티스토리 뷰
Paper/Neural Codec
[Paper 리뷰] Variable Bitrate Residual Vector Quantization for Audio Coding
feVeRin 2026. 1. 8. 12:50반응형
Variable Bitrate Residual Vector Quantization for Audio Coding
- Neural audio codec은 rate-distortion trade-off 측면에서 suboptimal 함
- VRVQ
- Frame 당 사용되는 codebook 수를 adapting 하여 efficient coding을 지원
- Importance map을 binary importance mask로 transform 하는 non-differentiable masking operation에 대한 gradient estimation method를 도입
- 논문 (ICASSP 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- 최근 SoundStream, EnCodec, DAC와 같은 Residual Vector Quantization (RVQ)-based codec은 low bitrate에서도 compact discrete representation을 생성할 수 있음
- 해당 neural codec은 raw waveform을 parallel token sequence로 encoding 한 다음, quantized residual vector의 summation을 통해 audio signal을 reconstruct 함
- BUT, RVQ-based neural codec은 모든 downsampled time frame에 동일한 수의 codebook을 allocate 하므로 silence와 같은 less-complex segment를 encoding 할 때 inefficient 함
- Variable Bitrate (VBR)을 활용하면 해당 inefficiency를 개선할 수 있지만 neural codec 측면에서는 아직 도입되지 않음
-> 그래서 VBR을 활용해 RVQ-based neural codec을 개선한 VRVQ를 제안
- VRVQ
- RVQ-based audio codec에 VBR coding을 도입
- Importance map의 non-differentiable operation에 대한 gradient estimation을 통해 training 과정에서 effective gradient flow를 보장
< Overall of VRVQ >
- VBR coding과 importance map을 활용한 RVQ-based neural codec
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 성능을 달성
2. Background
- Residual Vector Quantization
- Downsampled time frame $T$, latent representation dimension $D$에 대해,
- Input audio $x$에 대한 encoder $E$의 output을 $z_{e}=E(x)\in\mathbb{R}^{D\times T}$, $z_{e}$의 time $t$에 대한 $i$-th frame을 $z_{e}[t]$라고 하자
- 그러면 $N_{q}$의 quantizer를 가지는 RVQ는 $z_{e}[t]$를 input으로 사용해 $z_{q}[t]$를 compute 함:
(Eq. 1) $ z_{q}[t]=\sum_{i=1}^{N_{q}}Q_{i}(r_{i}[t])$
- $Q_{i}$ : $i$-th quantizer, $r_{i}[t]=z_{e}[t]-\sum_{j=1}^{i-1}Q_{j}(r_{j}[t])$
- Initial residual은 $r_{1}[t]=z_{e}[t]$로 주어짐 - 이후 $z_{q}$는 decoder $D$에 input 되어 audio estimation $\hat{x}$를 output 함
- Structured Codebook Dropout
- Target bitrate가 주어진 경우, 해당 $N_{q}$에 맞는 separate model을 training 할 수 있음
- 이때 separate training 대신 Structured Dropout을 사용하여 single RVQ model이 multiple target bitrate를 support 하도록 구성할 수 있음
- 먼저 training 시에는 모든 codebook을 사용하지 않고 first $n_{q}$ quantizer만 사용함
- 즉, $z_{q}[t]=\sum_{i=1}^{n_{q}}Q_{i}(r_{i}[t]))$
- 여기서 $n_{q}$는 각 batch 마다 $\{1,...,N_{q}\}$에서 randomly sample 됨 - 추론 시에는 target bitrate에 대한 desired $n_{q}$를 select 할 수 있음
- 즉, $z_{q}[t]=\sum_{i=1}^{n_{q}}Q_{i}(r_{i}[t]))$
- 결과적으로 Structured Codebook Dropout은 다음과 같이 formulate 됨:
