티스토리 뷰
Paper/SVS
[Paper 리뷰] TechSinger: Technique Controllable Multilingual Singing Voice Synthesis via Flow Matching
feVeRin 2025. 6. 1. 09:27반응형
TechSinger: Technique Controllable Mulitlingual Singing Voice Synthesis via Flow Matching
- Singing Voice Synthesis는 intensity, mixed voice, falsetto 등에 대한 precise control을 제공하지 않음
- TechSinger
- 다양한 technique에 대한 expressive control을 지원하기 위해 flow-matching-based model을 도입
- Training data의 diversity를 향상하기 위해 phoneme-level technique lable로 dataset을 automatically annotate 하는 technique detection model을 활용
- Prompt-based technique prediction model을 통해 desired vocal attribute를 specify 하여 synthesized singing에 대한 fine-grained control을 지원
- 논문 (AAAI 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- DiffSinger와 같은 Singing Voice Synthesis (SVS)는 pitch, pronunciation, emotional expression, vocal technique 등을 capture 하여 high-fidelity vocal performance를 달성하는 것을 목표로 함
- BUT, specific vocal technique에 대한 fine-grained control 측면에서는 여전히 한계가 있음
- Vibrato, breathy와 같은 stylistic nuance는 singing voice의 expressiveness를 향상하는데 중요함 - 특히 technique-controllable SVS를 위해서는 다음을 해결해야 함:
- 기존 SVS dataset은 singing technique에 대한 detailed annotation이 부족함
- 다양한 singing technique에 대한 fine-grained control이 가능해야 함
- Prompt를 통해 fine-grained phoneme-level annotation을 기반으로 SVS task를 control 할 수 있어야 함
- BUT, specific vocal technique에 대한 fine-grained control 측면에서는 여전히 한계가 있음
-> 그래서 위의 문제점들을 해결한 technique-controllable SVS model인 TechSinger를 제안
- TechSinger
- Technique-annotated dataset 문제를 해결하기 위해 technique information을 automatically annotate하는 Technique Detector를 도입
- Flow-matching-based model을 활용하여 multiple singing technique에 대한 fine-grained control을 지원
- 추가적으로 pre-trained language model을 사용하여 comprehensive prompt를 구축하고, technique predictor를 training 하여 natural language input에 대한 desired sining style을 반영
< Overall of TechSinger >
- Flow-matching model을 기반으로 한 Technique-Controllable SVS model
- 결과적으로 기존보다 뛰어난 성능을 달성
2. Preliminary: Rectified Flow Matching
- Generative model을 구성할 때 true data distribution $q(x_{1})$은 sample 할 수 있지만, 해당 density function은 inaccessible 함
- 먼저 probability path $p_{t}(x_{t})$가 존재한다고 가정하자
