티스토리 뷰
Paper/Vocoder
[Paper 리뷰] Vocos: Closing the Gap Between Time-domain and Fourier-based Neural Vocoders for High-Quality Audio Synthesis
feVeRin 2024. 5. 19. 12:20반응형
Vocos: Closing the Gap Between Time-domain and Fourier-based Neural Vocoders for High-Quality Audio Synthesis
- 기존의 neural vocoder는 time-domain에서 동작하는 Generative Adversarial Network을 활용함
- BUT, 해당 방식은 time-frequency representation이 제공하는 inductive bias를 무시하므로 redundant, computationally-intense 한 upsampling operation이 요구됨
- Vocos
- 더 빠른 계산과 human perception과의 align의 이점을 활용할 수 있는 Fourier-based time-frequency representation을 활용
- Complex-valued spectrogram reconstruction 과정에서 발생하는 phase recovery 문제를 해결하기 위해, 모델이 Fourier spectral coefficient를 직접 생성하도록 함
- 논문 (ICLR 2024) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- 기존의 neural vocoder는 time-domain에서 audio sample distribution을 모델링하여 음성 합성을 수행함
- 이때 time-domain vocoder는 크게 autoregressive, non-autoregressive model로 나누어짐
- WaveNet과 같은 autoregressive model은 sample을 sequential 하게 생성하여, 이전에 생성된 모든 sample에 대해 새로운 sample을 conditioning 함
- Non-autoregressive model은 모든 sample을 independent 하게 생성하므로 parallelizing이 가능함
- BUT, 이러한 time-domain audio 합성에서는 signal의 spectral representation을 생성하는 것이 어려움
- 특히 Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT)는 original signal을 완벽하게 reconstruct 하는 것이 가능하지만, 대부분의 경우에서 STFT의 magnitude만 사용하므로 information loss가 발생함
- STFT의 magnitude는 duration 동안 다양한 frequency component의 amplitude를 explicit 하게 나타내지만, phase information은 비직관적이기 때문에 manipulation 시 unpredictable 한 결과를 발생시키기 때문 - 따라서 phase distribution을 모델링하는 것은 time-frequency domain의 intricate nature로 인해 한계가 있음
- 아래 그림과 같이 phase spectrum은 periodic structure로 인해 $(-\pi,\pi]$ range 내에서 principal value를 wrapping 하게 만듦
- (b)와 같이 phase wrapping은 $-\pi$와 $\pi$ 주변에서 observe 되는 discontinuity를 발생시키지만, complex plane에서 해당 discontinuity는 continuous rotation을 나타냄
- (c)의 instantaneous phase는 $\varphi(t)=\arg\{\hat{s}(t)\}$로 계산됨
- $\hat{s}(t)$ : $s(t)=\sin(\omega t)$의 Hilbert transform
- 아래 그림과 같이 phase spectrum은 periodic structure로 인해 $(-\pi,\pi]$ range 내에서 principal value를 wrapping 하게 만듦
