티스토리 뷰
반응형
VoiceLDM: Text-to-Speech with Environmental Context
- Description prompt와 content prompt를 활용하여 audio를 생성할 수 있음
- Description prompt는 environmental context를 전달하고 content prompt는 linguistic information을 제공함 - VoiceLDM
- Latent diffusion model을 기반으로 하는 text-to-audio model을 채택하고 additional content prompt를 conditional input으로 활용할 수 있도록 확장
- Contrastive Language-Audio Pretraining과 Whisper를 활용하여 manual annotation, transcription 없이 training 됨
- 추가적으로 dual classifier-free guidance를 도입하여 controllability를 향상
- 논문 (ICASSP 2024) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- 최근의 Text-to-Audio (TTA)는 natural language prompt에서 제공하는 semantic context를 반영하여 fidelity, diversity 측면에서 뛰어난 성능을 보이고 있음
- BUT, TTA model은 speech를 생성하는 prompt에 대해 incoherent babbling voice를 생성하는 경우가 많음
- 한편으로 PromptTTS, PromptStyle, InstructTTS와 같이 Text-to-Speech (TTS)에서도 audio style control을 위해 prompt를 활용할 수 있음
- BUT, controllable diversity는 gender, emotion, volume과 같은 speech-related factor로만 제한됨
-> 그래서 TTA model을 기반으로 한 TTS model인 VoiceLDM을 제안
- VoiceLDM
- Spoken utterance의 linguistic content를 specifying 하는 content prompt와 audio의 environmental context를 characterize 하는 description prompt를 활용
- Latent diffusion model을 활용한 TTA system인 AudioLDM을 기반으로 additional content prompt를 incorporate 해 conditional input을 사용할 수 있도록 확장
- Contrastive Language-Audio Pretraining (CLAP)과 Whisper를 활용해 real-world audio data로 training을 수행
- 추가적으로 dual classifier-free guidance를 도입하여 controllability를 향상
< Overall of VoiceLDM >
- Content prompt에 대한 conditional input을 incorporate 하여 latent diffusion 기반의 TTA model을 TTS로 확장
- 결과적으로 TTA의 diverse audio generation capability를 확보하면서 TTS 수준의 speech intelligibilty를 달성

2. Method
- Model Overview
- VoiceLDM은 2개의 natural language prompt $\text{text}_{cont}, \text{text}_{desc}$가 주어졌을 때, 두 condition을 모두 input으로 따르는 audio $\mathbf{X}$를 생성하는 것을 목표로 함
- Description prompt $\text{text}_{desc}$는 pre-trained CLAP model에 의해 512-dimensional vector $\mathbf{c}_{desc}\in\mathbb{R}^{512}$로 변환됨
- CLAP은 modality를 동일한 latent space에 project 하도록 설계되었으므로 reference audio를 사용하여 $\mathbf{c}_{desc}$를 얻을 수도 있음 - Content prompt $\text{text}_{cont}$는 content encoder에 의해 hidden sequence $\mathbf{H}_{cont}\in\mathbb{R}^{L\times D}$로 encoding 됨
- $L$ : sequence length, $D$ : dimension size - 이후 differentiable durator는 hidden sequence를 $\mathbf{c}_{cont}\in\mathbb{R}^{N\times D}$로 upsampling 함
- $L\leq N$이고 differentiable durator는 NaturalSpeech와 동일하게 구성됨 - $\theta$로 parameterize 된 U-Net backbone은 $\mathbf{c}_{desc}, \mathbf{c}_{cont}$ condition을 모두 취한 다음, diffusion score $\epsilon_{\theta}$를 예측하기 위해 timestep embedding을 수행함
- Reverse diffusion process는 isotropic Gaussian distribution $z_{T}\sim\mathcal{N}(0,I)$에서 sampling 된 noise에서 시작하여,
- Predicted diffusion score $\epsilon_{\theta}$로 각 time step $t$에 대해 $z_{t}$를 iteratively denoise 해 initial audio prior $z_{0}$를 예측함
- 이후 $z_{0}$는 pre-trained Variational AutoEncoder (VAE)에 의해 mel-spectrogram으로 decode 됨
- 최종적으로 pre-trained HiFi-GAN vocoder를 사용하여 mel-spectrogram을 desired audio $\mathbf{X}$로 변환함
- Description prompt $\text{text}_{desc}$는 pre-trained CLAP model에 의해 512-dimensional vector $\mathbf{c}_{desc}\in\mathbb{R}^{512}$로 변환됨