- $x_{0}\sim p_{0}(x)$ : standard Gaussian distribution과 같은 known simple distribution
- $x_{1}\sim p_{1}(x)$ : realistic data distribution에 approximate 하는 distribution - Flow matching은 해당 probability path를 directly modeling 하는 것을 목표로 함
- 이는 다음의 Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE)로 나타낼 수 있음:
(Eq. 1) $\text{d}x=u(x,t)\text{d}t,\,\,\,t\in[0,1]$
- $u$ : target vector field, $t$ : time position - Vector field $u$가 known이면, reverse step을 통해 realistic data를 얻을 수 있고, 이때 flow matching objective를 사용하여 vector field estimator $v(\cdot)$로 vector field $u$를 regress 할 수 있음:
(Eq. 2) $\mathcal{L}_{FM}(\theta)=\mathbb{E}_{t,p_{t}(x)}\left|\left| v(x,t;\theta)-u(x,t)\right|\right|^{2}$
- $p_{t}(x)$ : timestep $t$에서 $x$의 distribution - Condition $c$를 incorporate 하여 regression을 guide 하기 위해 conditional flow matching을 사용할 수 있음:
(Eq. 3) $\mathcal{L}_{CFM}(\theta)=\mathbb{E}_{t,p_{1}(x_{1}),p_{t}(x|x_{1})}\left|\left| v(x,t|c;\theta)-u(x,t|x_{1},c)\right|\right|^{2}$
- 이는 다음의 Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE)로 나타낼 수 있음:
- Flow matching은 noise를 data로 변환하기 위해 straight path를 사용함
- 이를 위해 data $x_{1}$과 Gaussian noise sample $x_{0}$ 간에 linear interpolation schedule을 적용하여 sample $x_{t}=(1-t)x_{0}+tx_{1}$을 얻음
- 그러면 conditional vector field는 $u(x,t|x_{1},c)=x_{1}-x_{0}$와 같고 gradient descent에서 사용되는 Rectified Flow Matching (RFM) loss는:
(Eq. 4) $\left|\left| v(x,t|c;\theta)-(x_{1}-x_{0})\right|\right|^{2}$
- Vector field $u$를 얻을 수 있다면, sampled Gaussian noise를 다양한 ODE solver를 통해 discrete time에서 propagate 함으로써 realistic data를 생성할 수 있음
- 이때 reverse flow를 위해 일반적으로 Euler ODE를 사용함:
(Eq. 5) $x_{t+\epsilon}=x+\epsilon v(x,t|c;\theta)$
- $\epsilon$ : step size - 논문에서는 note, lyrics, technique을 condition $c$로 사용하고 data $x_{1}$은 fundamental frequency $F0$나 mel-spectrogram에 해당함
- 이때 reverse flow를 위해 일반적으로 Euler ODE를 사용함:
- 먼저 probability path $p_{t}(x_{t})$가 존재한다고 가정하자
3. Method
- Overview
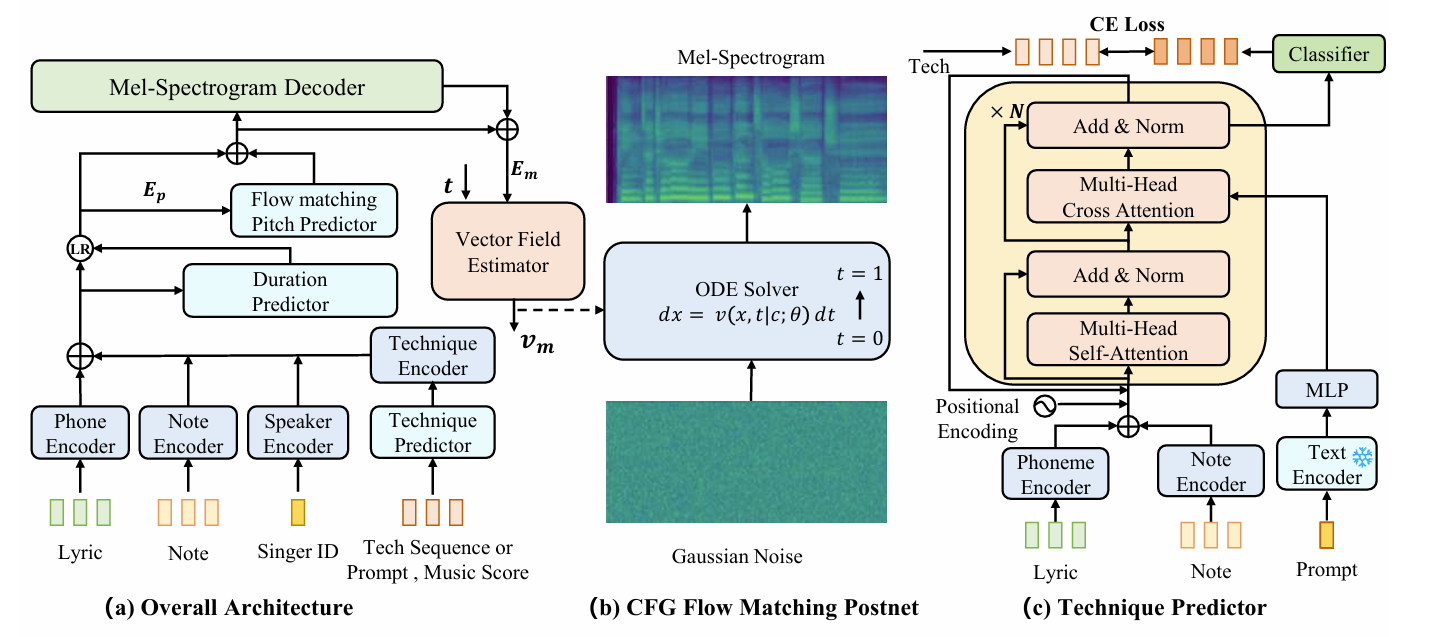
- TechSinger architecture는 아래 그림과 같음
- 먼저 phoneme encoder는 lyrics를 처리하고, note encoder는 note pitch, note duration, note type을 encoding 하여 musical rhythm을 capture 함
