티스토리 뷰
Paper/Representation
[Paper 리뷰] UniSpeech: Unified Speech Representation Learning with Labeled and Unlabeled Data
feVeRin 2026. 1. 19. 12:49반응형
UniSpeech: Unified Speech Representation Learning with Labeled and Unlabeled Data
- Speech representation learning을 위해 labeled, unlabeled data를 모두 활용할 수 있음
- UniSpeech
- Supervised phonetic CTC learning과 phonetically-aware contrastive self-supervised learning을 활용
- Resultant representation은 phonetic structure를 capture 하여 language, domain에 대한 generalization을 향상
- 논문 (ICML 2021) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) system은 다양한 language 뿐만 아니라 rich-resource language에서도 noisy, distortion condition과 같은 specific domain의 training data가 부족함
- 이를 위해 Wav2Vec 2.0과 같은 self-supervised method를 활용할 수 있지만 model이 speech에 대한 most valuable information을 학습한다는 보장이 없음
- 특히 model은 다양한 language, domain에서도 phonetic identity를 효과적으로 caputre 할 수 있는 robust representation을 학습해야 함
- 결과적으로 이를 기반으로 limited labeled data에서도 acceptable performance를 달성할 수 있음
-> 그래서 다양한 language, domain에서 phonetically-aware contextual representation을 학습할 수 있는 UniSpeech를 제안
- UniSpeech
- Wav2Vec 2.0을 기반으로 labeled high-resource data, unlabeled low-resource data로 model을 pre-training 한 다음, feature extractor를 freeze 하고 labeled low-resource data에 대해 fine-tuning을 수행
- 특히 pre-training 시에는 multitask learning manner를 사용하여 phonetic-aware codebook을 학습
< Overall of UniSpeech >
- Labeled, unlabeled data를 활용하여 multitask learning을 수행한 unified speech representation model
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 성능을 달성
2. Method
- Problem Formulation
- High-resource setting에서 $I$ dataset이 있다고 하면, $\mathbb{L}=\{(\mathbf{X}_{1}^{L},\mathbf{Y}_{1}^{L}),...,(\mathbf{X}_{I}^{L},\mathbf{Y}_{I}^{L})\}$과 같이 나타낼 수 있음
- 이때 각 datset은 large scale audio-text pair $(\mathbf{x},\mathbf{y})$를 포함함
- Evaluation을 위한 $J$ low-resource language/domain은 각각 large unlabeled dataset $\mathbb{M}=\{(\mathbf{X}_{1}^{M}),...,(\mathbf{X}_{J}^{M})\}$과 small labeled dataset $\mathbb{N}=\{(\mathbf{X}_{1}^{N},\mathbf{Y}_{1}^{N}),...,(\mathbf{X}_{J}^{N},\mathbf{Y}_{J}^{N})\}$을 가짐
- UniSpeech는 accessible large dataset $\mathbb{L},\mathbb{M}$을 활용해 robust representation을 학습한 다음, $\mathbb{N}$을 통해 fine-tuning 하여 low-resource setting에서 ASR 성능을 향상하는 것을 목표로 함
- Model Structure
- UniSpeech는 Wav2Vec 2.0 architecture를 따라 convolutional feature encoder, Transformer context encoder, vector quantizer로 구성됨
- 먼저 convolutional feature encoder $\mathcal{X}\rightarrow \mathcal{Z}$는 raw audio $\mathbf{x}$를 latent space $\mathcal{Z}$로 mapping 함
- 구조적으로는 layer normalization과 GELU activation을 포함한 7 temporal convolutional block으로 구성됨 - 이후 representation $z_{1},..., z_{T}$는 Transformer network $\mathcal {Z}\rightarrow \mathcal{C}$에 전달되어 context representation $c_{1},...,c_{T}$를 output 함
- Latent representation의 information bottleneck으로 사용되는 quantizer module $\mathcal{Z}\rightarrow \mathcal {Q}$는 $z_{i}$를 finite speech representation set $q_{i}$로 discretize 함
- 이때 quantizer는 $G=2$ codebook과 $V=320$ entry를 가짐
- 결과적으로 각 frame에 대해 두 codebook에서 두 entry를 independently select 하여 quantized representation $q$를 얻어, 총 $320^{2}$의 codeword를 생성함
- 먼저 convolutional feature encoder $\mathcal{X}\rightarrow \mathcal{Z}$는 raw audio $\mathbf{x}$를 latent space $\mathcal{Z}$로 mapping 함

