티스토리 뷰
Paper/Language Model
[Paper 리뷰] FELLE: Autoregressive Speech Synthesis with Token-wise Coarse-to-Fine Flow Matching
feVeRin 2025. 9. 30. 17:15반응형
FELLE: Autoregressive Speech Synthesis with Token-wise Coarse-to-Fine Flow Matching
- Language modeling과 flow matching을 integrate 할 수 있음
- FELLE
- Language model의 autoregressive nature와 flow matching의 generative efficacy를 기반으로 continuous-valued token을 predict
- 추가적으로 coarse-to-fine flow matching mechanism을 통해 speech quality를 향상
- 논문 (MM 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- VALL-E, VALL-E2와 같은 Large Language Model (LLM)은 zero-shot speech synthesis에서 우수한 성능을 달성함
- 이때 speech signal은 text와 달리 continuous 하므로 discrete-valued token으로 convert 하기 위한 quantization technique이 필요함
- BUT, quantization process는 fundamental constraint를 impose 하므로 discrete-token-based Text-to-Speech (TTS) system은 output quality의 한계가 있음 - 이를 위해 MELLE와 같은 autoregressive modeling을 고려할 수 있음
- BUT, 해당 model은 Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Mean Squared Error (MSE)와 같은 oversimplifed distributional assumption을 가짐
- 해당 assumption은 multi-modal structure나 complex feature를 반영하지 못하므로 blurred, oversimplified, averaged prediction으로 이어짐
- 추가적으로 autoregressive architecture는 temporal dependency를 explicitly modeling 하지 못함
- 즉, speech의 sequential characteristic을 preserve 하기 어려우므로 output naturalness가 저하됨
- 이때 speech signal은 text와 달리 continuous 하므로 discrete-valued token으로 convert 하기 위한 quantization technique이 필요함
-> 그래서 효과적인 speech synthesis를 위해 continuous-valued token modeling을 개선한 FELLE를 제안
- FELLE
- Language model의 autoregressive nature와 flow matching을 integrate 하여 preceding contextual information을 반영하고 각 frame의 prior distribution을 dynamically adjust
- 추가적으로 inter-frequency correlation을 capture 하는 Coarse-to-Fine Flow Matching (C2F-FM) module을 도입하여 speech quality를 향상
< Overall of FELLE >
- Token-wise flow matching과 AR framework를 combine 한 LLM-TTS model
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 성능을 달성
2. Preliminary
- Background
- Flow Matching은 prior distribution $p_{0}$를 target distribution $q(x)$로 mapping 하는 transformation을 학습함
- Flow Matching은 time에 따라 evolve 하며 prior distribution $p_{0}$를 target distribution $q(x)$로 transforming 하는 flow $\phi_{t}(x)$를 정의함
- 해당 flow $\phi_{t}(x)$는 vector field $v_{t}(x)$로 govern 되고 Ordinary Differential Equation $\frac{d}{dt}\phi_{t}(x)=v_{t}(\phi_{t}(x)),\,\, \phi_{0}(x)=x$를 만족함
- $\phi_{0}(x)=x$는 time $t=0$에서 flow $\phi_{t}(x)$가 identity mapping임을 의미