- Technique information은 technique sequence를 encoding 하여 제공되고, 이때 natural language prompt로부터 technique sequence를 생성하는 technique predictor가 사용됨 - 이후 technique embedding과 musical information을 사용하여 duration을 predict 하고 frame-level intermediate feature $E_{p}$를 생성함
- Flow-matching-based model은 해당 $E_{p}$를 condition으로 하여 fundamental frequency $F0$를 생성함
- Coarse mel-decoder는 coarse mel-spectrogram을 predict 하고, flow-matching-based postnet은 해당 prediction을 refine 하여 high-quality mel-spectrogram을 생성함
- 최종적으로는 mel-spectrogram을 audio signal로 변환하는 HiFi-GAN vocder를 적용함
- 먼저 phoneme encoder는 lyrics를 처리하고, note encoder는 note pitch, note duration, note type을 encoding 하여 musical rhythm을 capture 함
- Flow Matching Pitch Predictor
- $L1$ loss만 사용하여 $F0$를 reconstruction 하면, 다양한 technique과 $F0$간의 complex mapping을 modeling 하기 어려움
- 따라서 다양한 technique에 대한 pitch contour variation을 precisely modeling 하기 위해 논문은 Flow Matching Pitch Predictor (FMPP)를 도입함
- 먼저 $F0$는 1D continuous data로 취급할 수 있음
- 이때 condition $c$는 musical score와 technique sequence의 combination feature인 $E_{p}$로 주어지고, sampled $x_{1}$은 RMVPE를 통해 추출된 target $f0_{g}$에 해당함
- 그러면 $F0$ sample $x_{1}=f0_{g}$와 Gaussian noise $x_{0}$ 간에 linear interpolation을 적용하여 conditional probability path $x_{t}=(1-t)x_{0}+tx_{1}$을 얻을 수 있음
- 이후 vector field estimator $v_{p}$를 사용해 vector field를 predict 하고 $\mathcal{L}_{pflow}$ loss를 사용해 training 함:
(Eq. 6) $\min_{\theta}\mathbb{E}_{t,p_{1}(x_{1}|c),p_{0}(x_{0})}\left|\left| v_{p}(x,t|c;\theta)-(x_{1}-x_{0})\right|\right|^{2}$

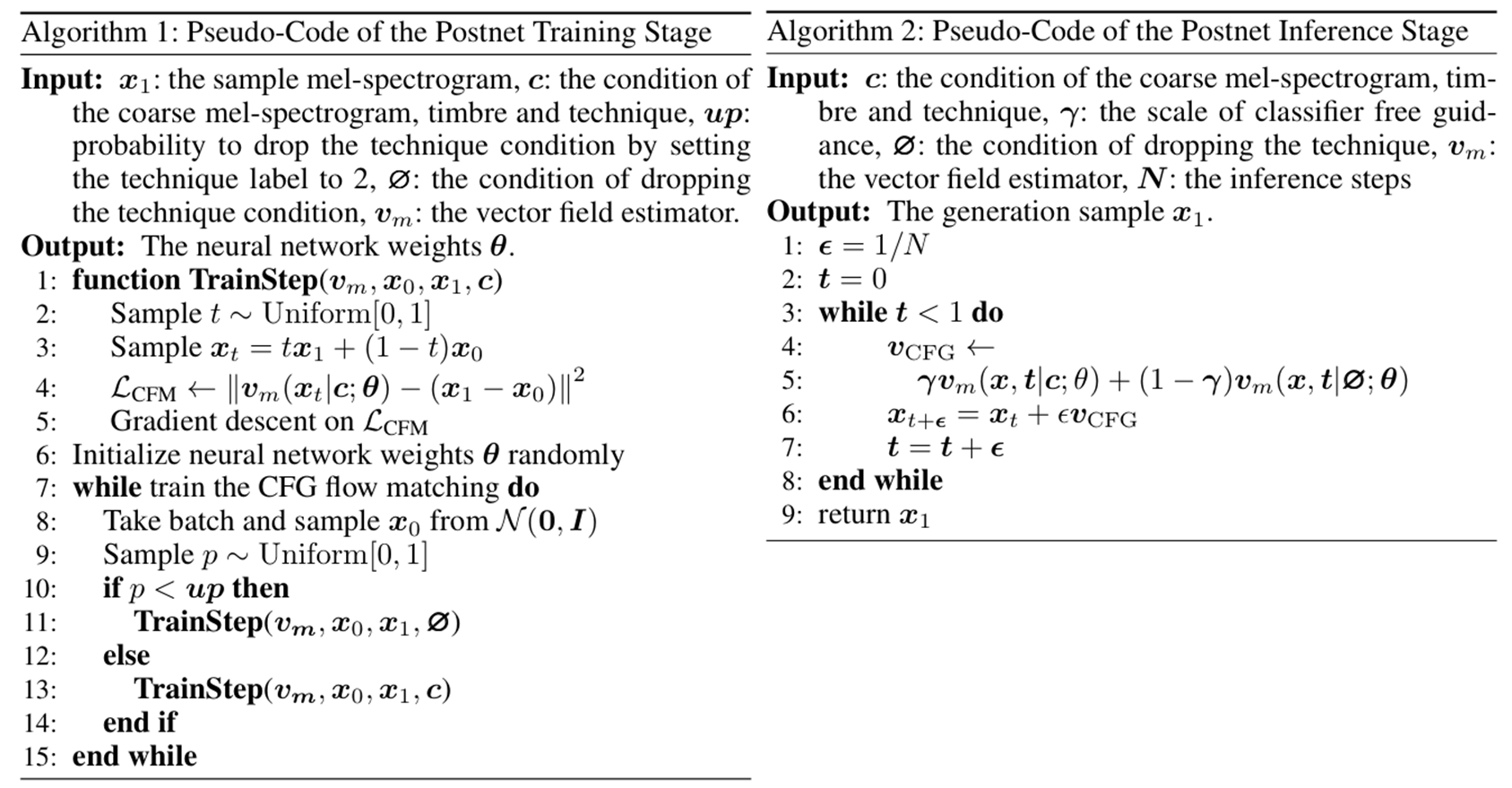
- CFG Flow Matching Postnet
- First stage에서는 mel-spectrogram decoder가 $L1, L2$와 같은 simple loss를 활용하여 generated mel-spectrogram을 reconstruct 함
- 이를 위해 논문은 pitch, technique을 combine 하고 $L2$ loss를 사용하는 stacked Feed Forward Transformer (FFT) block을 통해 training 함:
(Eq. 7) $\mathcal{L}_{mel}=\left|\left| \text{mel}_{p}-\text{mel}_{g}\right|\right|^{2}$
- 이는 FastSpeech2를 따름 - BUT, unimodal distribution을 가정하여 optimize 된 generator는 naturalness가 저하된 mel-spectrogram을 생성하므로, mel-spectrogram expressiveness를 향상하기 위해 CFG Flow Matching Mel Postnet (CFGFMP)를 도입함
