티스토리 뷰
Paper/Representation
[Paper 리뷰] EmotionRankCLAP: Bridging Natural Language Speaking Styles and Ordinal Speech Emotion via Rank-N-Contrast
feVeRin 2025. 9. 15. 17:02반응형
EmotionRankCLAP: Bridging Natural Language Speaking Styles and Ordinal Speech Emotion via Rank-N-Contrast
- Contrastive Language Audio Pre-training은 emotion의 ordinal nature를 capture 하지 못하고 audio, text embedding 간의 insufficient alignment가 나타남
- EmotionRankCLAP
- Emotional speech와 natural language prompt의 dimensional attribute를 활용하여 fine-grained emotion variation을 jointly capture
- Rank-N-Contrast objective를 활용하여 valence-arousal space를 기반으로 sample 간의 ordered relationship을 학습
- 논문 (INTERSPEECH 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Emotion은 ordinal nature를 가지고 인간은 absolute emotional state를 identifying 하는 것보다 relative change를 detecting 하는데 익숙함
- BUT, 기존 paralinguistic model은 dimensional attribute annotation에 의존하므로 emotional expression의 nuanced nature를 fully represent 하기 어려움
- 이때 natural language description을 활용하면 fine-grained, ordinal nature를 effectively capture 할 수 있음
- 대표적으로 Contrastive Language Audio Pre-training (CLAP)은 natural language supervision을 활용하여 audio, speech understanding을 크게 향상함
- 해당 CLAP representation은 Speech Emotion Recognition (SER), Emotional Text-to-Speech (TTS), Emotional Audio Retrieval (EAR) 등의 task에서 주로 활용됨
- BUT, CLAP은 categorical emotion에 제한되어 있으므로 intra-class variability가 overlook 됨
- 대표적으로 Contrastive Language Audio Pre-training (CLAP)은 natural language supervision을 활용하여 audio, speech understanding을 크게 향상함
- 특히 CLAP의 diagonal-constraint-based Symmetric Cross-Entropy (SCE) loss는 다음의 단점이 있음:
- Batch-level에서 SCE loss는 modality 간의 inter-emotion relationship을 capture 하지 못함
- Emotion-based CLAP model은 text, audio embedding 간의 modality gap이 발생함
-> 그래서 ordered emotion을 더 효과적으로 학습할 수 있는 EmotionRankCLAP을 제안
- EmotionRankCLAP
- Natural language prompt의 supervised setting을 활용하여 modality gap을 완화
- Rank-N-Contrast objective를 도입하여 target label space 내에서 sample position을 ranking 하여 ordered representation을 학습
< Overall of EmotionRankCLAP >
- Emotion의 ordered nature를 capture 하는 CLAP-based audio representation model
- 결과적으로 emotion-downstream task에서 기존보다 우수한 성능을 달성
2. Method
- EmotionRankCLAP은 Rank-N-Contrast learning objective를 활용하여 speech emotion의 ordinal nature를 반영함
- Problem Formulation
- $i\in\{1,...,N\}$에 대해 $\{X_{i}^{a},X_{i}^{t}\}$를 $\text{<speech, text>}$의 pair라고 하자
- Audio, text modality의 input은 2개의 separate encoder $f^{a}(\cdot), f^{t}(\cdot)$을 통해 encoding 되어 embedding을 생성함:
(Eq. 1) $\hat{X}_{i}^{a}=f^{a}(X_{i}^{a});\,\,\, \hat{X}_{i}^{t}=f^{t}(X_{i}^{t})$|
- $\hat{X}^{a}\in\mathbb{R}^{N\times V}, \hat{X}^{t}\in\mathbb{R}^{N\times U}$ - 논문은 audio encoder $f^{a}(\cdot)$으로 pre-trained WavLM-based dimensional SER model을 사용함