- Multitask Learning with Unified Representation
- 논문은 각 frame의 representation이 meaningful phonetic unit에 해당하고, representaiton이 target domain의 ASR task에 easily adpot 되는 것을 목표로 함
- 이를 위해 논문은 unified representation에 대한 multitask learning method를 도입함
- 특히 pre-training stage에서는 high-resource labeled dataset $\mathbb{L}$과 low-resource dataset $\mathbb{M}$을 활용해 model을 jointly training 함 - Training objecitve은 3가지로 구성됨:
- Dataset $\mathbb{L}$에 대한 Phonetic CTC loss $\mathcal{L}_{ctc}$
- Contextual representation을 phonetic unit과 align 하는 역할 - Dataset $\mathbb{L}$에 대한 Contrastive loss $\mathcal{L}_{c}$
- Representation $c$와 discrete feature $q$ 간의 distance를 줄여 phonetically-aware codebook을 생성하는 역할 - Dataset $\mathbb{M}$에 대한 Contrastive loss
- Model을 target language/domain에 adapt 하는 역할
- Dataset $\mathbb{L}$에 대한 Phonetic CTC loss $\mathcal{L}_{ctc}$
- Data pair $(\mathbf{x},\mathbf{y})$에 대해 UniSpeech는 context representation $c_{1},...,c_{T}$를 학습함
- 이때 phoneme token, blank token과 같은 observed label에 대한 distribution을 predict 하기 위해 softmax를 포함한 linear layer를 추가하여 $p(\pi|c_{1},...,c_{T})$를 얻음
- $\pi$는 legal CTC path로써 blank token/repetition의 occurrence를 allow 하는 transcription $\mathbf{y}$의 variaiton과 같음 - 결과적으로 CTC loss는 all possible legal path의 conditional probability를 maximize 함:
(Eq. 1) $ \mathcal{L}_{ctc}=-\log p_{ctc}(\mathbf{y}|\mathbf{x})=\sum_{\pi\in\Phi_{\mathbf{x},\mathbf{y}}} p(\pi|c_{1},...,c_{T})$
- $\Phi_{\mathbf{x},\mathbf{y}}$ : all valid alignment
- 이때 phoneme token, blank token과 같은 observed label에 대한 distribution을 predict 하기 위해 softmax를 포함한 linear layer를 추가하여 $p(\pi|c_{1},...,c_{T})$를 얻음
- 해당 CTC superviesd learning을 통해 model은 각 frame의 representation $c_{t}$를 phonetic unit에 explicitly mapping 할 수 있음
- 특히 generalization을 위해 논문은 labeled source data와 unlabeled data $\{\mathbf{X}_{i}|(\mathbf{X}_{i},\mathbf{Y}_{i})\in\mathbb{L}\vee\mathbf{X}_{i}\in\mathbb{M}\}$ 모두에 대해 self-supervised contrastive learning을 적용함
- 먼저 $\mathbf{x}$가 주어지면 convolutional feature encoder를 사용하여 feature representation $z_{1},...,z_{T}$를 얻을 수 있음
- Training 시에는 일부 frame을 mask 하고 masked feature $\tilde{\mathbf{z}}$를 Transformer에 전달함 - Masking 시에는 Wav2Vec 2.0을 따라 start index를 probability $p$로 randomly sampling 하고 consecutive 10 time step을 mask 함
- Model은 quantizer output $\mathbf{q}$를 contrastive target으로 사용하고, quantizer의 input은 unmask 함
- 그러면 $z_{i}$는 $l\in \mathbb{R}^{G\times V}$ logit으로 mapping 되고 probability에 따라 각 codebook에서 하나의 discrete entry $e$를 select 하기 위해 Gumbel Softmax를 적용함:
(Eq. 2) $p_{g,v}=\frac{\exp(l_{g,v}+n_{v})/\tau}{\sum_{k=1}^{V}\exp(l_{g,v}+n_{v})/\tau}$
- $G$ : codebook 수, $V$ : 각 codebook의 entry 수, $\tau$ : non-negative temperature
- $n=-\log(-\log(u))$, $u$ : $\mathcal{U}(0,1)$의 uniform sample - Forward pass에서 quantizer는 $i=\arg\max_{j}p_{g,j}$에 대해, 각 codebook에서 input $z$의 nearest $e_{g}(i)$를 find 함
- Resulting vector $e_{1},...,e_{G}$를 concatenate 한 다음, linear transformation을 적용하여 $q$를 얻음
- $q$는 Transformer encoder와 동일한 dimension을 가짐 - Backward pass에서는 pre-quantized vector $z$에 대한 loss의 gradient에 straight-through estimator를 적용하여 $\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}}{\partial z}\approx \frac{\partial \mathcal{L}}{\partial q}$로 approximate 함
- Resulting vector $e_{1},...,e_{G}$를 concatenate 한 다음, linear transformation을 적용하여 $q$를 얻음
- Masked time step $t$의 각 centered $c_{t}$에 대해 model은 $K+1$의 quantized candidate set $Q_{t}$에서 true quantized latent speech representation $q_{t}$를 identify 해야 함
- $K$ distractor는 same utterance의 다른 time step에서 uniformly sample 됨
- 이때 loss는:
(Eq. 3) $\mathcal{L}_{c}=-\log\frac{\exp(\text{sim}(c_{t},q_{t})/\kappa)}{\sum_{\tilde{q}\sim Q_{t}}\exp(\text{sim}(c_{t},\tilde{q})/\kappa)}$
- $\text{sim}(a,b)=\frac{a^{T}b}{||a||\,||b||}$ : cosine similarity - 해당 contrastive loss는 quantizer가 contextual representation $c$에 close 한 vector를 생성함
- 그러면 objective를 $\mathbb{L},\mathbb{M}$의 joint set에서 training 하여 codebook을 source/target domain 모두에서 generalize 할 수 있음
- Self-supervised objective는 $0.1$의 codebook diversity loss를 사용하여 augmented 됨:
(Eq. 4) $\mathcal{L}_{self}=\mathcal{L}_{c}+0.1*\mathcal{L}_{d}$
(Eq. 5) $\text{where}\,\,\, \mathcal{L}_{d}=\frac{1}{GV}\sum_{g=1}^{G}\sum_{v=1}^{V}\bar{p}_{g,v}\log \bar{p}_{g,v}$ - 결과적으로 final pre-training loss는:
(Eq. 6) $\mathcal{L}=\sum_{(\mathbf{x},\mathbf{y})\in\mathbb{L}}\left(\alpha\mathcal{L}_{ctc} +(1-\alpha)\mathcal{L}_{self}\right)+\sum_{(\mathbf{x}\in\mathbb{M})}\mathcal{L}_{self}$
- $\alpha$ : dataset $\mathbb{L}$에 대한 loss combination의 weight
- 이를 위해 논문은 unified representation에 대한 multitask learning method를 도입함
- Quantization module은 utterance 내의 phonetic content를 speaker identity와 분리하여 representation을 학습함
- BUT, 해당 unsupervised training 만으로는 ASR task를 위한 discrete representation을 보장할 수 없음
- 따라서 논문은 CTC loss calculation 시 continuous representation $c$를 probability $r$로 quantized version $q$로 replace 함
- 그러면 (Eq. 1)의 conditional probability는:
(Eq. 7) $ \sum_{\pi\in\Phi_{\mathbf{x},\mathbf{y}}}\prod_{t=1}^{T}p(\pi |c_{1}...c_{T})\rightarrow \sum_{\pi\in\Phi_{\mathbf{x},\mathbf{y}}}\prod_{t=1}^{T}p(\pi|c'_{1}...c'_{T})$
- $c'_{i}$ : $c_{i}$ 또는 $q_{i}$ - 여기서 $\mathbf{y}$는 phoneme sequence 이므로 $q_{i}$를 $\mathbf{y}$로 predict 하면 quantizer가 phoneme을 cluster 하고 codebook에 ASR-specific knowledge를 학습하도록 explicitly guide 할 수 있음
- 특히 (Eq. 7)을 통해 supervised/unsupervised representation은 동일한 space로 project 되므로 두 objective가 individually optimize 되는 것을 방지할 수 있음
- 그러면 (Eq. 1)의 conditional probability는:
- Pre-training 이후에는 CTC loss를 사용하여 $\mathbb{N}$에 대해 model을 fine-tuning 함
- Fine-tuning 시에는 pre-trained CTC layer를 target vocabulary에 대한 new layer로 replace 하고, feature encoder weight는 freeze 한 다음 Transformer만 fine-tuning 함
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : CommonVoice
- Comparisons : XLSR, m-CPC
- Results
- 전체적으로 UniSpeech의 성능이 가장 우수함

