티스토리 뷰
Paper/Language Model
[Paper 리뷰] Koel-TTS: Enhancing LLM based Speech Generation with Preference Alignment and Classifier Free Guidance
feVeRin 2025. 11. 19. 12:59반응형
Koel-TTS: Enhancing LLM based Speech Generation with Preference Alignment and Classifier Free Guidance
- Autoregressive speech token generation model은 hallucination과 undesired vocalization의 문제가 있음
- Koel-TTS
- Preference alignment와 Classifier Free Guidance를 활용하여 Language Model의 contextual adherence를 향상
- 특히 speech recognition model에서 derive 된 automatic metric을 사용하여 model output을 rank 하고 conditional, unconditional logit을 interpolate 하여 fine-grained control을 지원
- 논문 (EMNLP 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- VALL-E, AudioLM과 같은 speech Large Language Model (LLM)은 prompt-based cutomization을 통해 human-like intonation을 가지는 speech를 생성할 수 있음
- BUT, LLM-based Text-to-Speech (TTS) system은 hallucination으로 인해 repetition을 overemphasize 하거나 intended flow를 capture 하지 못할 수 있음
- 추가적으로 동일한 input에 대해 multiple output을 sampling 하는 경우 quality variation이 나타남
-> 그래서 LLM-based TTS의 contextual coherence를 향상한 Koel-TTS를 제안
- Koel-TTS
- Performance alignment를 위해 transcription accuracy와 target speaker similarity를 capture 하고 해당 metric을 reward system에 integrate
- Classifier Free Guidance (CFG)를 통해 unconditional, conditional logit을 interpolate 하여 naturalness를 향상
< Overall of Koel-TTS >
- Performance alignment와 CFG를 활용한 LLM-based TTS model
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 성능을 달성
2. Method
- Tokenization
- Speech
- 논문은 neural audio codec을 사용하여 raw speech signal을 tokenized representation으로 transform 함
- Audio signal $\mathbf{a}$가 주어지면 codec model은 2-dimensional acoustic matrix $\mathbf{C}_{T\times N}=\text{CodecModel}(\mathbf{a})$를 output 함
- Downsampled sequence length $T$, timestep 별 codebook 수 $N$에 대해 $\mathbf{C}_{T\times N}$은 $m$-bit discrete code로 구성됨
- 구조적으로는 codebook 간의 independence를 보장하는 Low Frame-rate Speech Codec을 채택하고 $N=8$ independent codebook을 사용함
- 해당 independence로 인해 model은 additional delay mechanism 없이 각 timestep에서 모든 $N$ codebook을 parallel predict 할 수 있음
- Text
- 논문은 phoneme, character tokenization을 고려함
- Phoneme의 경우 fundamental sound unit을 capture 할 수 있지만 language-specific Grapheme-to-Phoneme (G2P) conversion이 필요함
- Character-based tokenization의 경우 grapheme을 acoustic information으로 direct conversion 할 수 있음
- 결과적으로 논문은 English, German, Spanish에 대해서는 IPA phoneme, character tokenizer를 사용하고 다른 language에 대해서는 character tokenization만 사용함
- 논문은 phoneme, character tokenization을 고려함
- Model Architecture
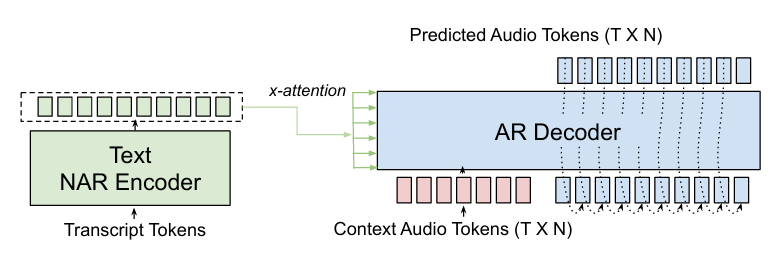