- BUT, Flow Matching은 해당 transformation을 위한 true vector field $u_{t}(x)$와 target distribution $q(x)$에 directly accessing 하기 어려움
- 이를 해결하기 위해 Conditional Flow Matching (CFM)은 flow와 vector field를 data $x_{1}$에 conditioning 하여 optimization process를 개선함
- 이때 CFM의 objective는 conditional true vector field $u_{t}$와 learned conditional vector field $v_{t}(x;\theta)$ 간의 discrepancy를 minimize 함
- 그러면 해당 discrepancy는 $\mathcal{L}_{CFM}=\mathbb{E}_{t,x_{1},x}||u_{t}-v_{t}(x;\theta)||^{2}$의 loss function과 같음
- Time $t$는 $\mathcal{U}[0,1]$에서 uniformly sample 되고, data point $x_{1}$은 target distribution $q(x_{1})$에서 추출되고, sample $x$는 conditional probability path $p_{t}(x|x_{1})$을 통해 생성됨
- Conditional vector field는 $u_{t}\equiv u_{t}(x|x_{1})$과 같음
- Problem Formulation
- MELLE의 autoregressive language modeling framework에 따라 논문은 각 prediction step에서 hierarchical flow-matching mechanism을 적용해 zero-shot TTS를 reformulate 함
- 각 mel-spectrogram fram $x^{i}\in\mathbb{R}^{D}$는 continuous token으로 취급되고, autoregressive process를 통해 sequentially generate 됨
- $D$ : mel-band dimension - Input text sequence $\mathbf{y}=[y^{0},...,y^{N-1}]$, speech prompt $\hat{x}$, previously generated token $x^{<i}=[x^{0},...,x^{i-1}]$이 주어지면,
- Model은 flow matching에 language model guidance를 integrate 하여 current token $x^{i}$를 predict 함
- 이때 joint distribution은 autoregressively decompose 됨:
(Eq. 1) $ p(X|\mathbf{y})=\prod_{i=0}^{L-1}p(x^{i}|x^{<i},\mathbf{y},\hat{x})$
$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, = \prod_{i=0}^{L-1}p_{\theta_{FM}}(x^{i}|z^{i}),\,\, z_{i}=f_{\theta_{LM}}(x^{<i},\mathbf{y},\hat{x})$
- $X=[x^{0},...,x^{L-1}]\in\mathbb{R}^{L\times D}$ : full mel-spectrogram sequence
- $L$ : total mel-spectrogram frame 수
- Language model $f_{\theta_{LM}}(\cdot)$은 linguistic content, acoustic context를 모두 capture 하는 hidden state $z^{i}$를 생성함
- $p_{\theta_{FM}}(\cdot |z^{i})$는 flow-matching module로써 prior distribution을 $z^{i}$에 condition 된 target distribution으로 transform 함
- 각 mel-spectrogram fram $x^{i}\in\mathbb{R}^{D}$는 continuous token으로 취급되고, autoregressive process를 통해 sequentially generate 됨
3. Method
- FELLE는 autoregressive language model과 flow matching mechanism을 combine 하여 high-fidelity speech를 progressive generate 함
- 먼저 autoregressive model $f_{\theta_{LM}}$은 text prompt $\mathbf{y}$와 speech prompt $\hat{x}$의 feature를 추출하여 latent representation $z^{i}$를 생성함
- 해당 latent representation은 flow matching의 conditional input으로 사용되고, flow matching mechanism은 Coarse-to-Fine strategy를 채택하여 high-quality mel-spectrogram frame $x^{i}$를 생성함