- Many-to-One cross-lingual transfer 측면에서도 뛰어난 성능을 보임
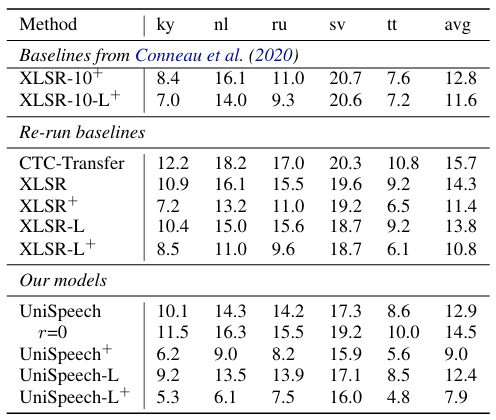
- Many-to-Many setting 역시 UniSpeech의 성능이 가장 우수함

- Domain Transfer
- UniSpeech는 domain transfer에서도 최고의 성능을 달성함
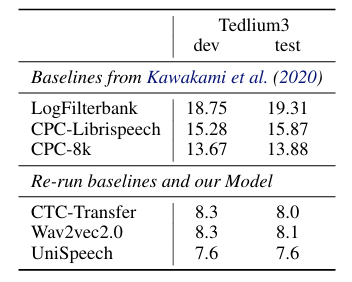
- Discrete Representation
- Discrete latent는 specific phonetic sound에 specialize 되어 있음

- Hyperparameter
- $r=0.5,\alpha=0.5, p=0.05$로 설정했을 때 최적의 결과를 얻을 수 있음

반응형
'Paper > Representation' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