- 논문의 speech generation model은 cross-attention 기반 non-autoregressive (NAR) Transformer encoder의 text encoding을 condition으로 사용하는 autoregressive (AR) Transformer decoder로 구성됨
- 해당 encoder-decoder architecture는 AR decoder의 self-attention을 interfering 하지 않으면서 attention prior와 cross-attention score에 대한 CTC loss를 통해 monotonic alignment를 보장함
- 이때 AR Transformer는 audio token을 frame-by-frame으로 predict 하고 previous prediction과 cross-attention input을 condition으로 하여 각 timestep에서 모든 $N$ codebook을 parallel generate 함
- 각 decoder timestep에서 input acoustic embedding은 $N$ codebook 각각의 embedding을 referencing 하고 summing 하여 얻어짐 - 추가적으로 context audio를 통한 speaker, style conditioning을 지원하기 위해 context audio token을 target audio token에 prepend 함
- Training Objective
- 각 decoder timestep의 output은 linear layer를 사용하여 size $N\times 2^{m}$의 vector로 mapping 되고 각 size가 $m$-bit인 모든 $N$ codebook에 대한 logit을 output 함
- 그러면 모든 decoder timestep에 대해 size $T\times N\times 2^{m}$의 logit $\ell$을 얻을 수 있고, 다음과 같이 cross-entropy를 calculate 할 수 있음:
(Eq. 1) $\mathcal{L}_{token}=\text{CE}(\text{softmax}(\ell),\text{target}_{N\times T})$ - 한편으로 text-speech alignment를 향상하기 위해 attention prior와 Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) loss를 도입할 수 있음
- Decoder layer $l$에서 $h$-th cross-attention head의 audio timestep $T$와 text timestep $M$ 간의 cross-attention matrix $\mathbf{A}^{l,h}_{T\times M}$이 주어지면
- 2D beta-binomial distribution을 사용하여 static prior $\mathbf{P}_{T\times M}$를 얻을 수 있고, 해당 prior에 대한 re-scaled attention score는:
(Eq. 2) $ \mathbf{A}_{T\times M}^{l,h}\leftarrow \mathbf{A}_{T\times M}^{l,h}\odot \mathbf{P}_{T\times M}$ - Attention prior는 first $10000$ training iteration에 적용된 다음, 이후 $5000$ iteration 동안 Uniform distribution으로 linearly anneal 되고 turn off 됨
- 2D beta-binomial distribution을 사용하여 static prior $\mathbf{P}_{T\times M}$를 얻을 수 있고, 해당 prior에 대한 re-scaled attention score는:
- 추가적으로 alignment matrix에서 valid monotonic sampling을 encourage 하기 위해 CTC algorithm을 사용하여 all possible monotonic reduction의 likelihood를 calculate 함
- 즉, alignment matrix $\mathbf{A}_{T\times M}^{soft_{l,h}}=\text{softmax}(\mathbf{A}_{T\times M}^{l,h})$가 주어졌을 때 decoder layer, head에 대한 alignment loss는:
(Eq. 3) $\mathcal{L}_{align}^{l,h}=\text{CTCLoss}\left(\mathbf{A}_{T\times M}^{soft_{l,h}},q_{M}\right)$
- $q_{M}=\{1,2,...,M\}$ : $1$에서 $M$까지의 target monotonic sequence - Alignment loss는 모든 cross-attention head, layer에 대해 $\mathcal{L}_{align}=\sum_{l,h}\mathcal{L}_{align}^{l,h}$와 같이 summation 됨
- 즉, alignment matrix $\mathbf{A}_{T\times M}^{soft_{l,h}}=\text{softmax}(\mathbf{A}_{T\times M}^{l,h})$가 주어졌을 때 decoder layer, head에 대한 alignment loss는:
- 결과적으로 얻어지는 final loss는 $\mathcal{L}=\mathcal{L}_{token}+\alpha\mathcal{L}_{align}$과 같음
- $\alpha=0.002$ : alignment loss coefficient
- 그러면 모든 decoder timestep에 대해 size $T\times N\times 2^{m}$의 logit $\ell$을 얻을 수 있고, 다음과 같이 cross-entropy를 calculate 할 수 있음:
- Preference Alignment
- 논문은 preference optimization을 활용하여 TTS output을 desirable result로 steer 함
- Text, context audio input $x=(x_{text},x_{audio})$가 주어지면 model의 response distribution $\pi(y|x)$는 다양한 alignment level의 potential output $y$의 range를 encompass 함
- 이때 특정 response $y_{c}$를 chosen, 다른 $y_{l}$을 reject로 explicitly label 한 dataset을 기반으로 preference optimization을 적용하면 model distribution을 preffered response로 shift 할 수 있음 - 대표적으로 Direct Preference Optimization (DPO)는 policy $\pi$를 reference policy $\pi_{ref}$와 contrasting 해 preference를 modify 함
- 먼저 input $x$와 rejected response $y_{l}$보다 prefer 되는 chosen $y_{c}$가 주어진다고 하자
- DPO는 $\frac{\pi(y_{l}|x)}{\pi_{ref}(y_{l}|x)}$에 대한 $\frac{\pi(y_{c}|x)}{\pi_{ref}(y_{c}|x)}$의 likelihood ratio를 증가시키는 것을 목표로 함:
(Eq. 4) $ \mathcal{L}_{DPO}=\mathbb{E}_{x,y_{c},y_{l}}\left[\beta\log \frac{\pi(y_{c}|x)}{\pi_{ref}(y_{c}|x)}-\beta\log\frac{\pi(y_{l}|x)}{\pi_{ref}(y_{l}|x)}\right]$
- $\beta$ : base reference policy $\pi_{ref}$에 대한 deviation을 control 하는 parameter - (Eq. 4)를 통해 $\pi$는 $y_{l}$보다 $y_{c}$와 유사한 response를 produce 하도록 encourage 되므로, model을 desired preference에 effectively align 할 수 있음
- DPO를 기반으로 reward difference의 magnitude를 반영하는 Reward-aware Preference Optimization (RPO)를 고려할 수 있음
- RPO의 경우 chosen, reject를 동일하게 취급하지 않고 scalar reward를 사용하여 chosen response가 rejected response 보다 얼마나 더 나은지를 측정함
- 이때 RPO objective는 reward gap $r^{*}(x,y_{c})-r^{*}(x,y_{l})$에 따라 preference를 update 함:
(Eq. 5) $\mathcal{L}_{RPO}(x,y_{c},y_{l})=\mathbb{D}\left[\left.\left.\beta\log\frac{\pi(y_{c}|x)}{\pi_{ref}(y_{c}|x)} -\beta\log\frac{\pi(y_{l}|x)}{\pi_{ref}(y_{l}|x)}\right|\right|\eta\left( r^{*}(x,y_{c})-r^{*}(x,y_{l})\right)\right]$
- $\eta$ : scaling parameter, $\mathbb{D}$ : distance metric으로써, $\mathbb{D}[a||b]:=\sigma(b)\log\frac{\sigma(b)}{\sigma(a)}+(1-\sigma(b))\log\frac{1-\sigma(b)}{1-\sigma(a)}$ - RPO는 reward difference에 따라 loss가 scaling 되므로 overffiting 문제를 mitigate 할 수 있음
- Text, context audio input $x=(x_{text},x_{audio})$가 주어지면 model의 response distribution $\pi(y|x)$는 다양한 alignment level의 potential output $y$의 range를 encompass 함

- Preference Data Creation and Reward System
- Preference dataset $(x,y_{c},y_{l})$을 구성하기 위해 다양한 text, speaker combination을 select 함
