티스토리 뷰
Paper/SVS
[Paper 리뷰] ExpressiveSinger: Multilingual and Multi-Style Score-based Singing Voice Synthesis with Expressive Performance Control
feVeRin 2025. 6. 13. 13:05반응형
ExpressiveSinger: Multilingual and Multi-Style Score-based Singing Voice Synthesis with Expressive Performance Control
- Singing Voice Synthesis는 timing, dynamics, pitch 측면에서 controllability가 부족함
- ExpressiveSinger
- Phoneme timing, $F0$ curve, amplitude envelope를 포함하는 expressive performance control signal을 생성
- Style guidance와 singer timbre embedding을 활용해 performance control signal에서 mel-spectrogram을 생성
- 논문 (MM 2024) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Singing Voice Synthesis (SVS)는 lyrics, symbolic music score를 기반으로 singing audio를 생성함
- BUT, 대부분의 SVS model은 Text-to-Speech (TTS) model에서 얻어지므로 musicality가 부족함
- Synthesized singing은 unnatural technique, poor dynamics와 같은 performance control 문제가 있음
- Performance control에는 symbolic score에서 miss 된 performance timing, dynamics, pitch contour, timbre control과 같은 music element가 encompass 됨
- 이는 natural sound music을 생성하는데 핵심적인 역할을 함
- 특히 SVS model은 단순한 text (lyrics) 외에도 symbolic score에서 singing을 생성하므로 high-level expressive performance control이 필요함
- 즉, MIDI, phonetic timing, pitch, loudness와 같은 performance control signal을 활용할 수 있어야 함
- BUT, 대부분의 SVS model은 Text-to-Speech (TTS) model에서 얻어지므로 musicality가 부족함
-> 그래서 performance control signal을 활용한 SVS model인 ExpressiveSinger를 제안
- ExpressiveSinger
- Performance timing, Pitch (Fundamental Frequency $F0$), Dynamics (loudness curve)를 생성하는 cascade diffusion model을 구성
- 추가적으로 다양한 musical style을 반영하기 위해 speaker/singer embedding을 활용
< Overall of ExpressiveSinger >
- Performance control signal을 기반으로 하는 diffusion-based expressive SVS model
- 결과적으로 기존보다 뛰어난 성능을 달성
2. Method
- ExpressiveSinger는 musical phrase에 해당하는 각 segment에 대해 score, lyrics, style token, singer information을 input으로 하여 expressive, realistic singing voice를 생성함
- Expressive Performance Control model은 phoneme-level performance timing, amplitude envelope, $F0$ curve의 control singal을 생성함
- Acoustic model은 performance control signal을 condition으로 mel-spectrogram을 생성함
- Vocoder는 mel-spectrogram, $F0$ curve로부터 waveform을 생성함
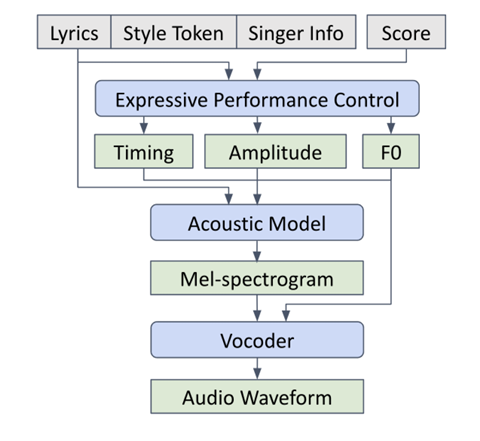
- Model Architecture
- Expressive control model과 acoustic model은 DiffWave와 유사한 architecture를 사용하고 diffusion-based training/inference를 채택함
- Training 시 diffusion process는 real data $x_{0}$를 whitened latent variable $x_{T}$로 gradually convert 하는 Markov chain으로 정의됨