- 즉, coarsely generated mel-spectrogram $\text{mel}_{p}$와 combined pitch, technique feature $E_{m}$을 conditioning information $c$로 활용하여 optimized mel-spectrogram $\text{mel}_{g}$에 대한 training, generation을 guide 함
- 이때 $\mathcal{L}_{mflow}$ loss는 (Eq. 6)의 $\mathcal{L}_{pflow}$ loss와 analogous 함
- Reverse process에서는 noise를 random sample 하고 Euler solver를 통해 sample을 생성함
- 이때 singing voice의 quality와 intended technique과의 alignment를 further control 하기 위해 Classifier Free Guidance (CFG) strategy를 활용함
- 먼저 conditional label $\{0, 1\}$과 unconditional label $2$를 도입하고, first two stage에서 entire phrase나 partial phoneme에 대해 technique label을 $0.1$ rate로 randomly drop 함
- 이후 sampling 중에 vector field를 다음과 같이 modify 함:
(Eq. 8) $v_{CFG}(x,t|c;\theta)=\gamma v_{m}(x,t|c;\theta)+(1-\gamma)v_{m}(x,t|\varnothing;\theta)$
- $\gamma$ : classifier-free guidance scale - Technique detector output은 error를 포함하고 있으므로 해당 random drop approach는 generative model이 label을 blindly trust 하지 않도록 함
- 이를 통해 model robustness를 향상할 수 있음
- 이를 위해 논문은 pitch, technique을 combine 하고 $L2$ loss를 사용하는 stacked Feed Forward Transformer (FFT) block을 통해 training 함:
- Technique Predictor
- TechSinger는 natural language를 통해 controllable singing synthesis를 지원함
- BUT, open-source dataset은 각 sample에 대한 prompt를 제공하지 않음
- 특히 gender, volume과 같은 simple control을 지원하는 Prompt-Singer와 달리 논문은 singer identity, technique, language를 prompt에 incorporate 함
- 이를 위해 dataset에서 singer identity information, global technique label을 collect 하고, GPT-4o를 사용하여 각 singer의 identity와 singing technique에 대한 synonym을 생성함
- 다음으로 global technique label, language, identity에 대한 placeholder를 가지는 prompt template를 구성함 - 이후 해당 template를 randomly selct 하고 technique, identity, language의 synonym으로 filling 하여 각 item에 대한 prompt description을 생성함
- 구조적으로 technique predictor는 semantic feature를 추출하는 frozen natural language encoder과 technique decoder의 2가지 component로 구성됨
- Natural language encoder는 BERT 또는 FALN-T5 encoder를 고려함
- Technique decoder의 경우, cross-attention Transformer를 통해 semantic condition을 inject 하여 linguistic cue를 effectively integrate 할 수 있도록 함
- 다양한 technique에 대해 multi-task, multi-label classification을 수행하도록 classification head가 add 됨
