티스토리 뷰
Paper/Representation
[Paper 리뷰] AxLSTMs: Learning Self-Supervised Audio Representations with xLSTMs
feVeRin 2025. 9. 20. 07:50반응형
AxLSTMs: Learning Self-Supervised Audio Representations with xLSTMs
- xLSTM은 Transformer와 비교할만한 성능을 가짐
- AxLSTM
- Self-supervised setting에서 xLSTM을 활용해 masked spectrogram patch로부터 general-purpose audio representation을 학습
- AudioSet dataset으로 pre-training 하여 다양한 downstream task에 대응
- 논문 (INTERSPEECH 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Transformer는 뛰어난 generalization ability와 data-agnostic nature를 가지지만 scaled dot-product로 인한 complexity의 한계가 있음
- 한편 Transformer 이전의 Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) 역시 sequence modeling에 효과적임
- RNN은 sequence length에 대해 linearly scale 되고 entire key-value (KV) cache를 store 할 필요가 없으므로 runtime memory requirement가 낮다는 장점이 있음 - BUT, 대표적인 RNN approach인 LSTM은 다음의 문제점을 가지고 있음:
- Storage decision을 revise 할 수 없음
- Information을 scalar cell state로 compressing 하므로 rare input token에 영향을 미침
- Memory mixing으로 인해 parallelizing이 어려움
- 이때 xLSTM을 활용하면 이러한 LSTM의 단점들을 해결할 수 있음
- 한편 Transformer 이전의 Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) 역시 sequence modeling에 효과적임
-> 그래서 xLSTM을 audio self-supervised learning에 적용한 AxLSTM을 제안
- AxLSTM
- xLSTM을 기반으로 spectrogram patch로부터 masked modeling framework를 적용
- AudioSet에 대한 pre-training을 수행하여 다양한 downstream task에 대한 성능을 향상
< Overall of AxLSTM >
- xLSTM architecture와 self-supervised learning을 활용한 general-purpose audio representation model
- 결과적으로 다양한 audio downstream task에서 우수한 성능을 달성
2. Method
- Prerequisites: xLSTM and mLSTM Block
- xLSTM은 sLSTM, mLSTM의 2가지 building block으로 구성되고, 논문은 mLSTM을 fundamental building block으로 채택함
- 먼저 parallelizable mLSTM block은 matrix memory cell $C\in \mathbb{R}^{d\times d}$를 사용하여 original LSTM cell을 개선함:
- mLSTM은 timestep $t$에서 $k_{t},v_{t}\in\mathbb{R}^{d}$의 key-value vector pair를 store 하고 relevant value vector는 query $q_{t+\tau}\in\mathbb{R}^{d}$를 통해 retrieve 됨
- 즉, mLSTM의 forward pass는:
(Eq. 1) $ C_{t}=f_{t}C_{t-1}+i_{t}v_{t}k^{\top}_{t}$
(Eq. 2) $n_{t}=f_{t}n_{t-1}+i_{t}k_{t}$
(Eq. 3) $h_{t}=o_{t}\odot C_{t}q_{t}/\max\left\{|n_{t}^{\top}q_{t}|,1\right\}$
(Eq. 4) $q_{t}=W_{q}x_{t}+b_{q}$
(Eq. 5) $k_{t}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{d}}W_{k}x_{t}+b_{k}$
(Eq. 6) $v_{t}=W_{v}x_{t}+b_{v}$
(Eq. 7) $i_{t}=\exp\left(w^{\top}_{i}x_{t}+b_{i}\right)$
(Eq. 8) $f_{t}=\exp\left(w_{f}^{\top}x_{t}+b_{f}\right)$
(Eq. 9) $o_{t}=\sigma(W_{o}x_{t}+b_{o})$
- $C_{t}$ : matrix memory cell, $h_{t}$ : normalizer state/hidden state, $i_{t}, f_{t},o_{t}$ : 각각 input/forget/ouput gate
- $W_{q},W_{k},W_{v}$ : weight로써 각각 query $q$, key $k$, value $v$에 대한 learnable projection matrix
- mLSTM은 timestep $t$에서 $k_{t},v_{t}\in\mathbb{R}^{d}$의 key-value vector pair를 store 하고 relevant value vector는 query $q_{t+\tau}\in\mathbb{R}^{d}$를 통해 retrieve 됨
- mLSTM에는 memory mixing이 없으므로 multiple memory cell과 multiple head는 equivalent 하고 forward pass는 parallelize 될 수 있음
- 추가적으로 mLSTM에는 storage decision을 revise 하기 위한 exponential gating이 적용됨
- 먼저 parallelizable mLSTM block은 matrix memory cell $C\in \mathbb{R}^{d\times d}$를 사용하여 original LSTM cell을 개선함:
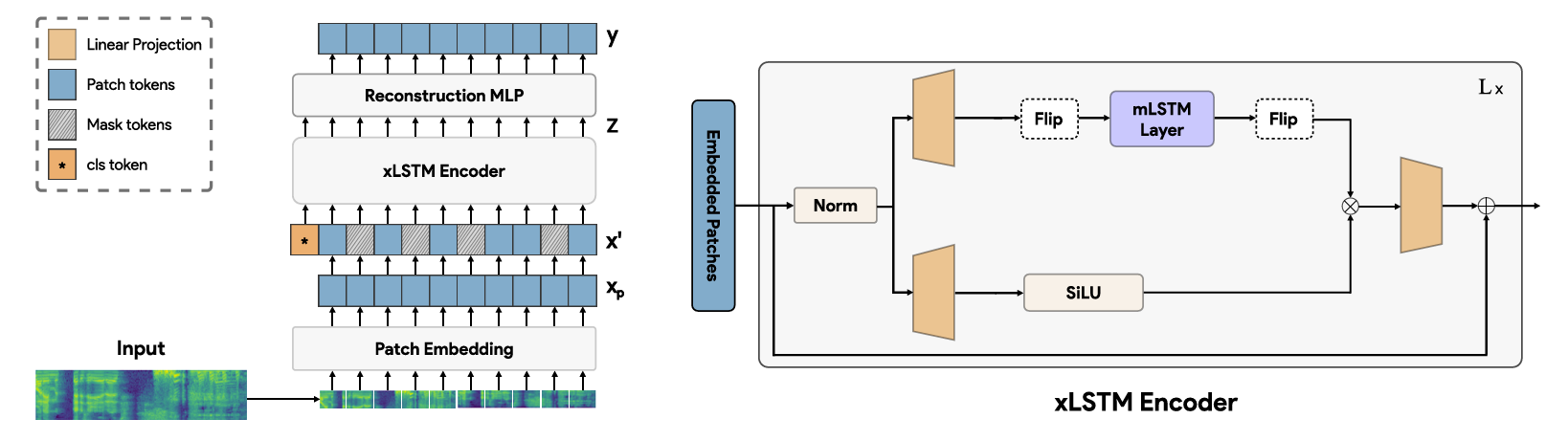
- AxLSTM: Modeling Masked Patches with xLSTMs
- Creating and Masking Patches
- Input spectrogram $\mathbf{x}\in\mathbb{R}^{T\times F}$가 주어지면, shape $\times f$의 non-overlapping patch를 compute 하여 $\mathbf{x}_{p}\in\mathbb{R}^{N\times (t\cdot f)}$ patch를 생성함
- 다음으로 patch는 $\mathbb{R}^{N\times d_{m}}$ dimensional space에 project 되고, fixed sinusoidal 2D positional embedding이 add 됨
