티스토리 뷰
Paper/Neural Codec
[Paper 리뷰] PURE Codec: Progressive Unfolding of Residual Entropy for Speech Codec Learning
feVeRin 2025. 12. 9. 13:04반응형
PURE Codec: Progressive Unfolding of Residual Entropy for Speech Codec Learning
- Neural speech codec은 Residual Vector Quantization으로 인한 reconstruction의 한계가 있음
- PURE Codec
- Pre-trained speech enhancement model을 활용하여 multi-stage quantization을 guiding
- First stage에서는 low-entropy, denoised speech embedding을 reconstruct 하고 second stage에서는 residual high-entropy component를 encode
- 논문 (ASRU 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Neural speech codec은 speech language modeling, generative audio synthesis 등에 활용되고 있음
-> 그래서 RVQ-based multi-stream codec의 한계점을 개선한 PURE Codec을 제안
- PURE Codec
- RVQ-based pipeline에 Enhancement-aware Supervision을 도입
- Pre-trained denoising model을 활용하여 clean, low-entropy representation을 reconstruct 하고 subsequent layer에서 residual entropy를 progressively unfolding
< Overall of PURE Codec >
- Enhancement-aware supervision과 progressive unfolding을 활용한 RVQ-based neural codec
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 성능을 달성
2. Background
- Quantization and Residual Vector Quantization
- Neural speech codec은 continuous acoustic signal을 compact, discrete representation으로 convert 함
- Codec architecture는 일반적으로 encoder $\text{Enc}(\cdot)$, quantizer $\text{Quant}(\cdot)$, decoder $\text{Dec}(\cdot)$으로 구성됨
- 이때 encoder는 input waveform $S\in \mathbb{R}^{1\times T_{s}}$가 주어지면 frame-level embedding sequence $Q=\text{Enc}(S)\in \mathbb{R}^{D\times T}$를 생성함
- $T_{s}$ : speech length, $D$ : feature dimension, $T$ : frame 수 - 한편으로 해당 embedding을 discretize 하기 위해 neural codec은 RVQ를 quantizer로 사용함
- 먼저 RVQ는 $B$ vector를 포함하는 $L$ codebook $\{\mathcal{B}^{1},...,\mathcal{B}^{L}\}$을 사용하고, frame-level embedding sequence $Q$는 embedding state sequence $[q_{1},...,q_{T}]$로 elaborate 됨
- 각 frame $t$에서 quantization은 raw embedding $r_{t}^{0}=q_{t}$에서 시작해 각 codebook의 nearest codeword embedding을 iteratively select 하여 residual error를 reduce 함:
(Eq. 1) $ c_{t}^{l}=\arg\min_{j}\left|\left| r_{t}^{l-1}-b_{j}^{l}\right|\right|_{2}^{2}\in\{1,...,B\}$
(Eq. 2) $\hat{q}_{t}^{(l)}=b^{l}_{c_{t}^{l}}$
(Eq. 3) $r_{t}^{l}=r_{t}^{l-1}-b^{l}_{c_{t}^{l}}$
- $c_{t}^{l}$ : stream $l$에서 select 된 index, $b^{l}_{c_{t}^{l}}$ : 해당 codeword embedding - Frame $t$에 대한 quantized embedding $\hat{q}_{t}$는 모든 stream에서 select 된 vector의 합과 같음:
(Eq. 4) $\hat{q}_{t}=\sum_{l=1}^{L}\hat{q}_{t}^{(l)}=\sum_{l=1}^{L}b^{l}_{c_{t}^{l}}$ - Decoder는 sequence $\hat{Q}=[\hat{q}_{1},...,\hat{q}_{T}]$로부터 $\hat{S}=\text{Dec}(\hat{Q})$를 통해 waveform을 reconstruct 함
- 전체 quantization process는 다음과 같음:
(Eq. 5) $\left(\hat{Q},\{c_{t}^{l}\}_{t=1,l=1}^{T,L}\right)=\text{Quant}(Q)$
3. Method
- General Framework
- PURE Codec은 input signal의 entropy profile을 기반으로 residual decomposition을 도입한 multi-stage, vector-quantized neural codec에 해당함
- 특히 RVQ framework를 기반으로 enhancement-guided hierarchy를 incorporate 함