- 여기서 singing technique은 mixed-falsetto, intensity에 대한 3가지 category, breathy, bubble, vibrato, pharyngeal의 4가지 binary category로 classify 됨
- Glissando technique은 word가 multiple note와 일치하는지를 판단하여 music score로부터 identify 됨 - 결과적으로 classification loss $\mathcal{L}_{tech}$는:
(Eq. 9) $ \mathcal{L}_{CE}^{(i)}=-\sum_{k=1}^{3}y_{k}^{(i)}\log\left(p_{k}^{(i)}\right),\,\,\, \mathcal{L}_{BCE}^{(j)}=-\left[y^{(j)}\log\left(p^{(j)}\right)+(1-y^{(j)})\log \left(1-p^{(j)} \right)\right]$
(Eq. 10) $\mathcal{L}_{tech}=\sum_{i=1}^{2}\mathcal{L}_{CE}^{(i)}+\sum_{j=1}^{4}\mathcal{L}_{BCE}^{(j)}$
- $\mathcal{L}_{CE}^{(i)}$ : $i$-th three-class technique group에 대한 cross-entropy loss
- $\mathcal{L}_{BCE}^{(j)}$ : $j$-th binary technique group에 대한 binary cross-entropy loss
- BUT, open-source dataset은 각 sample에 대한 prompt를 제공하지 않음

- Technique Detector
- Technique-labeled singing voice synthesis dataset에 대한 annotating cost, complexity로 인해 논문은 phone-level technique label을 얻을 수 있는 Singing Technique Detector를 도입함
- 이때 technique predictor와 동일한 방식으로 glissando technique sequence를 annotate 할 수 있음
- 먼저 mel-spectrogram, fundamental frequency $F0$, energy, breathiness와 같은 variance feature를 포함한 audio로부터 feature를 추출하여 encoding 한 다음, combine 하여 input feature로 사용함
- 다음으로 U-Net architecture를 활용하여 frame-level intermediate feature를 추출함
- 이때 high-level audio feature를 capture 하기 위해 SqueezeFormer를 채택함 - 이후 weight prediction average approach를 적용해 phone-level audio feature를 얻음
- Frame 수 $T$, channel 수 $C$에 대해, frame-level output이 $E_{f}\in\mathbb{R}^{T\times C}$라고 하면 linear layer와 sigmoid를 사용하여 weight $W_{f}=\sigma(E_{f}W_{A})$를 predict 할 수 있음
- 여기서 head 수 $N$에 대해, $W_{A}\in\mathbb{R}^{C\times N}$이고, $W_{f}\in\mathbb{R}^{T\times N}$ - 다음으로 element-wise multiply $E_{f}$에 weight를 적용하여 weighted feature $E_{wf}=E_{f}\odot W_{f}$를 얻고, 이때 phone $i$가 length $k$의 frame $j$에서 start 하는 sequence에 해당한다고 하자
- 그러면 frame-level embedding에 대해 weighted average method를 적용하여 final phoneme-level feature $E_{wp}$를 얻을 수 있음:
(Eq. 11) $ E_{wp}^{i}=\frac{\sum_{t=1}^{k}E_{wf}^{i+j+t}}{\sum_{t=1}^{k}W_{f}^{i+j+t}}$
