티스토리 뷰
Paper/Representation
[Paper 리뷰] UniSpeech-SAT: Universal Speech Representation Learning with Speaker Aware Pre-Training
feVeRin 2026. 1. 22. 12:41반응형
UniSpeech-SAT: Universal Speech Representation Learning with Speaker Aware Pre-Training
- Speaker characteristic modeling을 위해 Self-Supervised Learning을 활용할 수 있음
- UniSpeech-SAT
- Multi-task learning을 도입하여 utterance-wise contrastive loss를 Self-Supervised Learning objective와 integrate
- Utterance mixing strategy 기반의 data augmentation을 수행
- 논문 (ICASSP 2022) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Self-Supervised Learning (SSL)은 large-scale unlabeled data를 사용하여 universal representation을 학습할 수 있음
- 해당 representation은 뛰어난 generalizability, re-usability, effectiveness를 가지고 다양한 downstream task의 성능을 효과적으로 향상할 수 있음
- 대표적으로 Wav2Vec 2.0, HuBERT와 같은 SSL model은 Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) task에서 최고의 성능을 달성함 - BUT, 대부분의 speech SSL model은 spoken content information을 추출하는 것을 목표로 하므로 speech signal의 multi-fold information을 반영하지 못함
- 해당 representation은 뛰어난 generalizability, re-usability, effectiveness를 가지고 다양한 downstream task의 성능을 효과적으로 향상할 수 있음
-> 그래서 speaker-aware information을 추출할 수 있는 UniSpeech-SAT를 제안
- UniSpeech-SAT
- Utterance-wise contrastive loss를 integrate 하여 single-speaker information 추출을 개선
- Utterance mixing strategy를 통해 multi-speaker modeling을 향상
< Overall of UniSpeech-SAT >
- Utterance-wise contrastive loss, Utterance mixing을 활용한 SSL model
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 성능을 달성
2. Background
- HuBERT는 iterative clustering을 통해 representation을 학습함
- 먼저 HuBERT는 input signal의 MFCC를 기반으로 offline clustering을 수행하고, 각 frame의 cluster center를 pseudo-label로 indexing 함
- 이후 CNN feature extractor를 가지는 Transformer를 MFCC, pseudo-label을 기반으로 training 하여 first iteration의 representation을 얻음
- 이때 mask prediction loss를 training criteria로 채택하여 network가 input sequence에서 masked region의 pseudo-label을 predict 하도록 함
- 즉, $T$ feature frame의 speech utterance가 주어지면 해당 label은 $Z=\{z_{t}\}_{t=1}^{T}$와 같고, feature sequence $X=\{x_{t}\}_{t=1}^{T}$는 CNN Encoder를 통해 utterance로부터 추출됨 - $\{t\}_{t=1}^{T}$의 masked index set을 $M\subset \{t\}_{t=1}^{T}$, $\tilde{X}=r(X,M)$을 $t\in M$일 때 $x_{t}$가 random-initialized mask embedding $\tilde{x}_{t}$로 replace 된 corrupted $X$라고 하자
- 그러면 Transformer $f(\cdot)$은 corrupted feature sequence $\tilde{X}$가 주어졌을 때, 각 label에 해당하는 masked index $\{z_{t}|z_{t}\in Z, t\in M\}$을 Cross-Entropy loss를 통해 predict 하도록 training 됨:
