티스토리 뷰
Paper/Neural Codec
[Paper 리뷰] Language-Codec: Bridging Discrete Codec Representations and Speech Language Models
feVeRin 2025. 11. 27. 14:26반응형
Language-Codec: Bridging Discrete Codec Representations and Speech Language Models
- Discrete acoustic codec은 speech language model에서 intermediate representation으로 사용됨
- Language-Codec
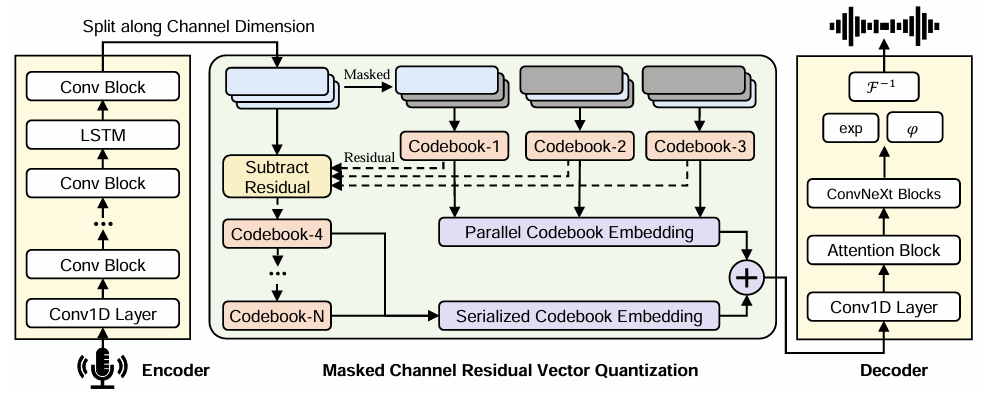
- Masked Channel Residual Vector Quantization을 도입하여 initial codebook의 excessive information 문제를 해결
- 추가적으로 Fourier transform structure, attention block, refined discriminator를 적용
- 논문 (ACL 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- VALL-E, SPEAR-TTS와 같은 Large-scale Language Model은 speech generation에서 우수한 성능을 보임
- 이때 SoundStream, EnCodec과 같은 discrete acoustic representation을 활용하면 효과적인 Transformer-based sequence-to-sequence modeling이 가능함
- 특히 codec model은 high-resolution audio signal을 2-dimensional discrete space로 compress 함
- 구조적으로 HiFi-Codec과 같은 대부분의 end-to-end discrete codec은 Encoder-Residual Vector Quantization (RVQ)-Decoder의 3-stage structure로 구성됨
- BUT, discrete codec model과 speech language model 간에는 다음의 gap이 존재함:
- Codec model은 information compression을 목표로 하므로 codec model은 reconstruction을 위해 codebook space에 상당한 information을 preserve 함
- 특히 RVQ structure는 codebook의 first channel에 excessive information이 포함되어 있어 downstream task에서 text와 같은 weak condition을 반영하기 어려움 - High-quality audio를 생성하기 위해 discrete representation rate를 증가시키면 codebook size가 exponentially grow 하므로 long token sequence 문제가 발생함
- Codec model은 information compression을 목표로 하므로 codec model은 reconstruction을 위해 codebook space에 상당한 information을 preserve 함
- 이때 SoundStream, EnCodec과 같은 discrete acoustic representation을 활용하면 효과적인 Transformer-based sequence-to-sequence modeling이 가능함
-> 그래서 downstream speech language model을 위한 Language-Codec을 제안
- Language-Codec
- First 3-channel의 quantizer가 specified space에서 compressed audio frame information만 학습하도록 restrict 하는 Maksed Channel Residual Vector Quantization (MCRVQ)를 도입
- Fourier transform structure와 attention block을 기반으로 한 decoder를 구성하고 multiple time-scale에 대한 complex STFT discriminator를 적용
< Overall of Language-Codec >
- Discrete representation과 speech language model 간의 gap을 해소한 neural codec model
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 성능을 달성
2. Method
- Overall
- Language-Codec은 raw audio signal $X$가 input 되면 reconstructed audio signal $\tilde{X}$를 output 함
- 먼저 original single-channel audio signal $X$는 1-dimensional vector sequence로 represent 됨:
(Eq. 1) $ X=\{x_{1},x_{2},...,x_{T}\},\,\,\,T=d*\text{sr}$
- $\text{sr}$ : sample rate, $d$ : audio duration - 이후 Language-Codec은 다음 3가지 module을 통해 raw audio $X$를 처리함:
- Encoder Network
- Input audio를 기반으로 latent feature representation $Z$를 생성하는 역할 - Parallel/serialized Quantization Layer $q$
- Compressed representation $Z_{q}$를 생성하는 역할 - Decoder
- Compressed latent representation $Z_{q}$로부터 audio signal $\tilde{X}$를 reconstruct 하는 역할
- Encoder Network
- Language-Codec은 end-to-end training 되고 time/frequency domain의 reconstruction loss와 다양한 resolution의 discriminator에 대한 perceptual loss를 optimizing 함
- 먼저 original single-channel audio signal $X$는 1-dimensional vector sequence로 represent 됨:
- Encoder and Decoder
- EnCodec을 따라 encoder는 $C$ channel, kernel size $7$의 1D convolution과 $B$ convolution block으로 구성됨