- Training
- VoiceLDM의 training은 latent diffusion model training을 따름
- 먼저 audio $\mathbf{X}$에서 시작하여 pre-trained VAE는 audio를 latent representation $z_{0}$로 compress 함
- 이후 predefined noise schedule에 따라 forward diffusion process를 통해 $z_{0}$에 noise를 적용하여 certain timestep에 대한 $z_{0}$의 noisy representation $z_{t}$를 얻음 - CLAP으로 인해 training 중에 $\mathbf{c}_{desc}$를 얻는 과정에서 manually annotated description prompt $\text{text}_{desc}$는 필요하지 않음
- 대신 CLAP을 사용해 original audio $\mathbf{x}$에서 descriptive condition $\mathbf{c}_{desc}$를 얻음 - Content encoder와 differentiable durator는 speech transcription $\text{text}_{cont}$를 content condition $\mathbf{c}_{cont}$로 encoding 함
- 최종적으로 VoiceLDM은 re-weighted training objective를 사용하여 added noise $\epsilon$을 예측하도록 training 됨:
(Eq. 1) $\mathcal{L}_{\theta}=|| \epsilon-\epsilon(z_{t},t,\mathbf{c}_{desc},\mathbf{c}_{cont})||_{2}^{2}$
- 이때 U-Net backbone, content encoder, differentiable durator의 parameter는 jointly training 됨
- Pre-trained CLAP model, pre-trained VAE, vocoder는 training 중에 freeze 됨
- 먼저 audio $\mathbf{X}$에서 시작하여 pre-trained VAE는 audio를 latent representation $z_{0}$로 compress 함
- Dual Classifier-Free Guidance
- VoiceLDM에서 reverse diffusion process에 대한 classifier-free guidance가 각각의 condition $\mathbf{c}_{desc},\mathbf{c}_{cont}$에 대해 independent 하게 적용될 수 있음
- 따라서 이를 통해 각 individual condition에 대해 mode coverage와 sample fidelity를 trade-off 하여 controllability를 향상할 수 있음
- 먼저 두 condition $\mathbf{c}_{desc}, \mathbf{c}_{cont}$를 unified condition으로 보고 classifier-free guidance를 적용할 수 있음:
(Eq. 2) $\tilde{\epsilon}_{\theta}(z_{t},\mathbf{c}_{desc},\mathbf{c}_{cont})= \epsilon_{\theta}(z_{t},\mathbf{c}_{desc},\mathbf{c}_{cont})+w\left(\epsilon_{\theta}(z_{t},\mathbf{c}_{desc},\mathbf{c}_{cont})-\epsilon_{\theta}(z_{t},\emptyset)\right)$
- $w$ : guidance strength, $\emptyset$ : null condition - 한편으로 dual classifier-free guidance를 사용하면 additional control이 가능하고, 이때 diffusion score $\tilde{\epsilon}$은:
(Eq. 3) $\tilde{\epsilon}_{\theta}(z_{t},\mathbf{c}_{desc},\mathbf{c}_{cont})= \epsilon_{\theta}(z_{t},\mathbf{c}_{desc},\mathbf{c}_{cont})+w_{desc}\left( \epsilon_{\theta}(z_{t},\mathbf{c}_{desc},\emptyset_{cont})-\epsilon_{\theta} (z_{t},\emptyset_{desc},\emptyset_{cont})\right)$
$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,+w_{cont}\left(\epsilon_{\theta}(z_{t},\emptyset_{desc},\mathbf{c}_{cont})-\epsilon_{\theta}(z_{t},\emptyset_{desc},\emptyset_{cont})\right)$
- $w_{desc}=w_{cont}$인 경우 (Eq. 2)와 동일 - 결과적으로 $w_{desc}, w_{cont}$를 manipulate 하여 individual condition에 대한 guidance strength를 regulate 할 수 있음
- $w_{cont}$를 증가시키고 $w_{desc}$를 감소시키면 style diversity와 linguistic accuracy가 향상된 audio를 얻을 수 있음 - 추가적으로 추론 시 dual classifier-free guidance를 사용하기 위해 training 중에 $\mathbf{c}_{desc},\mathbf{c}_{cont}$ condition이 independently random drop 됨
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : AudioSet, Common Voice, VoxCeleb, DEMAND
- Comparisons : FastSpeech2, SpeechT5, AudioLDM
- Results
- VoiceLDM은 input condition을 adhere 하면서 기존보다 뛰어난 합성 품질을 달성함
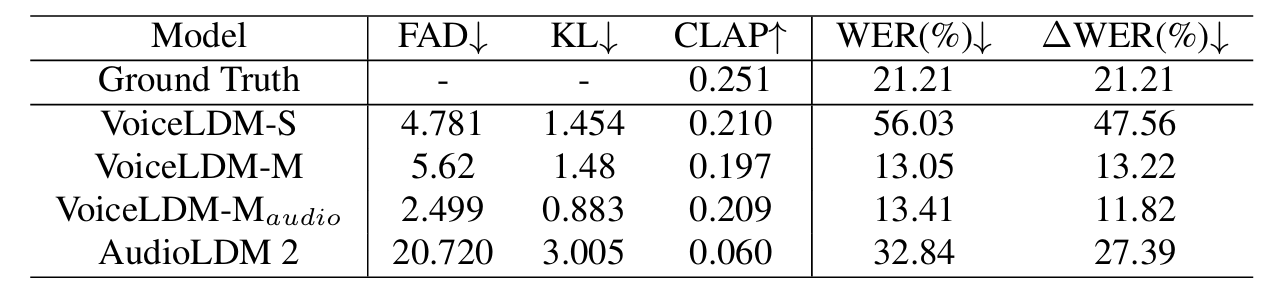
- Qualitative metric 측면에서도 우수한 성능을 보임

- Text-to-Speech Capability
- TTS 측면에서도 VoiceLDM은 ground-truth 이상의 linguistic intelligibility를 달성함
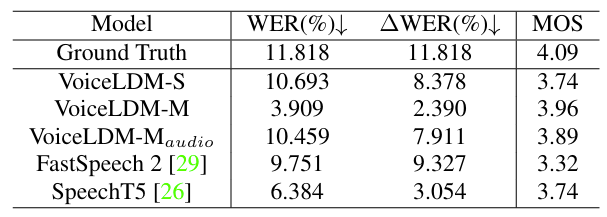
- Text-to-Audio Capability
- VoiceLDM은 TTA에 대해 specifically training 되지 않았음에도 불구하고 plausible audio를 생성함

- Effect of Dual Classifier-Free Guidance
- 높은 $w_{cont}$ 값을 사용하는 경우 speech intelligibilty가 높아지지만 description prompt에 대한 aherence는 감소함
- 반대로 $w_{desc}$를 높이는 경우 adherence는 향상할 수 있지만 intelligibilty가 저하됨

반응형
'Paper > TTS' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