(Eq. 1) $\mathcal{L}_{content} =\sum_{t\in M}\log f(z_{t}|\tilde{X},t)$
- 이때 mask prediction loss를 training criteria로 채택하여 network가 input sequence에서 masked region의 pseudo-label을 predict 하도록 함
- Second iteration부터는 MFCC feature 대신 이전 iteration의 generated embedding을 input으로 사용함
3. Method
- UniSpeech-SAT는 HuBERT를 기반으로 utterance-wise contrastive learning과 utterance mixing augmentation을 도입함
- Utterance-wise contrastive learning은 single speaker information 추출을 향상하여 speaker verification, speaker identification과 같은 downstream task를 개선함
- Utterance mixing augmentation은 speech diarization과 같은 multi-speaker task를 개선함
- Utterance-wise Contrastive Learning
- 논문은 unsupervised speaker information modeling을 향상하기 위해 utterance-wise contrastive loss를 도입함
- Contrastive loss에서는 utterance 내의 embedding을 positive instance로 취급하고 동일 batch의 다른 utterance embedding을 negative instance로 취급함
- Batch size $B$에 대해 input feature sequence를 $\{\tilde{X}^{b}\}_{b=1}^{B}$라고 하자
- 그러면 $\forall \tilde{X}^{b}$에 대해 intermediate Transformer encoder layer output으로부터 latent representation $L^{b}=\{l_{t}^{b}\}_{t=1}^{T}$를 얻을 수 있음
- 이후 latent representation $L^{b}$를 quantization module을 통해 speech representation의 finite set $Q^{b}=\{q_{t}^{b}\}_{t=1}^{T}$로 discretize 함
- Quantization module이 $V$ entry의 $G$ codebook을 가진다고 하면,
- 각 latent representation $l$을 logit $l'\in\mathbb{R}^{G\times V}$로 linear transform 하고 Gumbel Softmax를 사용하여 각 codebook에서 하나의 discrete entry $e$를 choice 할 수 있음
- 이때 $g$-th codebook에서 $v$-th entry를 choice할 probability는:
(Eq. 2) $ p_{g,v}=\frac{\exp(l'_{g,v}+n_{v})/\tau}{\sum_{k=1}^{V}\exp(l'_{g,v}+n_{k})/\tau}$
- $\tau$ : non-negative temperature
- $n_{u}=-\log (-\log(u))$이고 $u$는 $\mathcal{U}(0,1)$에서 uniformly sampling 되는 값 - 이후 selected vector를 $[e_{1},...,e_{G}]$와 같이 concatenate 하고 quantized representation $q$로 linear transform 함
- $b$-th utterance에서 mask step $t$를 중심으로 한 latent representation $l_{t}^{b}$에 대해, model은 동일한 utterance $\hat{Q}^{b}=\{q_{t}^{b}|q_{t}^{b}\in Q^{b}, t\in M^{b}\}$의 true quantized representation을
- Training batch 내의 모든 utterance의 masked time step에서 uniformly sample 된 quantized candidate representation set $\hat{Q}=\cup_{b=1}^{B}\hat{Q}^{b}$에서 identify 하도록 training 됨
- 그러면 $l_{t}^{b}, \hat{Q}$ 간의 utterance-wise contrastive loss는:
(Eq. 3) $\mathcal{L}_{contrastive}=\sum_{q_{t}^{b}\in\hat{Q}^{b}}\log \frac{\exp(\text{sim}(l_{t}^{b},q_{t}^{b})/\kappa)}{\exp(\text{sim}(l_{t}^{b},q_{t}^{b})/\kappa )+1} - \sum_{q_{t}^{b}\sim\hat{Q}\backslash\hat{Q}^{b}}\log \frac{1}{\exp(\text{sim}(l_{t}^{b}, q_{t}^{b})/\kappa)+1}$