- 이는 (Eq. 1)의 decreasing sequence $\alpha_{1:T}\in(0,1]^{T}$로 parameterize된 Gaussian transition을 통해 수행됨:
(Eq. 1) $ q(x_{1:T}|x_{0})=\prod_{t=1}^{T}q(x_{t}|x_{t-1})=\prod_{t=1}^{T}\mathcal{N}\left( \sqrt{\frac{\alpha_{t}}{\alpha_{t-1}}}x_{t-1},\left(1-\frac{\alpha_{t}}{\alpha_{t-1}}\right)I\right)$ - $x_{t}$는 (Eq. 2)와 같이 $x_{t-1}$과 noise variable $\epsilon$의 linear combination으로 나타낼 수 있음:
(Eq. 2) $x_{t}=\sqrt{\alpha_{t}}x_{t-1}+\sqrt{1-\alpha_{t}}\epsilon,\,\,\,\epsilon \sim\mathcal{N}(0,I)$
- 이는 (Eq. 1)의 decreasing sequence $\alpha_{1:T}\in(0,1]^{T}$로 parameterize된 Gaussian transition을 통해 수행됨:
- Reverse process에서는 non-Markovian (implicit) generation과 inference acceleration을 지원하는 Denoising Diffusion Implicit Model (DDIM)을 사용함
- Length $S$의 sub-sequence $\tau$가 $[1,...,T]$에서 select 되고, $\tau_{S}=T$라고 하자
- 여기서 $x_{T}$에서 $x_{0}$로의 denoising을 수행하는 reverse process는 $\theta$로 parameterize 됨:
(Eq. 3) $p_{\theta}(x_{0:T})=p_{\theta}(x_{T})\prod_{i=1}^{S}p_{\theta}^{(\tau_{i})}(x_{\tau_{i}-1}|x_{\tau_{i}})\times \prod_{t\in\bar{\tau}}p_{\theta}^{(t)}(x_{0}|x_{t}),$
$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, \text{where}\,\, p_{\theta}(x_{T})=\mathcal{N}(0,I),\bar{\tau}=[1,...,T]/\tau$
- $p_{\theta}^{(t)}(x_{0}|x_{t})$는 variational objective에만 involve 하므로, $T$보다 적은 $S$ step 만으로도 sampling을 speedup 할 수 있음 - 결과적으로 DDIM의 closed form equation은 다음과 같이 express 됨:
(Eq. 4) $x_{\tau_{i-1}}=\sqrt{\alpha_{\tau_{i-1}}}\left( \frac{x_{\tau_{i}}-\sqrt{1-\alpha_{\tau_{i}}}\epsilon_{\theta}(x_{\tau_{i}}) }{\sqrt{\alpha_{\tau_{i}}}}\right)+\sqrt{1-\alpha_{\tau_{i-1}}}\epsilon_{\theta}(x_{\tau_{i}})$
- DDPM과 달리 DDIM에서는 $x_{t-1}, x_{0}$이 주어졌을 때 forward process는 deterministic 함
- 아래 그림과 같이 각 time step $t$에서 noise $\epsilon_{\theta}$를 predict 하는 경우, input $x_{t}$는 model에 따라 control signal, mel-spectrogram 등 다양한 input을 사용함
- Additional input으로는 diffusion step $t$과 lyrics, style token 같은 contextual condition이 사용됨
- 해당 input은 encoder를 통해 처리되고 residual layer 이전에 embedding이 enhance 됨
- 각 residual layer는 bi-directional dilated convolution과 gated-tanh activation을 사용함 - 이후 각 layer output은 다른 layer output과 aggregate 되는 skip connection을 적용한 final output, subsequent embedded input $x_{t+1}$로 split 됨
- Diffusion step encoder는 DiffWave를 기반으로 swish activation을 가진 2개의 fully-connected layer가 사용됨
- 모든 convolution layer는 Kaiming normal distribution으로 initialize 되고 final output 이전의 last layer에는 zero initialization이 사용됨
- Training 시 diffusion process는 real data $x_{0}$를 whitened latent variable $x_{T}$로 gradually convert 하는 Markov chain으로 정의됨