- 이때 last Transformer layer에서 temporal dimension을 따라 attentive statistics pooling을 통해 1024-dimensional embedding을 추출함
- Text encoder $f^{t}(\cdot)$은 pre-trained DistilRoBERTa model을 사용하고 final layer $\text{[CLS]}$ token을 768-dimensional embedding으로 사용함
- 이후 해당 representation은 same dimension $D=512$로 project 됨:
(Eq. 2) $\hat{E}_{i}^{a}=\text{proj}^{a}(\hat{X}_{i}^{a});\,\,\,\hat{E}_{i}^{t}=\text{proj}^{t}(\hat{X}_{i}^{t})$
- $\hat{E}^{a},\hat{E}^{t}\in\mathbb{R}^{N\times D}$ : projected embedding
- $\text{proj}^{a},\text{proj}^{t}$ : ReLU activation을 가지는 linear transformation
- 결과적으로 EmotionRankCLAP은 emotion의 dimensional nature를 capture 하기 위해, ordinality를 preserving 하면서 2개의 modality를 same embeding space로 align 함
- Audio, text modality의 input은 2개의 separate encoder $f^{a}(\cdot), f^{t}(\cdot)$을 통해 encoding 되어 embedding을 생성함:
- Supervised Contrastive Learning with Rank-N-Contrast
- Emotion은 inherently continuous, ordinal 하므로 emotional speech와 해당 speaking style description 간에는 structured relationship이 존재함
- 이때 structured relationship은 각 possible pair에 대해 $N\times N$ cross-modal pair를 가질 수 있음
- 따라서 논문은 해당 structured relationship을 학습하기 위해 Rank-N-Constrast를 채택하여 valence-arousal label space의 ranking에 따라 sample을 contrast 함 - 논문은 label space에서 valence, arousal의 ordinality를 jointly modeling 함
- 여기서 valence는 utterance에서 express 된 sentiment를 reflect 하고 arousal은 activation의 level을 indicate 함 - Audio embedding anchor $\hat{E}_{i}^{a}$가 주어지면, text embedding $\hat{E}_{j}^{t}$에 대한 likelihood는 valence-arousal space 내에서 label 간의 relative distance의 영향을 받음
- Emotional distance는 $(\text{valence}_{i}^{a},\text{arousal}_{i}^{a}), (\text{valence}_{j}^{t},\text{arousal}_{j}^{t})$ 간의 $L2$ distance로 assess 됨
- $i,j$ : sample index - 이때 closer sample일수록 similar 한 emotion으로 취급함
- Emotional distance는 $(\text{valence}_{i}^{a},\text{arousal}_{i}^{a}), (\text{valence}_{j}^{t},\text{arousal}_{j}^{t})$ 간의 $L2$ distance로 assess 됨
- $ S_{i,j}:=\left\{\hat{E}_{k}^{t}|d\left(\hat{E}_{i}^{a},\hat{E}_{k}^{t}\right) >d\left(\hat{E}_{i}^{a},\hat{E}_{j}^{t}\right)\right\}$를 $\hat{E}_{i}^{a}$의 label distance에 대해 $\hat{E}_{j}^{t}$ 보다 높은 rank를 가지는 text embedding의 set이라고 하자
- 여기서 $d(\cdot, \cdot)$는 valence-arousal plane에서 두 label 간의 $L2$ distance를 의미함
- 그러면 $\hat{E}_{i}^{a}, S_{i,j}$가 주어졌을 때 $\hat{E}_{j}^{t}$의 normalized likelihood는:
(Eq. 3) $P\left(\hat{E}_{j}^{t}|\hat{E}_{i}^{a},S_{i,j}\right)=\frac{\exp\left( \text{sim}\left( \hat{E}_{i}^{a},\hat{E}_{j}^{t}\right)/\tau\right)}{\sum_{\hat{E}_{k}^{t}\in S_{i,j}}\exp\left( \text{sim}\left(\hat{E}_{i}^{a},\hat{E}_{k}^{t}\right)/\tau\right)}$
- $S_{i,j}$ : $\hat{E}_{i}^{a},\hat{E}_{j}^{t}$에 대한 ranking condition을 만족하는 모든 $\hat{E}_{k}^{t}$의 set - 해당 set는 positive pair $\hat{E}_{i}^{a},\hat{E}_{j}^{t}$에 대한 negative pair를 contain 하고, similarity function $\text{sim}(x,y)=\frac{x^{\top}y}{||x||\cdot||y||}$는 cross-modal feature 간의 cosine-similarity를 calculate 함