- BUT, 위의 어려움에도 불구하고 phase spectrum에 대한 효과적인 추정이 가능하면 audio에 대한 perceptual quality를 크게 향상할 수 있음
- 이때 time-domain vocoder는 크게 autoregressive, non-autoregressive model로 나누어짐

-> 그래서 audio 합성 성능 향상을 위해 Fourier-related coefficient 모델링을 generative model에 반영한 Vocos를 제안
- Vocos
- Audio의 complex STFT coefficient를 생성하도록 train 된 Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)-based vocoder
- Upsampling 시 transposed convolution을 사용하는 기존 time-domain vocoder와 달리, 모든 layer에 대해 동일한 feature temporal resolution을 유지하고 Inverse STFT (iSTFT)를 통해 upsampling을 수행함 - Phase angle 추정을 위해 unit circle로 정의된 activation function을 채택
- 이를 통해 implicit phase wrapping을 incorporate 하여 모든 phase angle에서 meaningful value를 보장함 - Network 전체에 걸쳐 low temporal resolution을 유지하기 위해, 기존 time-domain vocoder에서 사용되는 dilated convolution 대신 ConvNeXt block을 도입함
- Audio의 complex STFT coefficient를 생성하도록 train 된 Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)-based vocoder
< Overall of Vocos >
- Complex-valued spectrogram reconstruction 과정에서 발생하는 phase reconstruction 문제를 해결하기 위해, 모델이 Fourier spectral coefficient를 직접 생성하도록 함
- 이때 upsampling을 위해 time-frequency domain에 대한 iSTFT와 ConvNeXt block을 도입
- 결과적으로 기존 vocoder보다 뛰어난 합성 성능을 달성
2. Method
- Overview
- Vocos는 GAN을 기반으로하여 generator의 target data distribution으로써 Fourier-based time-frequency representation을 사용함
- 이때 Vocos는 transposed convolution을 사용하지 않고, 대신 iSTFT를 통해 upsampling을 수행함
- 기존 time-domain vocoder의 경우, transposed convolution으로 input feature를 target waveform의 resolution으로 변환하기 위해 수백 번의 upscaling이 요구됨
- 반면 Vocos는 iSTFT를 사용하므로 network 전체에 대해 동일한 temporal resolution을 유지하는 isotropic architecture를 활용할 수 있음
- 특히 transposed convolution은 aliasing artifact를 발생시키므로, Vocos는 learnable upsampling layer를 제거하고 well-established iSTFT를 사용함으로써 original-scale waveform을 artifact 없이 reconstruction 할 수 있음
- 여기서 mel-spectrogram을 audio signal로 변환할 때, temporal resolution은 STFT hop size로 결정됨 - 결과적으로 Vocos는 다음의 STFT를 사용하여 time-frequency domain의 audio signal을 represent함:
(Eq. 1) $\mathrm{STFT}_{x}[m,k]=\sum_{n=0}^{N-1}x[n]w[n-m]e^{-j2\pi kn/N}$
