티스토리 뷰
Paper/SVS
[Paper 리뷰] CSSinger: End-to-End Chunkwise Streaming Singing Voice Synthesis System based on Conditional Variational Autoencoder
feVeRin 2025. 6. 3. 08:56반응형
CSSinger: End-to-End Chunkwise Streaming Singing Voice Synthesis System based on Conditional Variational Autoencoder
- End-to-End modeling을 singing voice synthesis에 적용하면 우수한 합성 성능을 달성할 수 있음
- CSSinger
- End-to-End model의 latency 절감을 위해 Chunkwise Streaming inference를 도입
- Variational Autoencoder의 latent representation을 활용한 fully end-to-end streaming audio synthesis를 지원
- 논문 (AAAI 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Singing Voice Synthesis (SVS)는 music score를 input으로 하여 high-quality singing voice를 생성함
- Text-to-Speech (TTS)를 따라 SVS system은 일반적으로 acoustic model과 vocoder로 구성됨
- 한편으로 VITS와 같이 conditional Variational AutoEncoder (VAE)를 기반으로 한 end-to-end system을 활용할 수도 있음
- 해당 end-to-end system은 prior encoder, posterior encoder를 기반으로 latent representation을 학습하고 audio를 directly generate 하여 highly natural audio를 생성함 - SVS task에서도 마찬가지로 VISinger, VISinger2, SiFiSinger와 같이 variational inference 기반의 end-to-end model을 활용할 수 있음
- 한편으로 VITS와 같이 conditional Variational AutoEncoder (VAE)를 기반으로 한 end-to-end system을 활용할 수도 있음
- BUT, 해당 end-to-end SVS model은 singing signal에 대한 naturalness를 크게 향상할 수 있지만 computational resource와 latency 측면에서 한계가 있음
- Parallel computational model은 long sequence에 대해 상당한 computational strain을 가지기 때문
- 따라서 real-world constraint 하에서 synthesis를 수행하려면 streaming, autoregressive method를 고려해야 함
- Text-to-Speech (TTS)를 따라 SVS system은 일반적으로 acoustic model과 vocoder로 구성됨
-> 그래서 end-to-end chunk-based streaming SVS model인 CSSinger를 제안
- CSSinger
- Conditional VAE를 기반으로 각 chunk 간의 sequential generation과 parallel computation을 지원
- Causal streaming vocoder에 대한 input 문제를 해결하기 위해 longer real-valued latent representation을 padding으로 사용
- Fully streaming paradigm을 위해 chunk streaming acoustic model decoder를 활용
< Overall of CSSinger >
- SVS model의 latency 문제를 해결한 end-to-end chunkwise streaming SVS model
- 결과적으로 기존보다 낮은 latency와 우수한 합성 성능을 달성
2. Method
- CSSinger는 SiFiSinger의 conditional VAE에 따라 training 되고 chunk 기반의 semi-streaming scheme을 활용함
- Prior Encoder
- Semi-streaming framework에서 prior encoder의 structure는 SiFiSinger의 configuration을 따름
- Prior encoder는 music score (lyrics, duration, pitch) $c_{mscore}$를 input으로 length regulator를 통해 input sequence를 frame-level로 extend 하여 prior frame-level latent representation $z_{prior}$를 얻음
- 여기서 논문은 acoustic model training 중에 $F0$와 mel-cepstrum $\text{mcep}$에 대한 prediction loss $\mathcal{L}_{F0}, \mathcal{L}_{mcep}$와 duration loss $\mathcal{L}_{dur}$를 calculate 함
- 해당 duration loss는 duration predictor를 update 하는 역할로써, phone-level representation을 frame-level length로 extend 함
- 이후 acoustic decoder (AM Decoder)는 frame-level prior distribution을 생성함
- 구조적으로 $F0, \text{mcep}$ prediction module, AM Decoder는 FastSpeech의 Feed-Forward Transformer (FFT) block으로 구성됨
- 결과적으로 training process에서 사용되는 prior encoder의 loss function $\mathcal{L}_{am}$은:
(Eq. 1) $\mathcal{L}_{am}=\mathcal{L}_{F0}+\mathcal{L}_{mcep}+\mathcal{L}_{dur}$
- Prior encoder는 music score (lyrics, duration, pitch) $c_{mscore}$를 input으로 length regulator를 통해 input sequence를 frame-level로 extend 하여 prior frame-level latent representation $z_{prior}$를 얻음