- 각 convolution block은 single residual unit, stride $S$의 stridden convolution으로 구성된 downsampling layer를 가짐
- Residual unit은 kernel size $3$과 skip-connection을 가지는 2개의 convolution을 가짐
- Convolution block 다음에는 sequence modeling을 위한 2-layer LSTM과 kernel size $7$, $D$ output channel을 가지는 final 1D convolution이 추가됨
- 이때 논문은 $C=32, B=4, S=(2,4,5,8)$을 사용하고, ELU non-linear activation을 사용함 - 이를 통해 Language-Codec은 24kHz audio를 초당 $75$ latent step으로 output 함
- Residual unit은 kernel size $3$과 skip-connection을 가지는 2개의 convolution을 가짐
- Language-Codec은 mirrored decoder upsampling structure를 사용하지 않음
- 대신 Vocos를 따라 inverse Fourier transform을 통해 waveform upsampling을 수행함 - 이때 decoder에서 target audio signal $\tilde{X}$는 STFT를 통해 represent 됨:
(Eq. 2) $\text{STFT}\left(\tilde{X}_{[m,k]}\right)=\sum_{n=0}^{N}\tilde{X}[n]w[n-m]e^{-j2\pi kn/K}$
- $K$ : Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)를 수행한 후의 frequency point
- $N$ : sampled sequence의 point 수, $n$ : 특정 sample point, $m$ : index length - 한편으로 Language-Codec은 quantization 이후 intermediate signal $Z_{q}$를 represent 하기 위해 $Z_{q}$를 Conv1D layer, attention block, ConvNeXt block에 input 함
- 이후 real-valued signal에 대해 Fourier transform을 수행함 - 추가적으로 논문은 upsampling module의 sequence modeling capability를 향상하기 위해 decoder에 attention module을 도입함
- ConvNeXt block에서는 input feature를 hidden dimensionality로 embed 한 다음 convolutional block sequence를 적용함
- 각 block은 large-kernel-sized depthwise convolution으로 구성되고, pointwise convolution을 사용하여 feature를 higher dimensionality로 project 하는 inverted bottleneck이 추가됨
- Bottleneck에서는 GELU activation, Layer Normalization이 사용됨
- Real-valued signal transformation의 경우, single-side band spectrum을 사용하여 $n_{fft}/2+1$의 frame 당 coefficient를 얻음
- Hidden dimension의 activation은 $n_{fft}+2$ channel을 가진 tensor $h$로 project 된 후 split 됨:
(Eq. 3) $ q=h\left[1:n_{fft}/2+1\right];p=h\left[n_{fft}/2+2:n\right]$
- $q$ : magnitude, $p$ : argument - 결과적으로 얻어지는 complex-valued coefficient는:
(Eq. 4) $\text{STFT}=\exp(q)\cdot\left(\cos p+j\sin p\right)$
- 이후 inverse Fourier transform $\mathcal{F}^{-1}$을 사용해 final audio를 reconstruct 할 수 있음
- Hidden dimension의 activation은 $n_{fft}+2$ channel을 가진 tensor $h$로 project 된 후 split 됨:
- 각 convolution block은 single residual unit, stride $S$의 stridden convolution으로 구성된 downsampling layer를 가짐
- Masked Channel Residual Vector Quantization
- Masked Channel Residual Vector Quantization (MCRVQ) module은 initial codebook channel의 informational content를 minimize 하면서 constrained channel에서 compensate 되는 information을 augment 하는 것을 목표로 함
- 이를 위해 Language-Codec은 parallel/serial quantization을 combine 한 hybrid structure를 구성함
- Initial $N_{q}$ layer에서 각 quantizer는 original information의 segment를 independently process 함
- 이후 $N_{q}$에서 $N$ subsequent layer에서는 preceding quantizer에서 생성된 embedding vector를 sequentially subtract 하고 current quantization process의 input으로 사용함
- Initial $N_{q}=3$ layer에서 parallel operating 하는 quantizer는 Masked Channel mechanism을 활용하여 quantizer의 first $N_{q}$ channel에서 latent space information $Z$의 mean quantization을 얻음
- 이때 compressed audio frame을 $N_{q}$ equal part로 divide 하고 masked portion을 $M$, unmasked portion을 $\bar{M}$으로 represent 함
- 논문은 quantizer의 specified portion을 mask 하고 latent space information $Z$의 $\frac{1}{N_{q}}$를 retain 하여 quantizer에 directly feed 함 - 결과적으로 quantizer는 layer $i \,\,\, (1\leq i\leq N_{q})$에 대한 intermediate result $\hat{Z}_{i}$를 다음과 같이 얻을 수 있음:
(Eq. 5) $ P\left(\hat{Z}_{i}|\bar{M}Z\right)=P\left(\hat{Z}_{i}|(1-M)Z\right)=P\left(\hat{Z}_{i}|\frac{Z}{N_{q}}\right)$
- 이때 compressed audio frame을 $N_{q}$ equal part로 divide 하고 masked portion을 $M$, unmasked portion을 $\bar{M}$으로 represent 함
- $N_{q}$ channel 이후의 quantizer는 previous $N_{j}$ channel에서 $Z$의 residual을 substract 하여 얻은 $\hat{Z}_{j}$ information을 retain 한 후 quantizer $j\,\,\, (N_{q}+1\leq j\leq N)$에 feed 함
- 이때 first $N_{q}$ layer의 quantizer는 parallel architecture를 가지므로 $N_{q}+1$ layer의 quantizer input은 $Z-\hat{Z}_{j}$가 아닌 각 preceding layer의 representation을 sequentially substract 해야 함
- 즉, $N_{q}+1$ layer에 대한 generation process는:
(Eq. 6) $P\left(\hat{Z}_{N_{q}+1}|Z-\sum_{i=1}^{N_{q}}\hat{Z}_{i}\right)$
- $N$ quantizer를 통과한 다음, 각 channel information을 fusion 하여 final result $Z_{q}$를 얻음
- Fusion layer는 parallel/serial quantizer의 output embedding metric을 channel dimension을 따라 concatenate 함 - 결과적으로 MCRVQ mechanism은 다음과 같이 formulate 됨:
(Eq. 7) $P(Z_{q}|Z)=\prod_{i=1}^{N_{q}}P\left(\hat{Z}_{i}|\bar{M}Z\right)P\left(\hat{Z}_{N_{q}+1}|Z-\sum_{i=1}^{N_{q}}\hat{Z}_{i}\right)\times \prod_{j=N_{q}+1}^{N-1}P\left(\hat{Z}_{j+1}|Z-\hat{Z}_{j}\right)$
- 이를 위해 Language-Codec은 parallel/serial quantization을 combine 한 hybrid structure를 구성함
- Discriminator and Loss
- Adversarial loss는 perceptual quality를 향상하기 위해 사용됨
- 특히 논문은 HiFi-GAN의 Multi-Period Discriminator (MPD), UnivNet의 Multi-Resolution Discriminator (MRD), SoundStream의 Multi-Scale Discriminator (MSD), Complex STFT Discriminator를 사용함
- Discriminator를 training 하기 위해 논문은 다음의 objective를 optimize 함:
(Eq. 8) $\mathcal{L}_{dis}(X,\tilde{X})=\frac{1}{K}\sum_{k=1}^{K}\max\left(0,1-D_{k}(X)\right)+\max\left(0,1+D_{k}(\tilde{X})\right)$
- $K$ : discriminator 수, $D_{k}$ : $k$-th discriminator - Generator loss의 경우 quantization loss, mel-spectrum reconstruction loss, adversarial loss, feature matching loss로 구성됨
- 먼저 quantization loss는:
(Eq. 9) $ \mathcal{L}_{q}(Z,Z_{q})=\sum_{i=1}^{N}\left|\left| Z_{i}=\hat{Z}_{i}\right|\right|^{2}_{2}$ - Mel-spectrum reconstruction loss는:
(Eq. 10) $\mathcal{L}_{mel}(X,\tilde{X})=\left|\left| \text{Mel}(X)-\text{Mel}(\tilde{X})\right|\right|_{1}$ - Adversarial loss는 discriminator logit에 대한 hinge loss로 얻어짐:
(Eq. 11) $\mathcal{L}_{adv}=\frac{1}{K}\sum_{k=1}^{K}\max\left(0,1-D_{k}(\tilde{X})\right)$ - Feature matching loss는 $k$-th sub-discrimintor의 $l$-th feature map 간 distance를 평균하여 얻어짐:
(Eq. 12) $\mathcal{L}_{feat}=\frac{1}{K*L}\sum_{k}\sum_{l}\left|\left| D_{k}^{l}(X)-D_{k}^{l}(\tilde{X})\right|\right|_{1}$
- 먼저 quantization loss는:
- 결과적으로 얻어지는 generator loss는:
(Eq. 13) $\mathcal{L}_{gen}=\lambda_{q}\mathcal{L}_{q}+\lambda_{mel}\mathcal{L}_{mel}+\lambda_{adv}\mathcal{L}_{adv}+\lambda_{feat}\mathcal{L}_{feat}$
- $\lambda_{q},\lambda_{mel},\lambda_{adv},\lambda_{feat}$ : hyperparameter
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : LibriLight, DNS Challenge, CommonVoice, LibriTTS
- Comparisons : EnCodec, DAC, Vocos, SpeechTokenizer
- Results
- 전체적으로 Language-Codec의 성능이 가장 우수함

- Zero-Shot TTS
- VALL-E에 Language-Codec을 적용하면 최고의 성능을 달성할 수 있음

- Ablation Study
- MCRVQ를 제거하면 성능 저하가 발생함

반응형
'Paper > Neural Codec' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