- STFT는 signal의 successive windowed section에 Fourier transform을 적용함
- 실제로 STFT는 window function이 time에 따라 hop 되어 만들어진 overlapping, windowed data의 frame에 대해 Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) sequence를 적용하여 계산됨
- 이때 Vocos는 transposed convolution을 사용하지 않고, 대신 iSTFT를 통해 upsampling을 수행함

- Model
- Backbone
- Vocos는 ConvNeXt를 generator의 backbone으로 사용함
- 이를 위해 먼저 input feature를 hidden dimensionality로 embed 한 다음, 1D convolutional stack을 적용함
- 이때 각 block은 depthwise convolution로 구성되고 pointwise convolution을 사용하여 feature를 더 높은 dimensionality로 project 하는 inverted bottleneck이 추가됨 - GELU activation은 bottleneck 내에서 사용되고, 각 block 사이에는 Layer Normalization이 적용됨
- Head
- Real-valued signal의 Fourier transform은 conjugate symmetric 하므로, single-side band spectrum만 사용하여 frame당 $n_{fft}/2+1$의 coefficient를 얻음
- 여기서 phase, magnitude value를 output 하기 위해 model을 parameterize 하면, hidden-dim activation은 $n_{fft}/2+2$ channel을 사용하여 tensor $\mathbf{h}$에 project 되고 다음과 같이 split 됨:
(Eq. 2) $\mathbf{m},\mathbf{p}=\mathbf{h}[1:(n_{fft}/2+1)],\mathbf{h}[(n_{fft}/2+2):n]$
- Magnitude를 나타내기 위해 $\mathbf{m}$에 exponential function을 적용함: $M=\exp(\mathbf{m})$ - $\mathbf{p}$의 cosine과 sine을 계산하여 각각 $\mathbf{x},\mathbf{y}$를 얻고, $\mathbf{p}$를 unit circle에 mapping 하면:
(Eq. 3) $\mathbf{x}=\cos(\mathbf{p})$
(Eq. 4) $\mathbf{y}=\sin(\mathbf{p})$ - 최종적으로 complexed-value coefficient는 $\mathrm{STFT} = M\cdot (\mathbf{x}+j\mathbf{y})$로 얻어짐
- 해당 formulation을 통해 임의의 real argument $\mathbf{p}$에 대해 phase angle $\varphi = \mathrm{atan2}(\mathbf{y},\mathbf{x})$를 express 할 수 있음
- 결과적으로 $\varphi$가 desired range $(-\pi,\pi]$에 correctly wrapped 되도록 보장 가능
- Discriminator
- Loss
- Vocos의 training objective는 reconstruction loss, adversarial loss, feature matching loss로 구성됨
- 이때 least squares GAN objective 대신 hinge loss를 활용함:
(Eq. 5) $\ell_{G}(\hat{x})=\frac{1}{K}\sum_{k}\max(0,1-D_{k}(\hat{x}))$
(Eq. 6) $\ell_{D}(x,\hat{x})=\frac{1}{K}\sum_{k}\max(0,1-D_{k}(x))+\max(0,1+D_{k}(\hat{x}))$