- Early stage (Stream $1$)에서는 enhanced low-entropy content를 encode 하고 later stage (Stream $L$)에서는 noisy higher-entropy residual을 progressively cpature 함 - Basic encoder-decoder design에서 enhancement module은 $S$를 처리하여 denoised waveform $S^{enh}=\text{Enh}(S)$를 생성하고, encoding 하여 enhanced embedding $\tilde{Q}=\text{Enc}(S^{enh})$을 얻음
- 해당 enhanced embedding은 first quantization stream을 supervise 하는 low-entropy anchor로 사용됨 - Quantizer의 각 stream은 residual codebook lookup을 사용하여 $Q$의 approximation을 sequentially refine 함
- First stream은 $\tilde{Q}$를 approximate 하도록 explicitly training 되고 이후의 ($2$~$L$) stream은 residual을 modeling 함 - Quantized embedding $\hat{Q}=[\hat{q}_{1},...,\hat{q}_{T}]$는 decoder로 전달되어 $\hat{S}=\text{Dec}(E)$와 같이 waveform을 reconstruct 하는 데 사용됨
- 특히 RVQ framework를 기반으로 enhancement-guided hierarchy를 incorporate 함

- Progressive Unfolding of Residual Entropy
- PURE Codec의 entropy-guided quantization은 다음과 같이 formalize 됨
- 먼저 frame $t$의 enhanced embedding을 $\tilde{q}_{t}=\text{Enc}(S^{enh})_{t}$, original embedding을 $q_{t}=\text{Enc}(S)_{t}$라고 하자
- First quantization stage는 $\tilde{q}_{t}$와 해당 closest codebook entry 간의 error를 minimize 함:
(Eq. 6) $ c_{t}^{1}=\arg\min_{j}\left|\left|\tilde{q}_{t}-b^{1}_{j}\right|\right|_{2}^{2}\in\{1,...,B\}$
(Eq. 7) $\hat{q}_{t}^{(1)}=b^{1}_{c^{1}_{t}}$
(Eq. 8) $r^{1}_{t}=q_{t}=\hat{q}^{(1)}_{t}$
- $\hat{Q}^{(1)}=[\hat{q}_{1}^{(1)},...,\hat{q}_{T}^{(1)}]$ : quantized embedding - Residual $r_{t}^{1}$은 higher stage로 전달되고 각 stage는 (Eq. 1)-(Eq. 3)을 따라 approximation을 iteratively refine 함
- First quantization stage는 $\tilde{q}_{t}$와 해당 closest codebook entry 간의 error를 minimize 함:
- Final quantized embedding은 모든 stage의 summation으로 얻어짐:
(Eq. 9) $\hat{q}_{t}=\sum_{l=1}^{L}\hat{q}_{t}^{(l)}$
- $\hat{Q}=[\hat{q}_{1},...,\hat{q}_{T}]$ - Residual entropy에 대한 progressive unfolding은 각 quantization stage를 signal information structure의 specific portion과 align 함
- 이를 통해 model은 controllable representation을 생성할 수 있고, quantization hierarchy의 early stopping을 통해 다양한 bitrate constraint에도 gracefully adapt 할 수 있음
- 먼저 frame $t$의 enhanced embedding을 $\tilde{q}_{t}=\text{Enc}(S^{enh})_{t}$, original embedding을 $q_{t}=\text{Enc}(S)_{t}$라고 하자
- Training Strategy
- PURE Codec은 2-stage로 training 됨
- First stage에서는 encoder-decoder pair를 VAE로 pre-training 하고 second stage에서는 quantization과 enhancement-guided supervision을 도입함
- VAE pre-training stage에서 encoder, decoder는 $\ell_{1}$ waveform reconstruction loss, multi-resolution mel loss, KL divergence regularization term $D_{KL}$의 combination을 minimize 하도록 training 됨:
(Eq. 10) $ \mathcal{L}_{VAE}=\left|\left|S-\hat{S}\right|\right|_{1}+\text{MelLoss}(S,\hat{S})+\lambda_{KL}D_{KL}\left( q(z|S)||p(z)\right)$
- $z$ : approximate posterior에서 얻어지는 latent variable, $p(z)$ : standard Gaussian prior, $\lambda_{KL}$ : KL loss에 대한 hyperparameter
- 해당 pre-training stage는 model이 discrete bottleneck 없이 speech의 underlying structure를 학습하도록 하여 subsequent stage의 stable convergence를 지원함 - VAE pre-training 이후에는 quantization layer와 enhancement supervision을 도입함
