티스토리 뷰
Paper/Conversion
[Paper 리뷰] StreamVC: Real-Time Low-Latency Voice Conversion
feVeRin 2024. 8. 27. 09:11반응형
StreamVC: Real-Time Low-Latency Voice Conversion
- Lightweight, high-quality conversion을 지원하는 streaming voice conversion 모델이 필요함
- StreamVC
- SoundStream의 neural audio codec architecture를 활용
- Soft speech unit을 causal 하게 학습하고 pitch stability를 향상하기 위해 whitened fundamental frequency information을 제공
- 논문 (ICASSP 2024) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Voice Conversion (VC)는 linguistic content를 preserve 하면서 speech signal의 style을 변경하는 것을 목표로 함
- 기존에는 CycleGAN-VC, StarGAN-VC와 같은 direct conversion이나 AutoVC, AdaIN-VC와 같은 feature disentanglement에 기반한 auto-encoding 방식이 사용됨
- BUT, noticeable artifact가 발생하고 tuning 하기 어려운 information bottleneck에 의존한다는 한계가 있음 - 한편으로 FreeVC와 같이 speech recognition system이나 pretrained feature extraction network를 활용할 수도 있음
- BUT, non-causal multi-layer transformer network로 인해 computationally expensive 함
- 기존에는 CycleGAN-VC, StarGAN-VC와 같은 direct conversion이나 AutoVC, AdaIN-VC와 같은 feature disentanglement에 기반한 auto-encoding 방식이 사용됨
-> 그래서 low-latency, lightweight VC를 위한 StreamVC를 제안
- StreamVC
- Lightweight, causal convolution network를 활용하여 soft speech unit information을 capture
- SoundStream의 architecture와 training strategy를 채택하여 on-device, low-latency streaming inference를 지원
- Source speaker timbre를 leaking 하지 않고 pitch consistency를 개선할 수 있는 whitened fundamental frequency $f_{0}$를 도입
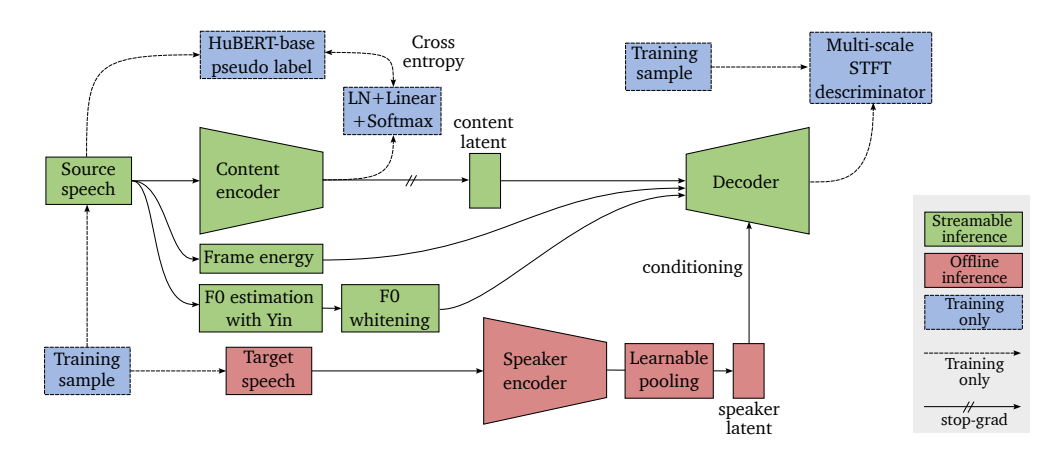
< Overall of StreamVC >
- Soft speech unit과 SoundStream architecture를 활용한 lightweight VC model
- 결과적으로 Pixel 7 스마트폰에서 동작하면서 합리적인 conversion 성능을 달성
2. Method
- Motivation
- StreamVC는 SoftVC와 SoundStream을 기반으로 함
- 먼저 SoftVC는 HuBERT에서 추출된 discrete speech unit을 content encoder network의 prediction target으로 사용함
- 이때 pretrained HuBERT를 사용하여 frame 당 pseudo-label을 derive 하여 content encoder의 학습을 지원
- Last layer activation에서는 logistic projection을 통해 speech content를 latent soft speech unit으로 represent 하여 decoder로 전달함 - Content encoder와 decoder는 SoundStream의 training strategy와 architecture를 따름
- 먼저 SoftVC는 HuBERT에서 추출된 discrete speech unit을 content encoder network의 prediction target으로 사용함
- Model Architecture
- Content Encoder
- Content encoder는 convolutional arhchitecture로 $C=64$의 scale, $D=64$ embedding dimension을 가지는 SoudnStream encoder를 따름
- 이때 conditioning을 적용하지 않으므로 Feature-wise Linear Modulation (FiLM) layer는 사용되지 않음
- Speaker Encoder
- Speaker enoder는 per-frame encoding part와 global (utterance-level) context aggregator로 구성됨
- 이때 per-frame encoding part에서는 $C=32$ scale, $D=64$ embedding dimension을 가지는 SoundStream encoder를 reuse함
- 해당 per-frame context embedding은 learnable pooling을 통해 single global context로 aggregate 됨 - Learnable pooling은 single learnabel query가 있는 attention mechanism으로부터 weight가 derive 된 average pooling을 의미
- Fundamental Frequency and Energy Estimation
- Decoder에 HuBERT의 soft speech unit embedding만 제공하면 flattened pitch envelope를 가지는 음성이 생성됨
- 특히 tonal, acoustic energy information은 phonetic unit discrimination에 존재하지 않으므로, content encoder output 외에도 해당 signal을 decoder에 제공할 수 있어야 함 - 따라서 pitch에 해당하는 $f_{0}$ estimation을 위해 논문은 Yin algorithm을 채택함
- 이때 $f_{0}$ estimation 외에도, 해당 algorithm으로 얻어지는 cumulative mean normalized difference value와 estimated unvoiced signal predicate를 사용