- $\tau$ : temperature parameter
- 결과적으로 batch의 모든 sample에 대해 해당 objective를 정의하면 Rank-N-Contrast cross-modal loss를 얻을 수 있음:
(Eq. 4) $\mathcal{L}_{RNC\text{-}CM}=\frac{1}{N^{2}}\sum_{i=1}^{N}\sum_{j=1}^{N}-\log P\left(\hat{E}_{j}^{t}|\hat{E}_{i}^{a},S_{i,j}\right)$
- $\mathcal{L}_{RNC\text{-}CM}$은 valence-arousal label space의 continuous structure를 활용함
- 이를 통해 emotional speech sample과 similar valence-arousal value를 가지는 speaking style description이 learned representation space 내에서도 close 하도록 보장할 수 있음 - Rank-N-Contrast formulation은 ranking criterion을 기반으로 positive-negative pair를 형성하기 위해 batch 내에서 모든 $N\times N$ speech-text pair를 사용하여 cross-modal alignment를 개선함
- 각 positive pair는 similarity rank에 따라 negative pair를 assign 하여 structured contrastive learning을 보장함
- 이때 structured relationship은 각 possible pair에 대해 $N\times N$ cross-modal pair를 가질 수 있음

- Illustrative Example of Positive/Negative Pair Selection
- 논문은 위 그림의 (a)와 같이 valence-arousal annotation이 있는 3개의 speech-text pair $(X_{i}^{a},X_{i}^{t}),\,\,(i\in\{1,2,3\})$의 batch를 고려함
- 이때 positive/negative pair selection을 위해 first speech utterance $X_{1}^{a}$를 anchor로 설정함
- 그러면 위 그림의 (b)와 같이 2개의 positive pair와 해당 negative pair를 얻을 수 있음 - Pair $(X_{a}^{1},X_{1}^{t})$가 positive라고 하면, 두 pair 모두 same label을 share 하므로 $d(X_{1}^{a},X_{1}^{t})=0$과 같음
- 이는 $X_{2}^{t}, X_{3}^{t}$가 negative sample이 되도록 만듦
- $d(X_{1}^{a},X_{2}^{t})>0, d(X_{1}^{a},X_{3}^{t})>0$이기 때문 - 마찬가지로 $X_{2}^{t}$가 $X_{1}^{a}$와 positive pair를 구성하면, $X_{3}^{t}$는 negative가 됨
- $d(X_{1}^{a},X_{3}^{t})>d(X_{1}^{a},X_{2}^{t})$이기 때문
- 이때 $X_{1}^{t}$는 $d(X_{1}^{a},X_{1}^{t})<d(X_{1}^{a},X_{2}^{t})$이므로 negative sample이 아님
- 이는 $X_{2}^{t}, X_{3}^{t}$가 negative sample이 되도록 만듦
- 즉, closer positive pair는 negative sample이 많아지므로 closeness가 reinforce 되고 distant positive pair는 negative sample이 적어지므로 attraction이 줄어들어 structured relationship이 형성됨
- 결과적으로 논문은 $N$ batch에 대해, $i=1,...,N$에서 각 $X_{i}^{a}$를 iterate 하여 anchor 당 $N$ relation을 구성하고, $N\times N$의 structured relationship을 얻음
- 이때 positive/negative pair selection을 위해 first speech utterance $X_{1}^{a}$를 anchor로 설정함
- Generation of Speaking Style Descriptions
- 기존의 speech emotion dataset은 emotion recognition을 위해 설계되어 categorical label과 dimensional attribute 측면에서 annotation을 제공함
- 한편으로 speech emotion captioning에서는 annotated speaking style description을 포함한 dataset이 적음
- 이를 위해 논문은 아래와 같은 prompt를 적용한 LLM을 활용해, valence, arousal을 기반으로 pseudo-caption을 생성함

3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : MSP-Podcast
- Comparisons : CLAP, CLAP4Emo, CLAP-SCE, SupConCLAP, ParaCLAP

- Results
- 전체적으로 EmotionRankCLAP을 사용하면 더 나은 retrieval 성능을 달성할 수 있음

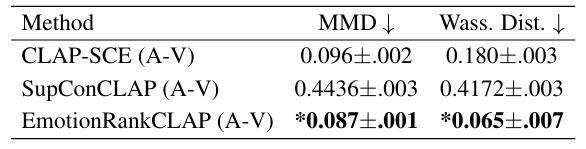
- Cross-modal alignment 측면에서도 우수한 성능을 보임
반응형
'Paper > Representation' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