- 이때 representative class token이 sequence beginning에 add 되어 fine-tuning을 지원함 - 이후 input patch의 $50\%$를 randomly mask 하고 해당 masked patch를 learnable mask token으로 replace 함
- 즉, encoder input은:
(Eq. 10) $ \mathbf{x}'=\left[\text{cls},\mathbf{x}_{p}^{1},\mathbf{x}_{p}^{2},...,\mathbf{x}_{p}^{N}\right] +E_{pos}$
- Encoding and Reconstruction
- Partially masked patch는 encoder에 전달되어 encoded representation $\mathbf{z}=\text{enc}(\mathbf{x}'), \mathbf{z}\in\mathbb{R}^{(N+1)\times d_{m}}$을 yield 함
- 구조적으로 encoder는 mLSTM block stack으로 구성되고, 각 block은 $d_{m}$ dimensional input을 expansion factor $E_{f}$로 expand 한 다음, $d_{m}$으로 다시 project 함
- 이로 인해 resulting block은 Transformer block 보다 더 적은 parameter를 가짐 - 추가적으로 input의 bidirectional modeling을 위해 input sequence order를 reverse 하는 $\text{flip}$ operation을 짝수 mLSTM block에 적용할 수 있음
- Encoding 이후에는 single hidden layer가 encoded representation $\mathbf{z}$로부터 patch를 reconstruct 하는 데 사용됨:
(Eq. 11) $\mathbf{y}'=\text{Linear}_{(t\cdot f)}\left(\sigma(\text{Linear}_{d_{m}}(\mathbf{z}))\right)$
- $\text{Linear}_{d}$ : dimension $d$의 parameterized linear projection
- $\sigma$ : GELU non-linear activation - 최종적으로 original input spectrogram과 reconstruction 간의 Mean Squared Error (MSE)는 masked patch에 대해서만 compute 되어 pre-training을 위한 loss로 사용됨
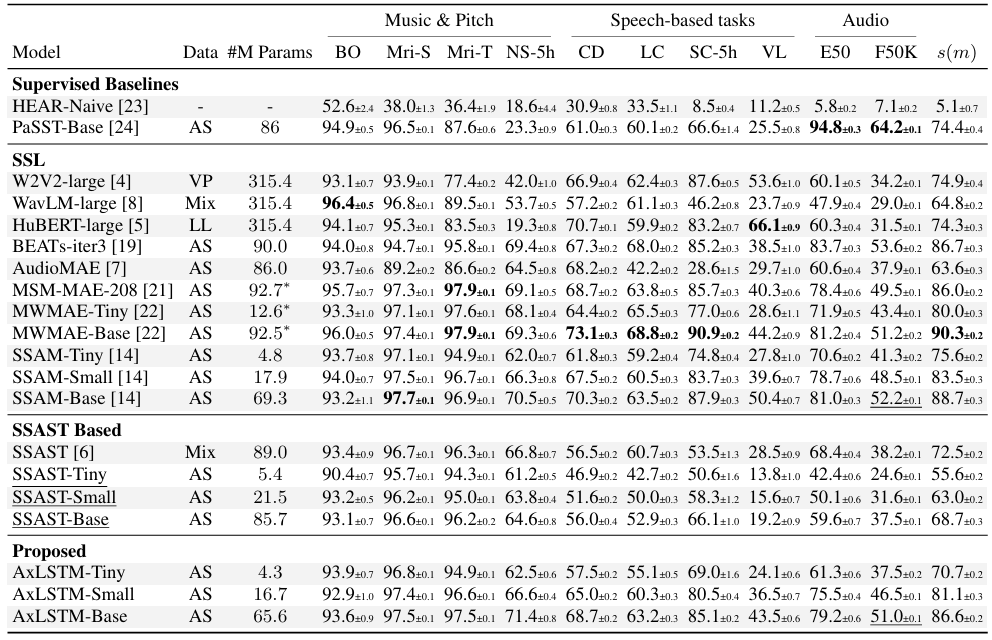
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : AudioSet
- Comparisons : Wav2Vec 2.0, WavLM, HuBERT, BEATs 등

- Results
- 전체적으로 AxLSTM은 각 downstream task에서 우수한 성능을 달성함
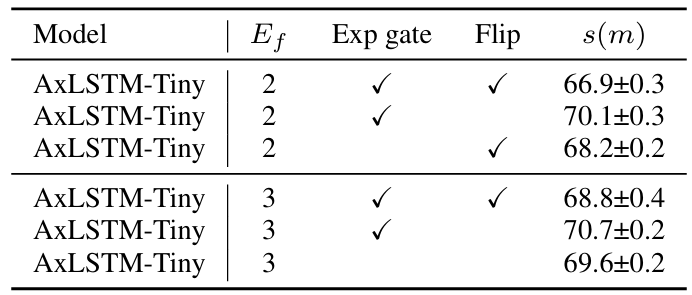
- Ablation Study
- Expansion factor $E_{f}=3$으로 설정했을 때 최적의 성능을 달성함

- Tiny model에서는 $(4,8)$의 patch size를 사용했을 때 뛰어난 성능을 보임

- Bidirectional modeling 보다 gating mechanism이 더 효과적임
반응형
'Paper > Representation' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