(Eq. 2) $z_{q}[t]=\sum_{i=1}^{N_{q}}\mathbb{1}_{i\leq n_{q}}\cdot Q_{i}(r_{i}[t])$
- $\mathbb{1}$ : indicator function
3. Method
- Importance Map-based Bit Allocation
- Time frame index $t$에 대한 bit allocation은 binary mask $m[t]\in\{0,1\}^{N_{q}}$에 의해 control 되고, 이때 $m_{i}[t]$는 $t$에서 $i$-th codebook usage를 결정함
- 해당 mask는 (Eq. 2)의 indicator function과 달리 $t$에 따라 time-varying 하므로, 논문은 compression efficiency를 위해 $i$에 대해 monotonically decrease 하도록 $m[t]$를 구성함
- 즉, $i<j$이면 $m_{i}[t]\geq m_{j}[t]$ - 추가적으로 논문은 desirable mask generation을 위해 Importance Map을 도입함
- 이를 위해 encoder $E$의 intermediate feature map에서 importance map을 compute 하고 bit allocation을 위해 importance map을 기반으로 mask를 생성함 - 먼저 $E$를 shared part $E_{1}$, encoding-specific part $E_{2}$에 대한 2개의 component $E=E_{2}\circ E_{1}$으로 decompose 하여 intermediate feature map을 얻음
- Audio $x$가 주어지면 learnable subnetwork $E_{p}$가 $E_{1}(x)$를 input으로 사용하여 importance map $p=E_{p}(E_{1}(x))\in(0,1)^{T}$를 output 함
- 다음으로 각 time frame index $t$에 대해 importance map-to-mask function $\text{I2M}: (0,1)\rightarrow \{0,1\}^{N_{q}}$를 사용하여 $p[t]$를 기반으로 $m[t]\in\{0,1\}^{N_{q}}$를 생성함:
(Eq. 3) $m[t]=\text{I2M}(p[t]):=\left[H^{0}\left(S(p[t])\right),...,H^{N_{q}-1}\left( S(p[t])\right)\right]^{\top}$
- $S(p)=N_{q}\cdot p$ : scaling function - $H^{k}(s)$는 heaviside step function으로써:
(Eq. 4) $H^{k}(s):=\left\{\begin{matrix}
1, & \text{if}\,\,k\leq s \\
0, & \text{if}\,\, k>s\\
\end{matrix}\right.$ - 얻어진 mask $m[t]$는 (Eq. 2)의 indicator function을 replace 하여 quantized vector $z_{q}$를 calculate 함:
(Eq. 5) $z_{q}[t]=\sum_{i=1}^{N_{q}}m_{i}[t]\cdot Q_{i}(r_{i}[t])$
- Audio $x$가 주어지면 learnable subnetwork $E_{p}$가 $E_{1}(x)$를 input으로 사용하여 importance map $p=E_{p}(E_{1}(x))\in(0,1)^{T}$를 output 함
- 해당 mask는 (Eq. 2)의 indicator function과 달리 $t$에 따라 time-varying 하므로, 논문은 compression efficiency를 위해 $i$에 대해 monotonically decrease 하도록 $m[t]$를 구성함

- Gradient Estimation for Binarized Variables
- Baseline
- $H^{k}$는 non-continuous function이므로 encoding-decoding framework 내에서 importance map을 jointly training 하기 위해서는 gradient estimation이 필요함
- 이때 saturated identity function $f_{I}^{k}$는 backpropagation 시 $H^{k}$에 대한 surrogate로 사용될 수 있음:
(Eq. 6) $f_{I}^{k}(s):=\max\left(\min(s-k,1),0\right)$ - BUT, 해당 function은 $\max, \min$ operation으로 인해 large region에서 gradient가 flow 하지 않으므로 suboptimal result로 이어질 수 있음
- 특히 $\text{I2M}$ function에서는 single $k\in \{0,...,N_{q}-1\}$에 대해서만 non-zero gradient가 존재함
- Smooth Approximation
- 앞선 baseline의 문제를 해결하기 위해, 논문은 $f_{I}^{k}$를 relax 하여 모든 range에서 gradient를 compute 할 수 있는 smooth surrogate function을 구성함:
(Eq. 7) $f_{\alpha}^{k}(s):=\frac{1}{2\alpha}\log\left(\frac{\cosh\left( \alpha(s-k)\right)}{\cosh\left(\alpha(-s+k+1)\right)}\right)+\frac{1}{2}$ - 해당 surrogate function은 hyperparameter $\alpha\in\mathbb{R}_{>0}$에 의해 parameterize 됨
- $\alpha$가 무한대에 가까울수록 해당 function은 모든 $s\in\mathbb{R}$에 대해 $f_{I}^{k}$에 approach 함
- 즉, $f_{\infty}^{k}(x):=\lim_{\alpha\rightarrow \infty}f_{\alpha}^{k}(s)=f_{I}^{k}(s)$
- 결과적으로 $\text{I2M}$의 $H^{k}$를 $f_{\alpha}^{k}$로 substitute하여 $\text{I2M}$의 surrogate function인 $\text{I2M}^{\alpha}_{soft}$를 얻을 수 있고, backpropagation을 위해 straight-through estimator를 적용할 수 있음:
(Eq. 8) $\text{I2M}_{soft}^{\alpha}(p[t]):=\left[f_{\alpha}^{0}\left(S(p[t])\right),..., f_{\alpha}^{N_{q}-1}\left(S(p[t])\right)\right]$
(Eq. 9) $p[t]\mapsto \text{I2M}_{soft}^{\alpha}(p[t])+\text{sg}\left(\text{I2M}(p[t])-\text{I2M}^{\alpha}_{soft}(p[t])\right)$
- $\text{sg}$ : stop-gradient
- 앞선 baseline의 문제를 해결하기 위해, 논문은 $f_{I}^{k}$를 relax 하여 모든 range에서 gradient를 compute 할 수 있는 smooth surrogate function을 구성함:

- Training
- Compression model과 importance map sub-network을 training 하기 위해,
- Rate loss $\mathcal{L}_{R}$은 다음과 같이 정의됨:
(Eq. 10) $\mathcal{L}_{R}=\frac{1}{T}\sum_{t=1}^{T}E_{p}\left(E_{1}(x)\right)[t]$ - VRVQ는 DAC의 training framework를 기반으로 Rate-Distortion (R-D) trade-off loss $\mathcal{L}_{D}+\lambda \mathcal{L}_{R}$을 optimize 함
- $\mathcal{L}_{D}$ : DAC의 training objective, $\mathcal{L}_{R}$ : rate loss, $\lambda$ : hyperparameter - 한편으로 importance map은 한번 train 되면 identical input audio $x$에 대해 항상 fixed output $p$를 output 하므로 rate control 측면에서 flexibility를 restrict 함
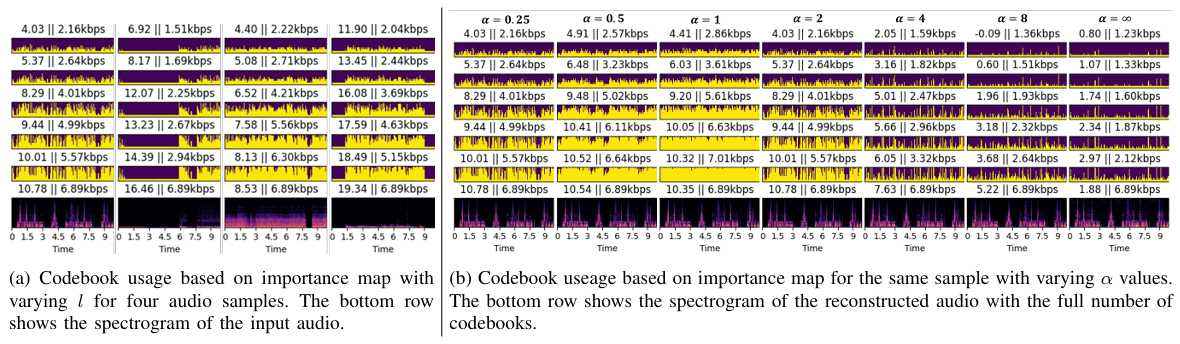
- 이를 해결하기 위해 논문은 continuous uniform distribution $\mathcal{U}\left([L_{\min},L_{\max}]\right)$에서 scaling factor $l$을 sampling 함
- $L_{\max}>N_{q}$ - 이후 training 시 (Eq. 3)과 (Eq. 8)의 scaling function $S(p)$를 $S_{l}(p)=l\cdot p$로 replace 하여 single model이 VBR mode에서 multiple bitrate를 handle 하도록 함
- 이를 해결하기 위해 논문은 continuous uniform distribution $\mathcal{U}\left([L_{\min},L_{\max}]\right)$에서 scaling factor $l$을 sampling 함
- Rate loss $\mathcal{L}_{R}$은 다음과 같이 정의됨:
4. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : DAPS, CommonVoice, VCTK, DNS Challenge 4, MUSDB18, Jamendo
- Comparisons : DAC
- Results
- $\alpha$가 증가함에 따라 VRVQ의 성능은 $f_{I}$에 가까워짐
- 특히 SI-SDR 측면에서 VRVQ는 DAC 보다 더 나은 성능을 보임

- Importance map의 diversity가 감소하면 high-bitrate에서 성능 저하가 발생함
- Ablation Study
- Quantizer 수를 늘리면 더 나은 성능을 달성할 수 있음

반응형
'Paper > Neural Codec' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