- Posterior Encoder
- Posterior encoder는 1D convolutional layer와 LayerNorm으로 구성됨
- Posterior encoder는 real acoustic feature $F0,\text{mcep}$을 conditional input $c_{acous}$로 사용하여 frame-level posterior distribution의 mean $\mu_{\phi}(x)$, variance $\sigma_{\phi}(x)$를 predict 하고, posterior distribution $z_{post}$를 sampling 함
- 한편으로 conditional VAE training framework 하에서 training objective는 marginal log-likelihood $\log p_{\theta}(x|c_{mscore})$의 variational lower bound를 maximize 하는 것과 같음
- 이는 reconstruction loss $\mathcal{L}_{recon}$과 KL divergence의 summation으로 볼 수 있음:
(Eq. 2) $ \mathcal{L}_{kl}=\log q_{\phi}(z|x)-\log p_{\theta}(z|c_{mscore}),\,\,\, z\sim q_{\phi}(z|x)=\mathcal{N}(z;\mu_{\phi}(x),\sigma_{\phi}(x))$
- $p_{\theta}(z|c_{mscore})$ : $c_{mscore}$로 condition 된 latent variable $z$의 prior distribution
- $q_{\phi}(z|x)$ : approximate posterior distribution
- CSSinger의 full-stream framework에서, 논문은 posterior encoder의 모든 convolution을 causal convolution으로 replace 하여 entire posterior encoder를 causal 하게 구성함
- 이를 통해 full-stream framework에서 ChunkStream decoder는 chunk 간의 dependency를 effectively capture 할 수 있으므로 prior distribution modeling을 개선할 수 있음
- Posterior encoder는 real acoustic feature $F0,\text{mcep}$을 conditional input $c_{acous}$로 사용하여 frame-level posterior distribution의 mean $\mu_{\phi}(x)$, variance $\sigma_{\phi}(x)$를 predict 하고, posterior distribution $z_{post}$를 sampling 함
- Causal HiFi-GAN Generator
- AudioDec을 따라 HiFi-GAN generator에서 convolution과 transposed convolution을 causal version으로 replace 함
- Waveform $\hat{y}$를 chunk로 생성할 때 causal convolution은 receptive field size를 기반으로 previous chunk information을 retain 할 수 있음
- 이를 통해 chunkwise로 합성된 audio의 discontinuity를 방지할 수 있음 - 이때 reconstruction loss $\mathcal{L}_{recon}$은 real waveform $y$, synthesized waveform $\hat{y}$ 간의 mel-spectrogram을 통해 얻어짐:
(Eq. 3) $\mathcal{L}_{recon}=|| \text{mel}(y)-\text{mel}(\hat{y})||_{1}$ - 추가적으로 논문은 generator loss $\mathcal{L}_{adv}(G)$, discriminator loss $\mathcal{L}_{adv}(D)$, feature matching loss $\mathcal{L}_{fm}(G)$를 도입하고, 이때 얻어지는 total training loss는:
(Eq. 4) $\mathcal{L}=\mathcal{L}_{recon}+\mathcal{L}_{am}+\mathcal{L}_{kl}+\mathcal{L}_{adv}(G)+\mathcal{L}_{fm}(G)$
- 논문의 adversarial training, discriminator는 SiFiSinger를 따름
- Waveform $\hat{y}$를 chunk로 생성할 때 causal convolution은 receptive field size를 기반으로 previous chunk information을 retain 할 수 있음
- Natural Padding
- Semi-streaming context에서, 논문은 latent representation $z$를 chunk로 directly segment 한 다음, 앞선 causal HiFi-GAN generator를 사용하여 audio waveform으로 reconstruct 함
- 특히 entire HiFi-GAN generator는 causality를 가지도록 training 되고 input을 chunking 하면 generator가 처리해야 하는 size가 reduce 됨
- 이를 통해 chunk boundary에서 discontinuity가 발생하지 않고 systematic latency도 크게 줄일 수 있음 - BUT, 실제로 HiFi-GAN generator를 general causal convolution, causal transposed convolution으로 구성하여 $z$의 chunk를 sequentially process 해보면, extensive artifact가 발생하여 audio quality가 저하됨
- 이는 default causal convolution이 padding value가 constant 한 zero-padding, replication padding과 같은 one-sided padding을 사용하기 때문
- 특히 latent representation $z$는 각 training step에서 randomly slice 되어 $z$의 pattern은 training 중에 evolve 하므로, constant value는 ambiguous 함
- 따라서 일반적인 padding strategy를 적용하면 fragile training process로 인해 training, inference mismatch가 발생하므로 audio quality가 저하됨
- 이는 default causal convolution이 padding value가 constant 한 zero-padding, replication padding과 같은 one-sided padding을 사용하기 때문
- Original causal transposed convolution에서 각 layer는 $(\text{kernel_size}//\text{stride}-1)$ length의 left padding을 수행하고, output sequence를 both side에서 $\text{stride}$ length만큼 trim 함
- 이는 causality를 보장하고 output length에 대한 padding impact를 eliminate 함 - 이와 달리 논문은 Natural Padding Strategy를 도입함
- 먼저 causal HiFi-GAN generator의 모든 causal convolution, causal transposed convolution에서 manual one-side padding operation을 제거함
- 대신 각 training step에서 randomly sliced $z$의 beginning에 additional $z$ value를 padding으로 extend 하여 generator에 대한 input segment를 구성함 - 이후 해당 input segment는 generator 내의 causal convolution, causal transposed convolution layer를 통과하지만, 각 layer나 entire generator에 대한 exact receptive field를 precisely calculate하지는 않음
- 특히 generator output length가 original length $(\text{sliced_length}\times \text{hop_size})$를 exceed 하도록 natural padding length가 보장하는 한, receptive field overflow는 발생하지 않음 - 최종적으로 final valid output을 생성하기 위해, original length과 match 하여 tail을 trim 함
- 먼저 causal HiFi-GAN generator의 모든 causal convolution, causal transposed convolution에서 manual one-side padding operation을 제거함
- e.g.) Natural padding process에 대한 예시는 아래 그림과 같음:
- Length $2$의 input sequence는 $\text{kernel_size}=4, \text{stride}=1$인 causal convolution을 통과한 다음, $\text{kernel_size}=4, \text{stride}=2$인 causal transposed convolution을 통과함
- 이때 transposed convolution의 upsampling ratio를 기반으로 한 valid output length는 $4$와 같음 - 다음으로 input sequence의 beginning을 $z$-value로 natural padding 하여 extend 함
- Output이 제공되면, both side에서 $\text{stride}$ length를 trim 하고 tail에서 valid length $4$를 취하여 final output을 얻음
- 즉, process 전체에서 receptive field overflow는 발생하지 않고 valid output은 expected upsampling ratio에 따라 strictly obtain 됨
- Length $2$의 input sequence는 $\text{kernel_size}=4, \text{stride}=1$인 causal convolution을 통과한 다음, $\text{kernel_size}=4, \text{stride}=2$인 causal transposed convolution을 통과함
- 특히 entire HiFi-GAN generator는 causality를 가지도록 training 되고 input을 chunking 하면 generator가 처리해야 하는 size가 reduce 됨