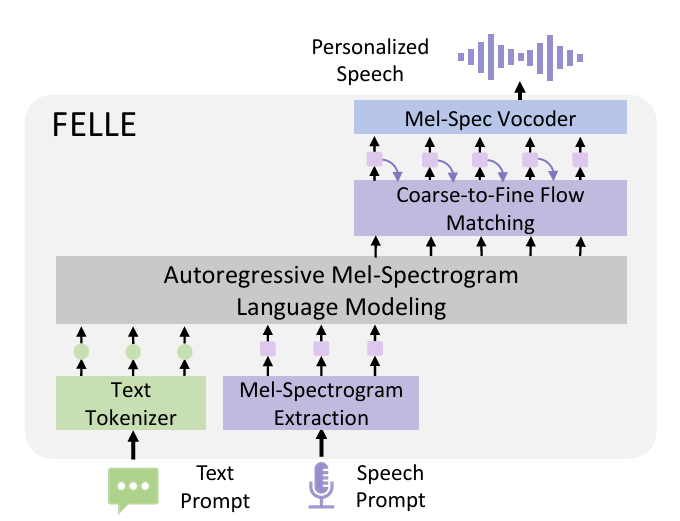
- Autoregressive Language Model
- Language model은 Transformer decoder로 구성되고 text sequence와 mel-spectrogram prompt를 활용하여 acoustic feature를 generate 함
- Initial step에서는 text token이 embed 되고 pre-net은 mel-spectrogram을 language model의 dimensional space로 mapping 함
- 이후 language model $f_{\theta_{LM}}$은 multi-head attention과 feed-forward layer를 통해 combined text $\mathbf{y}$, speech prompt $\hat{x}$, acoustic embedding $x^{<i}$의 relationship을 capture 함
- 각 timestep의 output은 coarse-to-fine flow matching module의 conditioning input으로 사용되어 next-frame acoustic feature를 생성함
- Coarse-to-Fine Flow Matching
- High-quality mel-spectrogram generation을 위해 논문은 coarse-to-fine flow matching을 도입함
- 이는 각 mel-spectrogram frame을 preceding frame을 기반으로 생성하여 sequence 전반의 temporal consistency를 maintain 함
- Generation process는 Coarse generation phase와 Fine refinement phase로 구성됨
- Prior Distribution
- VoiceBox, Matcha-TTS와 같은 flow-matching-based TTS model은 simple prior distribution을 채택함
- BUT, target distribution과 closely align 하는 prior distribution을 활용하면 computatinoal efficiency와 synthesis quality를 향상할 수 있음 - 따라서 논문은 preceding token을 informative prior로 사용하여 current token에 대한 flow matching을 guide 함
- 먼저 current frame $x^{i}$의 initial state $x_{0}^{i}$에 대한 prior distribution $p_{0}$는 previous frame $x^{i-1}$의 mel-spectrogram으로부터 derive 됨:
(Eq. 2) $ p_{0}(x_{0}^{i}|x^{i-1})=\mathcal{N}(x_{0}^{i}|x^{i-1},\sigma^{2}I)$
- $\sigma^{2}I$ : Gaussian noise의 covariance matrix - $i=0$ 일 때 initial state는 standard Gaussian distribution으로부터 drawn 됨
- 먼저 current frame $x^{i}$의 initial state $x_{0}^{i}$에 대한 prior distribution $p_{0}$는 previous frame $x^{i-1}$의 mel-spectrogram으로부터 derive 됨:
- VoiceBox, Matcha-TTS와 같은 flow-matching-based TTS model은 simple prior distribution을 채택함
- Coarse-to-Fine Generation
- FELLE는 autoregressive language modeling과 hierarchical flow matching을 combine 함
- 각 step $i$는 2-stage process를 따름:
- Initial low-resolution mel-spectrogram representation을 생성하는 coarse flow-matching phase
- Coarse representation과 language model output을 기반으로 output을 개선하는 fine flow-matching phase
- 먼저 coarse generation stage는 downsampling operation $x^{i,c}=\text{Downsample}(x^{i})$를 통해 $i$-th frame의 low-resolution component $x^{i,c}$를 생성함