- 이후 $f_{0}$ esitmation에 대한 uncertainty information을 convey 하기 위해 Yin algorithm output을 3가지의 threshold $0.05, 0.1, 0.15$와 concatenate 함
- 이를 통해 channel dimension에서 content latent와 concatenate 된 20ms 당 9개의 value가 생성됨
- 한편으로 decoder에 speaker timbre parameter가 제공되지 않도록 utterance-level mean, standard deviation을 기반으로 $f_{0}$ envelope를 normalize 함
- Streaming inference 중에는 causality를 위해 해당 parameter의 running average를 사용 - 추가적으로 $f_{0}$ information 외에도 sample variance를 통해 얻어진 20ms audio frame energy를 decoder에 대한 side information으로 제공
- Decoder에 HuBERT의 soft speech unit embedding만 제공하면 flattened pitch envelope를 가지는 음성이 생성됨
- Decoder
- SoundStream의 decoder를 따르고 $C=40$의 scale과 $D=64$의 embedding dimensionality를 사용함
- FiLM layer는 residual unit 사이에서 speaker latent embedding form으로 conditioning signal을 integrate 하기 위해 사용됨
- 이때 Speaker latent를 input으로 하는 2개의 separate linear layer에서 계산된 scale, bias parameter를 활용하여 neural network feature를 transform 함
- Training Strategy
- Soft-Label Creation and Content Encoder Training
- Content encoder training을 위한 soft speech unit을 얻기 위해 SoftVC를 활용함
- 먼저 pretrained HuBERT에서 7-th transformer layer의 activation을 추출하고
- Mini-batch $k$-means clustering을 적용하여 nearest-centroid vector quantization에 사용되는 100개의 centroid를 찾음
- 이후 50Hz frequency에서 content encoder에 대한 learning target으로 100-class pseudo-label을 정의
- 추가적으로 decoder에서 content encoder로의 gradient flow를 방지함
- 이를 통해 content latent embedding을 통해 additional speaker information을 leaking 하지 않도록 함
- Content encoder training을 위한 soft speech unit을 얻기 위해 SoftVC를 활용함
- Training Loss
- HuBERT pseudo-label prediction에서 content encoder latent projection을 위해 adversarial loss, reconstruction loss, cross-entropy loss를 도입
- 해당 loss는 SoundStream과 MelGAN을 따름
- Real-Time Inference
- Streaming Inference
- 논문은 online inference를 위해 streaming-aware convolution module을 도입함
- StreamVC의 모든 convolution layer는 causal 하지만, limited lookahead가 있는 strided, transposed convolution으로 인해 architecutral latency가 발생하기 때문 - 특히 content latent의 temporal resolution이 audio보다 320배 더 coarser 하므로, 최소 inference frame size는 320 sample가 됨
- 이는 16kHz에서 sample 된 20ms audio에 해당하고, network inference는 50Hz의 rate로 trigger 됨
- 논문은 online inference를 위해 streaming-aware convolution module을 도입함
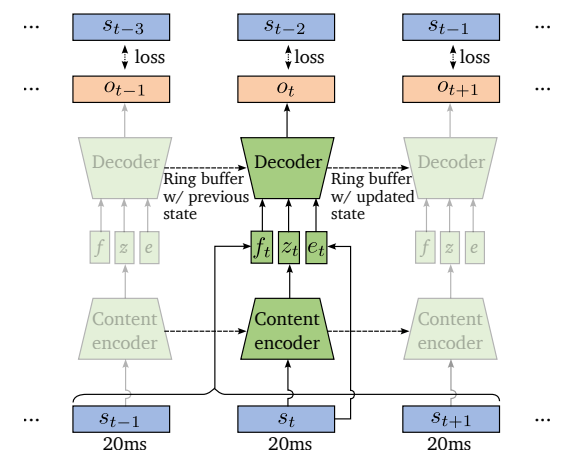
- Lookahead and Architectural Latency
- 아래 그림과 같이 loss computation을 위해 output frame $o_{t}$와 input frame $s_{t-2}$를 pairing 하여 2-frame lookahead를 도입함
- 그러면 time step $t$에서 decoder로 전달된 $f_{0}$ information $f_{t}$는 세 frame $(s_{t-1},s_{t},s_{t+1})$에 span 되어 있는 context window로 계산됨
- 이는 time step $t+1$까지의 input이 time step $t-2$에 대한 output을 계산하는데 필요하다는 것을 의미하므로, 60ms의 architectural latency와 같음
- Computational Latency
- 논문은 inference latency를 profile 하기 위해 XNNPACK을 활용함
- 일반적으로 Pixel 7 스마트폰의 single CPU core에서 content encoder와 decoder를 running 하면 20ms audio chunk 당 10.8ms가 소요됨
- 전체 pipeline을 streaming 방식으로 continuously running 하면, end-to-end inference latency는 70.8ms로 얻어짐
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : LibriTTS
- Comparisons : Diff-VCTK, BNE-PPG-VC, VQMIVC, QuickVC
- Results
- StreamVC는 Pixel 7 스마트폰에서 70.8ms의 latency를 달성하면서 우수한 합성 성능을 유지함

반응형
'Paper > Conversion' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