- $E_{wp}\in\mathbb{R}^{L\times C\times N}$, $L$ : phone length - 이후 서로 다른 head를 average 하여 final phoneme-level feature $z\in \mathbb{R}^{L\times C}$를 얻음
- 최종적으로 technique predictor와 같은 multi-task, multi-label technique classification task를 optimize 하기 위해 cross-entropy loss $\mathcal{L}_{p}$를 적용함
- 다음으로 U-Net architecture를 활용하여 frame-level intermediate feature를 추출함

- Training and Inference Procedures
- TechSinger의 training procedure는 two-stage로 구성됨
- First stage에서는 post-processing flow-matching network를 제외한 entire model을 optimize 하고, $\mathcal{L}_{1}$ loss를 minimize 하기 위해 gradient descent를 적용함:
(Eq. 12) $\mathcal{L}_{1}=\mathcal{L}_{pflow}+\mathcal{L}_{mel}+\mathcal{L}_{dur}$
- $\mathcal{L}_{pflow}, \mathcal{L}_{mel}, \mathcal{L}_{dur}$ : 각각 $F0$ flow matching, mel-spectrogram, duration loss - Second stage에서는 first phase에서 training 된 component를 freeze 하고,
- Predicted $F0$, coarse mel-spectrogram, technique encoding의 adding feature $E_{m}$을 condition으로 하여 classifier-free flow matching postnet $\mathcal{L}_{mflow}$를 optimize 함 - 추론 시에는 input, prompt statement을 기반으로 technique sequence를 얻고, lyrics, note와 combine 하여 coarse mel-spectrogram을 얻음
- 이후 flow matching network는 coarse mel-spectrogram을 refine 하여 final output을 생성함
- First stage에서는 post-processing flow-matching network를 제외한 entire model을 optimize 하고, $\mathcal{L}_{1}$ loss를 minimize 하기 위해 gradient descent를 적용함:
4. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : GTSinger, M4Singer
- Comparisons : DiffSinger, VISinger2, StyleSinger
- Results
- 전체적으로 TechSinger의 성능이 가장 우수함

- Mel-spectrogram 측면에서 TechSinger의 $F0$는 다른 model과 비교하여 더 많은 detail, variation을 포함함

- Controllability 측면에서
- 아래의 (a)는 technique이 적용되지 않은 control group을 의미함
- (b)는 bubble 적용 결과로써 cry-like tone을 반영하고, strong intensity인 (c)는 singing의 resonance와 intensity를 향상하고, breathy tone인 (d)는 breathy sound를 반영함

- Technique Predictor
- Encoder size가 증가할수록 model 성능도 증가함
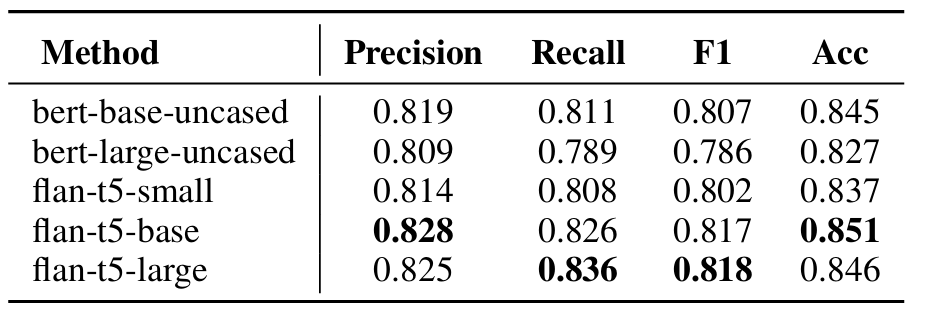
- Prompt strategy를 사용하면 Ground-Truth 수준의 MOS를 달성할 수 있음

- Ablation Study
- Technique Detector의 경우 full skill detector의 성능이 가장 우수함

- 각 component를 제거하는 경우 성능 저하가 발생함

반응형
'Paper > SVS' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