- 해당 framework에서 coarse flow-matching model은 language model에서 추출된 linguistic feature $z^{i}$로 condition 되어 vector field $v_{t}^{c}(x^{i,c},z^{i};\theta_{FM}^{c})$를 predict 함 - Fine stage에서는 original frame $x^{i}$와 upsampled coarse component $\text{Upsample}(x^{i,c})$ 간의 residual로 represent 되는 fine-grained detail $x^{i,f}$를 recovering 하여 approximation을 refine 함
- Secondary flow-matching model은 vector field $v_{t}^{f}(x^{i,f},z^{i},x^{i,c};\theta_{FM}^{f})$를 predict 하고 feature $z^{i}$와 coarse component를 conditional input으로 사용하여 해당 process를 governing 함
- Training 시에는 ground-truth coarse feature $x^{i,c}$를 사용하고, 추론 시에는 predicted value $\tilde{x}^{i,c}$를 predict 함 - 해당 hierarchical conditioning을 통해 fine model은 local detail에 focus 하면서 coarse stage의 global coherence를 preserve 할 수 있음
- Secondary flow-matching model은 vector field $v_{t}^{f}(x^{i,f},z^{i},x^{i,c};\theta_{FM}^{f})$를 predict 하고 feature $z^{i}$와 coarse component를 conditional input으로 사용하여 해당 process를 governing 함
- 그러면 step $i$의 training objective는 두 stage의 loss를 combine 하여 얻어짐:
(Eq. 3) $ \mathcal{L}_{C2F\text{-}FM}=\mathbb{E}_{t,x_{1}^{i,c},x^{i,c}}|| u_{t}^{c}-v_{t}^{c}(x^{i,c}-v_{t}^{c}(x^{i,c},z^{i};\theta_{FM}^{c}))||^{2}+ \mathbb{E}_{t,x_{1}^{i,f},x^{i,f}}|| u_{t}^{f}-v_{t}^{f}(x^{i,f},z^{i},x^{i,c};\theta_{FM}^{f})||^{2}$
- $u_{t}^{c}, u_{t}^{f}$ : 각각 coarse/fine component에 대한 true conditional vector field, $t\sim \mathcal{U}[0,1]$
- Initial state $x_{0}^{i,c}, x_{0}^{i,f}$는 (Eq. 2)의 prior를 사용하여 initialize 됨 - 결과적으로 coarse-to-fine strategy는 low-resolution structure learning과 high-detail refinement를 decoupling 하여 temporal consistency를 autoregressive dependency를 통해 maintain 함
- Classifier-Free Guidance
- Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG)는 flow matching에서 생성된 output의 controllability를 향상하기 위해 사용됨
- 특히 논문은 conditional, unconditional objective를 모두 사용하여 coarse/fine flow matching model의 joint training을 수행하는 방식으로 CFG를 적용함
- Training 시에는 unconditional learning을 위해 probability $p_{drop}$으로 speech prompt를 randomly masking 하고 이를 통해 각 model이 dual vector field를 학습하도록 함
- 추론 시에는 guided vector field를 linear blending으로 compute 함:
(Eq. 4) $\hat{v}_{t}^{*}(x^{*};\cdot)=wv_{t}^{*}(x^{*},c;\theta_{FM}^{*})+(1-w)v_{t}^{*}(x^{*},\bar{c};\theta_{FM}^{*})$
- $*\in \{c,f\}$ : model stage, $c$ : full condition, $\bar{c}$ : prompt가 masking 된 reduced conditioning, $w$ : guidance scale

- Training Objective
- FELLE는 coarse-to-fine loss $\mathcal{L}_{C2F\text{-}FM}$ 외에도 condition loss $\mathcal{L}_{cond}$를 integrate 함
- $\mathcal{L}_{cond}$는 $L1, L2$ norm을 combine 한 hybrid loss로써, $\mathcal{L}_{cond}=||z_{i}-x_{i}||_{1}+||z_{i}-x_{i}||_{2}^{2}$로 정의됨
