티스토리 뷰
Paper/Representation
[Paper 리뷰] DQ-Data2Vec: Decoupling Quantization for Multilingual Speech Recognition
feVeRin 2026. 1. 15. 14:13반응형
DQ-Data2Vec: Decoupling Quantization for Multilingual Speech Recognition
- Data2Vec의 masked representation generation은 multi-layer averaging에 의존적임
- DQ-Data2Vec
- $K$-means quantizer를 사용하여 masked prediction을 위한 language, phoneme information을 decoupling
- 특히 quantization을 shallow, middle layer 모두에 적용하여 irrelevant feature를 explicitly decoupling
- 논문 (TASLP 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- XLSR과 같은 Self-Supervised Learning (SSL)-based speech model을 활용하면 Automatic Speech Reocognition (ASR) 성능을 크게 향상할 수 있음
- 대부분의 speech SSL model은 extensive unlabeled dataset에 대한 pre-training 이후 limited labeled dataset에 대한 fine-tuning을 수행하는 2-stage process를 활용함
- 대표적으로 Data2Vec은 teacher-student framework를 기반으로 continuous, contextual target speech representation을 추출함 - BUT, Data2Vec architecture는 monolingual scenario에 맞춰져 있어 cross-lingual shared phoneme, language identificaiton과 같은 multilingual ASR task에 활용하기 어려움
- 대부분의 speech SSL model은 extensive unlabeled dataset에 대한 pre-training 이후 limited labeled dataset에 대한 fine-tuning을 수행하는 2-stage process를 활용함
-> 그래서 multilingual task를 위한 Data2Vec-based SSL model인 DQ-Data2Vec을 제안
- DQ-Data2Vec
- Data2Vec backbone과 2개의 online $K$-means quantizer를 활용하여 language, phoneme을 decoupling
- 추가적으로 weakly-supervised scenario에서 language label과 non-target language text label에 대한 supervised loss를 활용하여 SSL 성능을 향상
< Overall of DQ-Data2Vec >
- Data2Vec을 기반으로 online $K$-means quantizer를 적용한 decoupled SSL representation model
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 성능을 달성
2. Method
- DQ-Data2Vec은 BERT-style SSL model로써 teacher-student backbone과 2개의 online $K$-means vector quantizer로 구성됨
- Teacher-Student Backbone
- Data2Vec은 teacher-student framework를 기반으로 한 speech SSL model로써 teacher branch는 여러 layer를 통해 다양한 unmaksed information을 express 할 수 있음
- BUT, SSL model은 pre-training 시 collapse가 발생할 수 있고, multiple quantizer를 사용하는 경우 더욱 취약해짐
- 실제로 initial training stage에서 teacher branch의 intermediate layer output이 apparent 하지 않은 경우, quantizer는 low-quality speech representation을 생성함 - 구조적으로 Data2Vec backbone은 Convolutional Feature Encoder, Teacher Transformer Encoder, Student Transformer Encoder로 구성됨
- 먼저 Convolutional Feature Encoder는 raw speech audio를 latent representation으로 mapping 함
- 이후 masked latent representation은 Student branch로 전달되고 unmasked raw latent representation은 Teacher branch로 전달됨
- 그러면 Teacher branch의 top $K$ layer result는 Instance Normalization을 통과한 다음 average 되어 target speech representation $\mathbf{y}_{t}$를 output 함
- Student branch의 last layer output $\mathbf{x}_{t}$는 Linear Predictor $\text{Pred}_{t}$를 통해 $\mathbf{x}'_{t}$로 transform 되고, $\mathbf{x}'_{t}$의 masked frame은 Smooth L1 (SL1) loss를 통해 $\mathbf{y}_{t}$의 frame을 reconstruct 하도록 optimize 됨
- SL1 loss $\mathcal{L}_{sl1}$은 다음과 같이 compute 됨:
(Eq. 1) $ \left\{\begin{matrix}
\mathbf{y}_{t}=\frac{1}{K}\sum_{i=L-K+1}^{L}\text{InsNorm}(\mathbf{y}_{i}) \\
\mathbf{x}'_{t}=\text{Pred}_{t}(\mathbf{x}_{t}) \\
\end{matrix}\right.$
(Eq. 2) $\mathcal{L}_{sl1}=\left\{\begin{matrix}
\frac{1}{2}(\mathbf{y}_{t}-\mathbf{x}'_{t})^{2}/\beta, & \text{if}\,\,|\mathbf{y}_{t}-\mathbf{x}'_{t}|\leq \beta \\
|\mathbf{y}_{t}-\mathbf{x}'_{t}|-\frac{1}{2}\beta, & \text{otherwise} \\
\end{matrix}\right.$
- $L=8$ : Transformer encoder layer 수, $K=12$ : teacher branch의 top layer 수, $\beta$ : hyperparameter
- BUT, SSL model은 pre-training 시 collapse가 발생할 수 있고, multiple quantizer를 사용하는 경우 더욱 취약해짐

- Shallow Decoupling
- SSL model backbone에서 서로 다른 layer는 distinctive information을 encompass 하고 있음