- Chunkwise Fully-Streaming Framework
- Semi-streaming architecture에서 AM decoder는 attention mechanism을 가지는 FFT block으로 구성됨
- Attention mechanism은 fully parallel computation approach를 활용하지만, computational complexity는 sequence length의 제곱에 비례함
- 즉, long sequence를 처리할 때 상당한 computational resource와 time cost가 필요함 - 따라서 논문은 semi-streaming architecture를 기반으로 chunk-based fully streaming inference method를 구성하기 위해, ChunkStream decoder를 사용하여 latent representation $z$의 generation을 chunk-based streaming으로 변환함
- 특히 Emformer의 attention mechanism을 활용하여 complete input feature vector를 fixed-length chunk로 break down 함
- 이후 chunk-by-chunk attention calculation을 위해, previous chunk에서 추출된 contextual key, value, memory bank embedding이 제공되어 contextual, global information loss를 방지함
- Memory bank는 autoregressive manner로 prior context information을 제공함 - 결과적으로 해당 attention computation process는 다음과 같이 formulate 됨:
(Eq. 5) $\left[\hat{\mathbf{C}}_{i}^{n},\hat{\mathbf{R}}_{i}^{n}\right]=\text{LayerNorm}\left( \left[\mathbf{C}_{i}^{n},\mathbf{C}_{i}^{n}\right]\right)$
(Eq. 6) $\mathbf{K}_{i}^{n}=\left[\mathbf{W}_{k}\mathbf{M}_{i}^{n},\mathbf{K}_{L,i}^{n},\mathbf{W}_{k}\mathbf{C}_{i}^{n}, \mathbf{W}_{k}\mathbf{R}_{i}^{n}\right]$
(Eq. 7) $\mathbf{V}_{i}^{n}=\left[\mathbf{W}_{v}\mathbf{M}_{i}^{n}, \mathbf{V}_{L,i}^{n},\mathbf{W}_{v}\mathbf{C}_{i}^{n},\mathbf{W}_{v}\mathbf{R}_{i}^{n}\right]$
(Eq. 8) $\mathbf{h}_{C,i}^{n}=\text{Attn}\left(\mathbf{W}_{q}\hat{\mathbf{C}}_{i}^{n}, \mathbf{K}_{i}^{n},\mathbf{V}_{i}^{n}\right)+\mathbf{C}_{i}^{n}$
(Eq. 9) $\mathbf{h}_{R,i}^{n}=\text{Attn}\left(\mathbf{W}_{q}\hat{\mathbf{R}}_{i}^{n}, \mathbf{K}_{i}^{n}, \mathbf{V}_{i}^{n}\right)+\mathbf{R}_{i}^{n}$
(Eq. 10) $\mathbf{m}_{i}^{n+1}=\text{Attn}\left(\mathbf{W}_{q}\mathbf{s}_{i}^{n};\mathbf{K}_{i}^{n}, \mathbf{V}_{i}^{n}\right)$
(Eq. 11) $\mathbf{C}_{i}^{n+1}=\text{FFN}\left(\mathbf{h}_{C,i}^{n}\right)$
(Eq. 12) $\mathbf{R}_{i}^{n+1}=\text{FFN}\left(\mathbf{h}_{R,i}^{n}\right)$
- $\mathbf{C}_{i}^{n}$ : layer $n$의 $i$-th input chunk, $\mathbf{R}_{i}^{n}$ : right contextual block
- $\mathbf{s}_{i}^{n}$ : summary vector로써, $\mathbf{C}_{i}^{n}$의 average
- $\mathbf{M}_{i}^{n}$ : memory vector로써, previous chunk의 lower layer로부터 얻어짐
- $\mathbf{K}_{L,i}^{n}, \mathbf{V}_{L,i}^{n}$ : left contextual key, value matrix로써, additional compuation 없이 previous chunk에서 compute 된 key, value projection으로부터 directly retrieve 됨 - Entire attention operation은 sequential training 없이도 parallelize 될 수 있음
- 해당 attention mechanism에서 chunk 간 contextual dependency는 key, value, memory bank vector를 통해 capture 됨
- 이때 boundary effect를 further reduce 하기 위해 2개의 1D causal convolution과 LayerNorm으로 구성된 Causal Smooth Layer를 도입함
- 특히 1D causal convolution은 receptive field length를 기반으로 previous chunk $\mathbf{C}_{i-1}$의 same layer에서 feature를 retain 함
- Current chunk의 tail도 causal receptive field length의 feature를 slice 하여 next chunk $\mathbf{C}_{i+1}$에 전달됨 - 이를 통해 boundary에서 finer smoothing을 제공하고 audio quality의 naturalness와 fluency를 향상할 수 있음
- Attention mechanism은 fully parallel computation approach를 활용하지만, computational complexity는 sequence length의 제곱에 비례함