- 이때 논문은 stochastic scheduling mechanism을 통해 first quantization stage가 enhanced/original embedding과 align 될지 여부를 결정함
- Fixed probability $p_{enh}$이면 enhanced embedding $\tilde{Q}=\text{Enc}(\text{Enh}(S))$를 first-stage quantization의 target으로 사용하고, 그렇지 않으면 $Q=\text{Enc}(S)$를 사용함 - 해당 stochastic scheduling은 training robustness와 flexibility를 balance 하는 데 사용되고, 이때 loss는:
(Eq. 11) $\mathcal{L}_{enh}=\mathbb{E}_{\text{Bernoulli}(p_{enh})}\left[\left|\left| \hat{Q}^{(1)}-\tilde{Q}\right|\right|_{2}^{2}\right]$
- 이때 논문은 stochastic scheduling mechanism을 통해 first quantization stage가 enhanced/original embedding과 align 될지 여부를 결정함
- PURE Codec의 full-training은 GAN-based modeling paradigm을 따름
- 여기서 codec은 encoder, quantizer, decoder module로 구성된 generator $\mathcal{G}$로 취급되고, multi-scale discriminator $\mathcal{D}$는 $\mathcal{G}$의 waveform을 distinguish 하는 데 사용됨
- Reconstruction loss는 waveform, perceptual-level fidelity를 promote 함:
(Eq. 12) $\mathcal{L}_{rec}=\left|\left| S-\hat{S}\right|\right|_{1}+\text{MelLoss}(S,\hat{S})+\text{MelLoss}\left(\text{Dec}(\text{Enc}(S)),S\right)$
- $\text{MelLoss}$ : multi-resolution mel-spectrogram loss - Vector quantization loss는:
(Eq. 13) $\mathcal{L}_{vq}=\sum_{l=1}^{L}\left(\left|\left| \text{sg}[Q]-M^{l}\right|\right|_{2}^{2}+\beta\left|\left| Q-\text{sg}\left[M^{l}\right]\right|\right|_{2}^{2}\right)$
- $\text{sg}[\cdot]$ : stop-gradient operator, $\beta$ : hyperparameter
- $M^{l}=\left[\sum_{k=1}^{l}\hat{q}_{1}^{(k)},...,\sum_{k=1}^{l}\hat{q}_{T}^{(k)}\right]$ : stage $l$의 codebook output - Adversarial generator loss는:
(Eq. 14) $\mathcal{L}_{adv}^{\mathcal{G}}=\mathbb{E}_{\hat{S}}\left[(\mathcal{D}(\hat{S})-1)^{2}\right]$
- 이는 synthesized waveform $\hat{S}$가 discriminator judgement에서 real waveform과 indistinguishable 하도록 함 - 그러면 generator $\mathcal{G}$는 다음의 loss를 통해 optimize 됨:
(Eq. 15) $\mathcal{L}_{\mathcal{G}}=\lambda_{enh}\mathcal{L}_{enh}+\lambda_{rec}\mathcal{L}_{rec}+\lambda_{vq}\mathcal{L}_{vq}+\lambda_{adv}\mathcal{L}_{adv}^{\mathcal{G}}$
- $\lambda_{enh},\lambda_{rec},\lambda_{vq}, \lambda_{adv}$ : hyperparameter - Discriminator $\mathcal{D}$는 real/generated sample을 distinguish 하도록 training 됨:
(Eq. 16) $\mathcal{L}_{\mathcal{D}}=\mathbb{E}_{S}\left[(\mathcal{D}(S)-1)^{2}\right]+\mathbb{E}_{\hat{S}}\left[ (\mathcal{D}(\hat{S}))^{2}\right]+\mathcal{L}_{feat}(S,\hat{S})$
- $\mathcal{L}_{feat}(S,\hat{S})$ : feature matching loss - 결과적으로 PURE Codec의 full-training process는 다음의 min-max optimization으로 express 됨:
(Eq. 17) $ \min_{\mathcal{G}}\max_{\mathcal{D}}\mathcal{L}_{PURE}(\mathcal{G},\mathcal{D})=\mathcal{L}_{\mathcal{G}}-\lambda_{adv}\cdot\mathcal{L}_{\mathcal{D}}$
4. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : OWSM-v3.2, CommonVoice, URGENT
- Comparisons : DAC

- Results
- 전체적으로 PURE Codec이 더 나은 성능을 보임
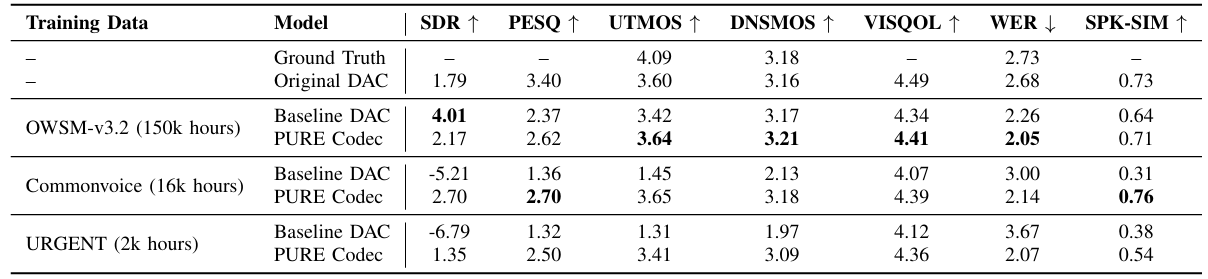
- Ablation Study
- (Eq. 11)의 sampling probability $p_{enh}$를 $0.25$로 설정하면 높은 PESQ를 달성할 수 있음

- SpeechLM-based TTS
- TTS task에서도 PURE Codec을 사용하면 더 나은 결과를 얻을 수 있음

반응형
'Paper > Neural Codec' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

