여 high-quality waveform을 생성하고, timbre를 변경하는 high-quality Voice Conversion model로도 활용할 수 있음
- 이때 LSCodec token은 timbre를 decently remove 하므로 strong timbre controllability를 가진 CTX-Vec2Wav를 vocoder로 채택함
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : LibriTTS
- Comparisons : SemantiCodec, StableCodec, TiCodec, DAC, WavTokenizer
- Results
- Reconstruction 측면에서 LSCodec이 가장 우수한 성능을 보임

- Any-to-Any Voice Conversion task에 LSCodec을 활용하면 우수한 성능을 얻을 수 있음

- Speaker Information Probing
- LSCodec은 가장 낮은 probing accuracy를 보이므로, speaker timbre를 효과적으로 remove 할 수 있음

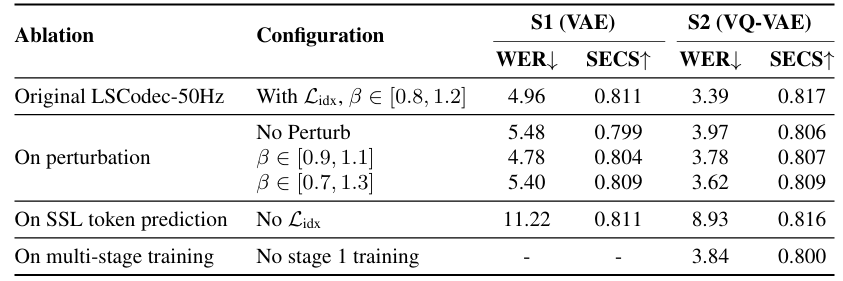
- Ablation Study
- 각 component를 제거하는 경우 성능 저하가 발생함
반응형
'Paper > Neural Codec' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