3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : OpenCPop, PopCS, Baker
- Comparisons : SiFiSinger
- Results
- 전체적으로 CSSinger가 가장 뛰어난 성능을 보임
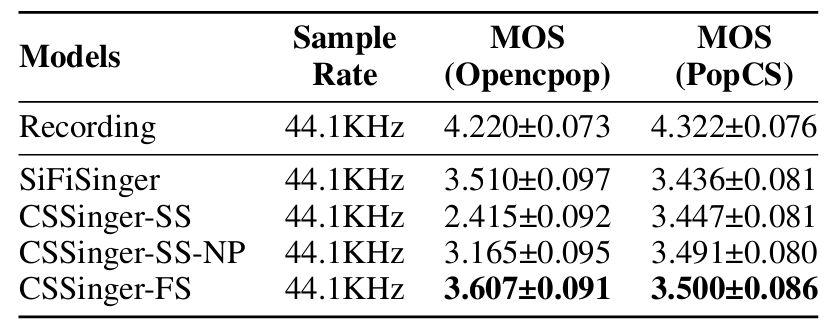
- Objective evaluation 측면에서도 CSSinger의 성능이 가장 우수함

- Mel-spectrogram 측면에서 CSSinger는 upward pitch transition을 successfully modeling 함

- Evaluation on Text-to-Speech
- TTS task에 대해서도 CSSinger는 가장 뛰어난 성능을 달성함

- Latency Evaluation
- CSSinger는 가장 빠른 latency, RTF를 달성함

반응형
'Paper > SVS' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