- 먼저 각 text, speaker prompt에 대해 $\text{temperature}=0.7$의 multinomial sampling을 사용하여 $P$ audio sample을 생성함
- 이후 Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) model을 사용하여 generated audio의 transcript와 input text 간의 Character Error Rate (CER)을 얻고,
- Speaker Verification (SV) model을 사용하여 context audio와 generated audio 간의 cosine-similarity (SSIM)을 구함
- 먼저 각 text, speaker prompt에 대해 $\text{temperature}=0.7$의 multinomial sampling을 사용하여 $P$ audio sample을 생성함
- 해당 CER, SSIM을 기반으로 주어진 input pair을 기반으로 생성된 $P$ generated audio sample에 Pareto optimal ranking을 수행함
- 먼저 다른 어떤 sample에도 dominate 되지 않는 audio sample로 구성된 Pareto front를 identify 함
- First Pareto front가 identify 되면 해당 sample을 remove 하고 나머지 audio에 대해 동일한 process를 반복하여 next front를 find 함
- 해당 process를 반복하고, 각 Pareto front 내에서는 CER score가 낮은 sample에 higher rank를 assign 하여 sample을 정렬함
- CER이 같다면 SSIM이 높은 sample을 기준으로 ranking 함
- Ranking 이후 DPO는 highest-rank를 chosen으로, lowest-rank를 reject로 사용하고, RPO는 top-2와 bottom-2를 pair 하여 사용함
- 추가적으로 RPO에 대한 scalar reward assign을 위해 chosen, rejected 간의 CER, SSIM difference를 normalize 하고 reward gap을 다음과 같이 설정함:
(Eq. 6) $ r^{*}(x,y_{c})-r^{*}(x,y_{l})=\Phi(\Delta\tilde{\text{CER}})+\Phi(\Delta\tilde{\text{SSIM}})$
- $\Phi$ : standard Normal distribution의 Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF)
- $\Delta\tilde{\text{CER}},\Delta\tilde{\text{SSIM}}$ : chosen, reject 간 CER, SSIM의 normalized difference
- Preference dataset $(x,y_{c},y_{l})$을 구성하기 위해 다양한 text, speaker combination을 select 함

- Classifier Free Guidance
- Autoregressive token prediction model에 CFG를 적용하기 위해, text와 context/speaker conditioning을 randomly dropping 하여 conditional, unconditional model을 training 함
- 추론 시에는 conditional, unconditional output을 combine 하여 generation을 guide 하여 pronunciation, prosody, robustness를 향상함
- 특히 논문은 training 시 audio와 text conditioning input을 probability $10\%$로 randomly drop 하고, 추론 시에는 conditional logit $\ell_{c}$와 unconditional logit $\ell_{u}$를 interpolate 함:
(Eq. 7) $ \ell_{cfg}=\gamma*\ell_{c}+(1-\gamma)*\ell_{u}$
- $\gamma\geq 1$ : CFG interpolation scale
- 이때 higher scale은 generation이 text/audio input을 따르도록 하고 lower scale은 variation을 허용함

3. Experiments
- Settings
- Results
- 전체적으로 Koel-TTS의 성능이 가장 우수함

- MOS 측면에서도 Koel-TTS가 가장 선호됨
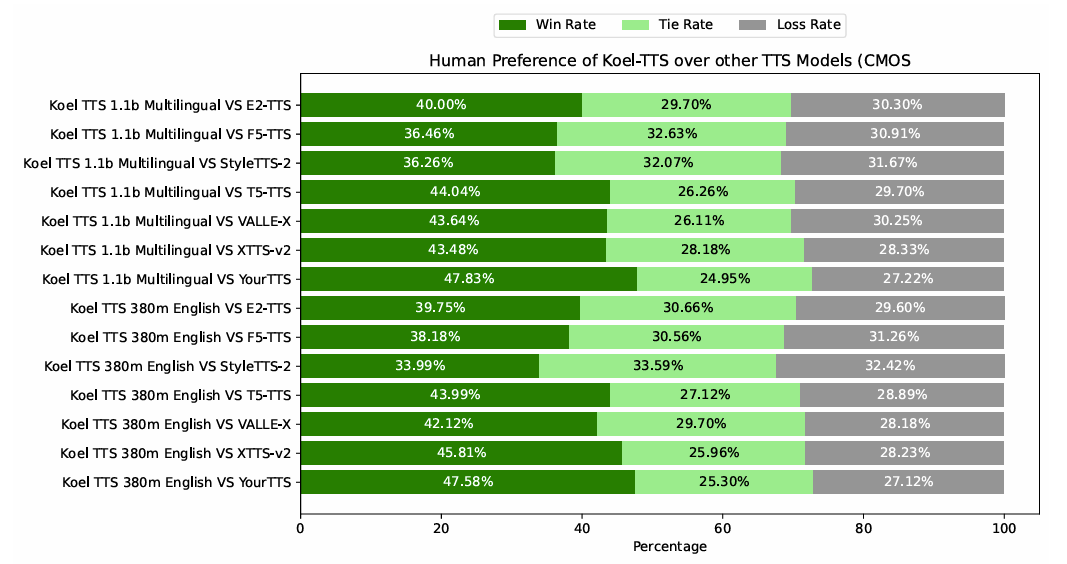
- Preference alignment와 CFG를 모두 활용하면 intelligibility와 speaker similarity를 향상할 수 있음

- Koel-TTS는 multilingual setting에서도 뛰어난 성능을 보임

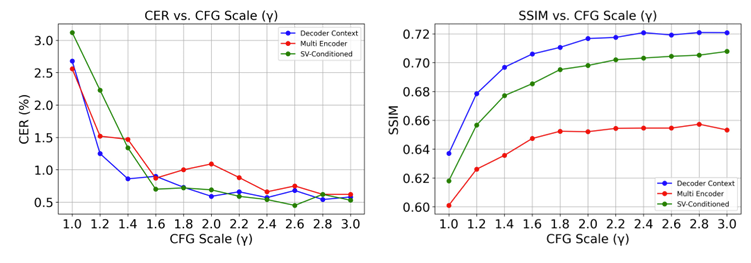
- $\gamma=2.5$의 CFG scale을 사용했을 때 최적의 성능을 달성함
반응형
'Paper > Language Model' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