- $\text{sim}(a,b) = a^{\top}b/||a||\,||b||$ : cosine similarity - 이후 utterance-wise contrastive loss는 모든 codebook entry를 equally use 하기 위해 codebook diversity loss로 augment 됨:
(Eq. 4) $\mathcal{L}_{d}=\frac{1}{GV}\sum_{g=1}^{G}\sum_{v=1}^{V}\bar{p}_{g,v}\log\bar{p}_{g,v}$
- $\bar{p}_{g,v}$ : utterance batch에 대한 averaged $p_{g,v}$
- 결과적으로 speaker informaiton modeling은 다음과 같이 정의됨:
(Eq. 5) $\mathcal{L}_{speaker}=\mathcal{L}_{contrastive}+\alpha\mathcal{L}_{d}$
- $\alpha$ : hyperparameter - 이를 기반으로 UniSpeech-SAT는 speaker loss와 content loss의 combination을 통해 training 됨:
(Eq. 6) $\mathcal{L}=\mathcal{L}_{speaker}+\beta\mathcal{L}_{content}$
- $\beta$ : hyperparameter

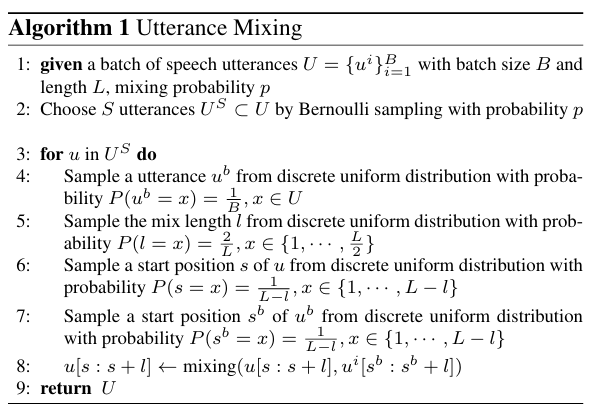
- Utterance Mixing Augmentation
- 논문은 speaker diarization과 같은 multi-speaker task에서 speaker information modeling을 향상하기 위해 utterance mixing strategy를 도입함
- 여기서 utterance mixing은 single-speaker pre-training data만 주어지는 경우에도 self-supervised pre-training을 위해 multi-speaker speech를 simulate 하는 것을 목표로 함
- 먼저 batch size $B$의 speech utterance batch $U=\{u^{i}\}_{i=1}^{B}$가 주어지면, batch에서 $S$ utterance $\{u^{i}\}_{i=1}^{S}$를 randomly select 함
- 이후 각 utterance $u$에 대해 batch에서 utterance $u^{b}\in U$를 randomly select 하고 $u^{b}$의 random length chunk를 crop 하여 $u$의 random region과 mix 함
- 이를 기반으로 model은 single-speaker information loss를 사용해 mixed audio에서 main speaker information을 추출하고, content modeling loss를 통해 main speaker에 해당하는 content information을 학습함
- 이때 각 utterance에서 mixing portion은 $50\%$ 이하로 constrain 하여 label permutation 문제를 방지함
- Large and Diverse Pre-training Data
- 논문은 model의 robustness를 향상하기 위해 large-scale unsupervised data를 활용함
- 이를 위해 다음의 dataset을 고려할 수 있음:
- GigaSpeech (10K hours)
- VoxPopuli (24K hours)
- 결과적으로 논문은 LibriVox, VoxPopuli, GigaSpeech를 포함한 94,000 hours의 dataset을 사용함
- 이를 위해 다음의 dataset을 고려할 수 있음:
4. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : LibriVox, VoxPopuli, GigaSpeech
- Comparisons : Wav2Vec, Wav2Vec 2.0, VQ-Wav2Vec, HuBERT 등
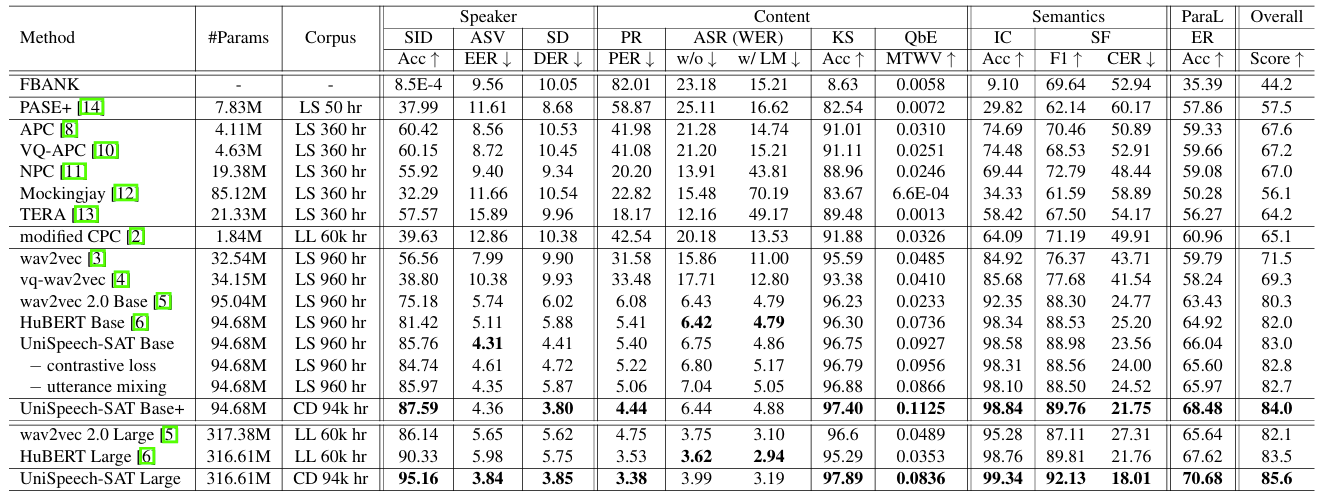
- Results
- 전체적으로 UniSpeech-SAT의 성능이 가장 우수함
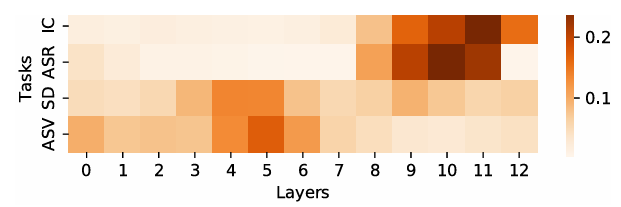
- Weight Analysis
- Speaker verification, diarization의 경우 lower layer가 더 많이 contribute 하고 ASR, intent classification의 경우 higher layer가 contribute 함
- Mixing Ratio
- $20\%$의 mixing ratio를 사용했을 때 최적의 trade-off를 달성함

반응형
'Paper > Representation' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