- Conditional context encoder는 아래 그림과 같이 구성됨
- 각 context item은 서로 다른 embedding architecture를 통해 처리된 다음, concatenate 되고 pojection 됨
- Lyrics phoneme은 6개의 Transformer encoder layer를 통해 encoding 됨 - 해당 model의 non-autoregressive nature로 인해, 논문은 각 segment phrase 내에서 frame/beat position, phoneme, score note 등의 sequential dependency를 capture 하는 positional encoding을 도입함
- 각 context item은 서로 다른 embedding architecture를 통해 처리된 다음, concatenate 되고 pojection 됨

- Expressive Performance Control
- Expressive Performance Control (EPC) module에서는 score, lyrics, singer, style token을 input으로 사용하여 phoneme-level에서 expressive performance timing을 생성함
- 생성된 timing은 $F0$ curve와 amplitude envelope를 생성하는 데 사용됨 - Expressive Timing
- Expressive timing model은 word-level aligned lyrics와 score를 input으로 사용하여 각 phoneme에 대한 performance timing onset을 생성함
- Style token, singer information도 personalized style control을 위해 input condition context에 include 됨
- 이때 rest는 regular note와 동일하게 처리되므로 duration과 offset을 omitting 하고 onset modeling에 focus 함
- 즉, note offset이 subsequent note onset과 동일하므로 해당 note onset sequence를 통해 duration과 offset을 implicitly define 할 수 있음
- Generation process는 two-stage로 구성됨
- 먼저 rule-based algorithm은 beat로 count 된 score-word timing을 word boundary timing을 변경하지 않고 각 phoneme의 second timing으로 split 함
- Second stage에서는 diffusion model을 사용하여 rule-based score phoneme timing과 final phoneme timing output 간의 onset deviation을 생성함
- 이를 통해 diffusion Gaussian distribution 가정하에서의 training을 simplify 할 수 있음 - $n$이 data segment의 phoneme length라고 할 때, model input $x$는 onset deviation $[\sigma(1),...,\sigma(n)], \sigma(i)=\text{perform_onsets}(i)-\text{score_onsets}(i),i\in[1,n]$과 같음
- $\text{score_onsets}(i)$ : first-step의 rule-based phoneme onset
- $\text{perform_onsets}(i)$ : expressive timing model의 final output
- 먼저 rule-based algorithm은 beat로 count 된 score-word timing을 word boundary timing을 변경하지 않고 각 phoneme의 second timing으로 split 함
- 구체적으로 first-stage rule-based algorithm은 다음과 같이 동작함:
- 먼저 multiple word가 single score note에 해당하는 경우, 모든 word phoneme을 순서대로 concatenate 함
- 하나의 word가 multiple score note에 해당하는 경우, multiple syllable의 presence를 assess 함
- 여기서 syllable count가 score note count와 exactly match 되는 경우, 각 syllable은 해당 note에 sequentially assign 됨
- Syllable count가 score note count와 align 되지 않는 경우, 모든 score note의 onset, duration을 single onset, duration으로 merge 함 - 다음으로 note duration을 consonants, vowels, silences $\text{SP}$, breath sounds $\text{AP}$를 포함하는 phoneme에 distribute 함
- 여기서 각 $\text{SP},\text{AP}$에 0.03s의 duration을 assign 하고 각 consonant에 0.1s를 assign 함
- 남은 duration은 vowel에 evenly allocate 됨 - 해당 allocation으로 인해 vowel duration이 consonant보다 짧아지면 distribution을 adjust 함:
- $\text{SP}$는 0s, $\text{AP}$는 0.02s로 설정되고, 남은 length는 consonant $40\%$, vowel $60\%$로 split 됨
- Expressive timing model은 word-level aligned lyrics와 score를 input으로 사용하여 각 phoneme에 대한 performance timing onset을 생성함
- $F0$ Curves and Amplitude Envelopes
- $F0$ curve, amplitude envelope generation은 2개의 structually identical model을 통해 수행됨
- 이때 model의 condition context input은 timing model과는 다름:
- Score timing은 generated performance timing으로 substitute 됨
- Frame-wise positional encoding이 적용됨
- 논문은 subsequent mel-spectrogram, audio waveform synthesis를 위한 compatibility를 보장하기 위해, target mel-spectrogram의 frame-length에 해당하는 $F0$ curve, amplitude envelope를 생성함
- 결과적으로 각 phoneme에 대한 condition context는 generated phoneme timing에 기반하여 mel-spectrogram frame length로 expand 되어야 함
- $F0$ model의 경우, input $x$는 $[F0(1),...,F0(m)]$과 같이 정의되고, amplitude model은 $x=[\text{amp}(1),...,\text{amp}(m)]$과 같이 정의됨
- $m$ : target mel-spectrogram의 frame length - Training 이전에 $F0$는 $[-1,1]$ range로 linearly transform 되고 amplitude는 diffusion process에서 approximate Gaussian distribution과 conform 하기 위해 $\mathcal{N}(0,I)$로 normalize 됨
- Sampling 중에 amplitude는 denormalize 됨
- $F0$ model의 경우, input $x$는 $[F0(1),...,F0(m)]$과 같이 정의되고, amplitude model은 $x=[\text{amp}(1),...,\text{amp}(m)]$과 같이 정의됨

- Acoustic Model
- Acoustic model은 performance control signal (phoneme timing, $F0$ curve, amplitude envelope)와 lyrics, style token, singer timbre를 incorporate 함
- 해당 acoustic model은 score information을 제외하고 expressive performance control에만 의존함
- 특히 $F0$ value의 Hz가 256 discrete bin으로 quantize 되는 quantized $F0$ curver를 포함함 - 추가적으로 acoustic model은 singer ID 대신 각 singer의 unique timbre를 capture 하는 singer embedding을 활용하여 generalization을 지원함
- Positional encoding은 $F0$, amplitude generation model에 적용된 것과 동일함
- 이때 input $x$는 80-bin 2D mel-spectrogram으로 represent 되고 mel-spectrogram의 각 bin은 training 이전에 $[-1,1]$ range로 mix-max normalize 됨
- 해당 acoustic model은 score information을 제외하고 expressive performance control에만 의존함
- Vocoder
- 논문은 mel-spectrogram으로부터 final audio waveform을 얻기 위해 BigVGAN을 vocoder로 사용함
- 이때 acousitc model과 동일한 quantization method를 사용하여 additional conditioning input으로 quantized $F0$ curve를 incorporate 함
- 추가적으로 BigVGAN의 $F0$ frequency range를 11kHz로 modify 하여 high-frequency component를 include 함
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : OpenCPop, M4Singer, Children Song Dataset (CSD), VocalSet, PopCS, OpenSinger
- Comparisons : VISinger2, DiffSinger
- Results
- ExpressiveSinger는 기존보다 우수한 MOS를 달성함

- 각 style, language, technique에 대해서도 ground-truth와 큰 차이를 보이지 않음

- ExpressiveSinger는 ground-truth와 가장 비슷한 $F0$ curve를 합성함

- Expressive Performance Control
- Expressive Performance Control (EPC)를 제거하는 경우 CMOS가 크게 저하됨

- Zero-Shot Synthesis
- ExpressiveSinger는 zero-shot synthesis 측면에서도 우수한 성능을 달성함

반응형
'Paper > SVS' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