- $D_{k}$ : $k$-th sub-discriminator - 그러면 reconstruction loss $L_{mel}$은 ground-truth sample $x$와 합성된 sample $\hat{x}$간의 mel-scaled magnitude spectrogram의 $L1$ distance로 정의됨:
$L_{mel}=|| \mathcal{M}(x)-\mathcal{M}(\hat{x})||_{1}$ - Feature matching loss $L_{feat}$는 $k$-th sub-discriminator의 $l$-th feature map 간 distance의 평균으로 계산됨:
$L_{feat}=\frac{1}{KL}\sum_{k}\sum_{l}|| D_{k}^{l}(x)-D_{k}^{l}(\hat{x})||_{1}$
- 이때 least squares GAN objective 대신 hinge loss를 활용함:
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Results
- Objective Evaluation
- 거의 모든 metric에서 제안된 Vocos가 가장 우수한 성능을 보임
- 추가적으로 ablation study 측면에서 다음을 비교해 보면,
- Vocos with Absolute Phase
- $[-\pi, \pi]$ range로 scale 된 tanh nonlinearity를 사용해 phase angle을 예측하는 경우, phase에 periodic nature를 제공하지 못하므로 품질 저하가 발생함
- 즉, Vocos의 implicit phase wrapping이 성능 개선에 효과적이라는 것을 의미 - Vocos with Snake Activation
- BigVGAN과 같은 time-domain vocoder에서는 Snake activation이 효과적이지만 Vocos에서는 유의미한 개선을 보이지 못함
- Snake activation은 time-domain에 periodicity를 반영하기 위해 사용되는데, Vocos는 Fourier basis function을 통해 periodicity를 충분히 explicit 하게 반영하고 있기 때문 - Vocos without ConvNeXt
- ConvNeXt block을 dilated convolution이 있는 ResBlock으로 대체하는 경우 성능 저하가 발생함
- 즉, Vocos에서 ConvNeXt block은 성능 향상에 유효함
- Vocos with Absolute Phase

- Subjective Evaluation
- MOS, SMOS 측면에서도 제안된 Vocos는 뛰어난 성능을 보임

- Out-of-Distribution Data
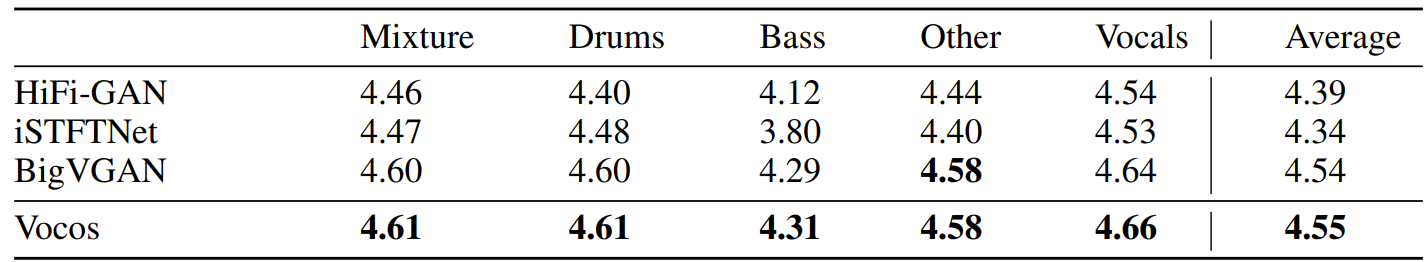
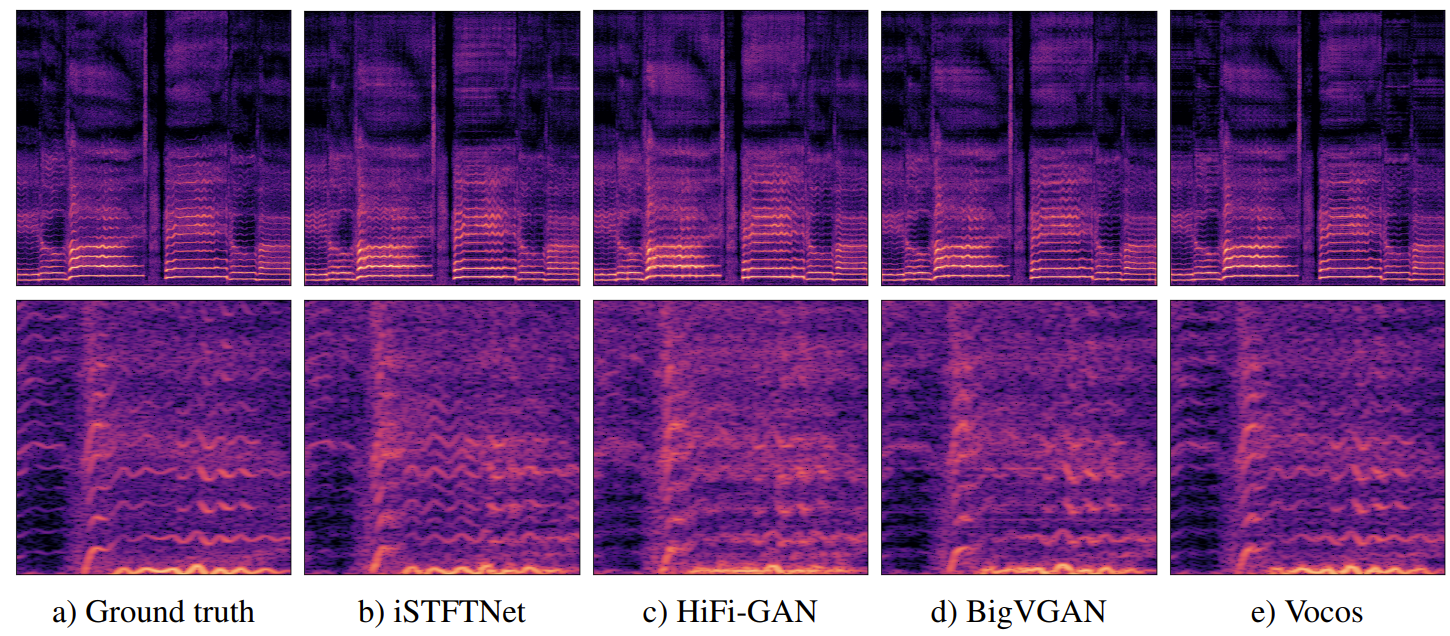
- Unseen acoustic condition에 대한 generalizability를 확인해 보기 위해, MUSDB18 dataset에 대한 평가를 수행
- 결과적으로 Vocos는 out-of-distribution data에 대해서도 우수한 합성 성능을 달성함
- Mel-sepctrogram 측면에서 Vocos는 artifact 없이 harmonics를 더 정확하게 reconstruction 하는 것으로 나타남
- Audio Reconstruction
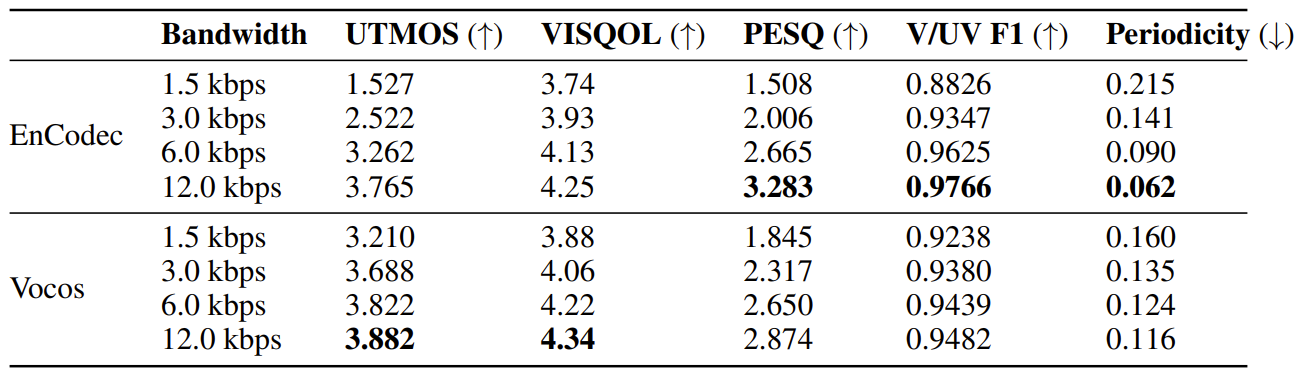
- 추가적으로 neural codec과 audio reconstruction 성능을 비교해 보면
- Vocos는 EnCodec 보다 다양한 bandwidth에서 더 뛰어난 reconstruction 성능을 보임

- Inference Speed
- 추론 속도 측면에서 Vocos는 HiFi-GAN 보다 13배, BigVGAN 보다 70배 빠르게 동작할 수 있음
- 이는 transposed convolution 대신 iSTFT를 사용하기 때문
- 한편으로 Vocos의 ConvNeXt block을 depthwise separable convolution으로 대체하는 경우 추가적인 속도 향상을 달성할 수 있음

반응형
'Paper > Vocoder' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