- 이는 step $i$의 conditional input을 regularize 함 - 추가적으로 논문은 autoregressive language model에 stop prediction module을 추가함
- 해당 module은 각 step에서 language model이 output 한 hidden state를 linear layer를 통해 stop signal probability로 transform 함
- Training 시에는 Binary Cross-Entropy loss $\mathcal{L}_{stop}$을 활용함 - 이를 통해 model은 preset length rule 없이도 generation stop을 automatically determine 할 수 있음
- 해당 module은 각 step에서 language model이 output 한 hidden state를 linear layer를 통해 stop signal probability로 transform 함
- 결과적으로 얻어지는 overall training loss는:
(Eq. 5) $\mathcal{L}=\mathcal{L}_{C2F\text{-}FM}+\lambda\mathcal{L}_{cond}+\alpha\mathcal{L}_{stop}$
- $\lambda, \alpha$ : control parameter
- $\mathcal{L}_{cond}$는 $L1, L2$ norm을 combine 한 hybrid loss로써, $\mathcal{L}_{cond}=||z_{i}-x_{i}||_{1}+||z_{i}-x_{i}||_{2}^{2}$로 정의됨
- Inference
- 추론 시에는 autoregressive language model이 textual, speaker prompt를 기반으로 hidden representation을 progressively generate 함
- 이때 각 step $i$의 computed latent state $z_{i}$는 다음 2가지 목적을 가짐
- 먼저 coarse flow matching module에 conditional guidance를 제공하여 previous mel-spectrogram approximation $\tilde{x}^{i-1,c}$에서 current coarse structural estimate $\tilde{x}^{i,c}$로의 gradual transformation을 지원함
- 해당 coarse estimation process 이후 $\tilde{x}^{i,c}, z_{i}$의 integrated information이 fine flow matching module로 전달되어 fined mel-spectrogram frame $\tilde{x}^{i,f}$를 생성함
- Final output frame $\tilde{x}^{i}$는 해당 complementary coarse/refined prediction을 integrate 하여 얻어짐
- Stop prediction module을 통해 처리된 latent state $z_{i}$는 stop probability를 compute 하고, pre-defined threshold와의 비교를 통해 process terminate를 결정함
- Iterative generation은 stop criterion을 만족할 때까지 수행되고, 이후 neural vocoder를 통해 mel-spectrogram을 final speech waveform으로 convert 함
4. Experiments
- Settings
- Results
- FELLE가 가장 높은 MOS를 달성함
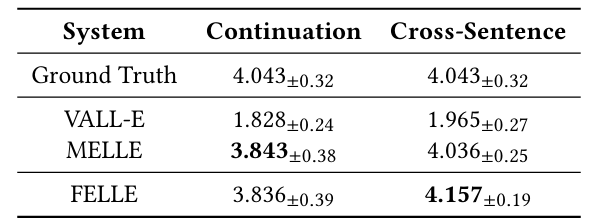
- 전체적으로 FELLE의 성능이 가장 뛰어남

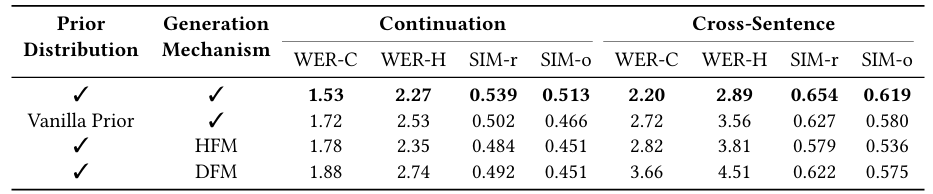
- Ablation Study
- Prior distribution, Generation mechanism을 모두 사용하는 경우 최적의 성능을 얻을 수 있음
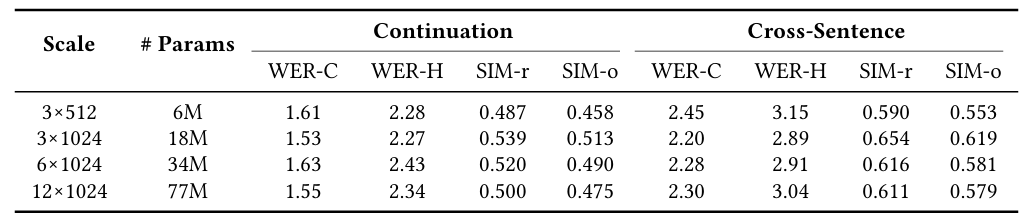
- Parameter Analysis
- Number of Function Evaluation (NFE) 측면에서 excessive refinement는 over-smoothing을 일으킴
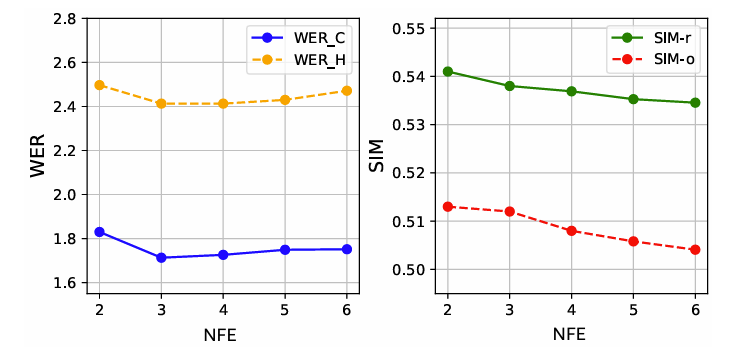
- C2F-FM을 scaling 하면 더 나은 WER을 달성할 수 있음
- CFG scale은 $1.6$에서 가장 낮은 WER을 달성함

- Cross-sentence continuity는 tighter prior conditioning (lower $\sigma^{2})$에 의존함

반응형
'Paper > Language Model' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