- 대표적으로 shallow layer는 speaker/language-related information, middle layer는 phoneme/word-related information, deep layer는 masked representation을 reconstruct 하는 information을 capture 함
- BUT, 하나의 layer에서 얻어진 result는 여전히 multiple information을 encompass 할 수 있으므로 specific layer를 target speech representation으로 directly use 하기 어려움 - 따라서 논문은 2개의 online $K$-means quantizer를 도입하여 specific target을 decoupling 함
- 특히 speaker 수와 language 수의 차이를 활용하여 clustering result를 language와 close 하게 만듦 - 해당 shallow decoupling은 labeled data 없이 layer position, cluster center 수, pooling 여부 만으로 speech representation의 content를 specify 하는 것을 목표로 함
- 대표적으로 shallow layer는 speaker/language-related information, middle layer는 phoneme/word-related information, deep layer는 masked representation을 reconstruct 하는 information을 capture 함
- Layer Results
- 논문은 language quantization을 위해 teacher branch의 shallow layer result $\mathbf{y}_{l}$을 select 하고 phoneme quantization을 위해 intermediate layer $\mathbf{y}_{p}$를 select 함
- $\mathbf{y}_{l}=\{4,5,6\}$ layer, $\mathbf{y}_{p}=\{7,8,9\}$ layer - 여기서 $\mathbf{y}_{l},\mathbf{y}_{p}$에 대한 level-related pre-processing은 normalization, pooling, averaging만 involve 하여 구성됨:
- Utterance-level Pre-processing
- Language-specific information은 temporal pooling 이후에만 나타나고, 동일한 batch 내의 other utterance 와는 independent 하므로 $L2$ normalization을 고려함:
(Eq. 3) $\mathbf{y}'_{l}=\text{L2Norm}\left(\text{Pool}\left(\frac{1}{N_{l}}\sum \mathbf{y}_{i}\right)\right),\,\,\, \mathbf{y}_{i}\in\mathbf{y}_{l}$
- $N_{l}$ : $\mathbf{y}_{l}$의 layer 수 - Frame-level Pre-processing
- Phoneme-related information은 context-dependent 하고 utterance 내에서 feature dimension을 time step에 따라 normalize 하여 capture 할 수 있음
- 결과적으로 frame-level pre-processing은 Instance Normalization을 사용하여 얻어짐:
(Eq. 4) $\mathbf{y}'_{p}=\text{InsNorm}\left(\frac{1}{N_{p}}\sum\text{InsNorm}(\mathbf{y}_{i})\right), \,\,\, \mathbf{y}_{i}\in\mathbf{y}_{p}$
- $N_{q}$ : $\mathbf{y}_{p}$의 layer 수
- Utterance-level Pre-processing
- 논문은 language quantization을 위해 teacher branch의 shallow layer result $\mathbf{y}_{l}$을 select 하고 phoneme quantization을 위해 intermediate layer $\mathbf{y}_{p}$를 select 함
- Online $K$-means Quantizer
- Online $K$-means quantizer는 randomly initialize 된 codebook을 backpropagation을 통해 update 할 수 있음
- 이때 codebook 내에서 input vector $\mathbf{e}$로부터 smallest Euclidean distance를 가지는 codeword $\mathbf{c}_{i}$를 quantization result $\mathbf{q}$로 choice 함:
(Eq. 5) $\left\{\begin{matrix}
i=\arg\min_{j}||\mathbf{e}-\mathbf{c}_{j}||^{2},\,\,\mathbf{c}_{j}\in\mathbb{R}^{N\times D} \\
\mathbf{q}=\mathbf{c}_{i}
\end{matrix}\right.$
- $N$ : codeword 수 (논문에서는 language 수로 설정), $D$ : input vector의 feature dimension (논문에서는 phoneme 수로 설정) - Backpropagation 시에는 Mean Squared Error (MSE) loss를 사용하여 codebook과 input vector가 가까워지도록 guide 함:
(Eq. 6) $\mathcal{L}_{km}=||\text{sg}(\mathbf{e})-\mathbf{q}||^{2}+\gamma||\mathbf{e}-\text{sg}(\mathbf{q})||^{2}$
- $\text{sg}$ : stop-gradient operation, $\gamma=0.25$ : hyperparameter
- 이때 codebook 내에서 input vector $\mathbf{e}$로부터 smallest Euclidean distance를 가지는 codeword $\mathbf{c}_{i}$를 quantization result $\mathbf{q}$로 choice 함:
- 한편으로 DQ-Data2Vec에서는 EMA method를 사용할 때 Teacher branch의 모든 layer output이 gradient stopping에 영향을 받음
- 즉, $\mathbf{y}'_{l},\mathbf{y}'_{p}$를 quantizer input vector $\mathbf{e}$로 사용하면 (Eq. 6)의 second term은 어떤 parameter도 update 하지 않음 - 따라서 논문은 $\mathbf{y}'_{l},\mathbf{y}'_{p}$에 temporal convolution layer $\mathbf{e}=\text{Conv1D}(\mathbf{y}')$를 도입하여 (Eq. 6)의 second term에 대한 significance를 부여함
- Online $K$-means quantizer는 randomly initialize 된 codebook을 backpropagation을 통해 update 할 수 있음
- Quantization Learning Objective
- DQ-Data2Vec은 3가지 target speech representation $\mathbf{y}_{t}, \mathbf{q}_{l},\mathbf{q}_{p}$를 가지므로 Student branch는 해당 representation을 simultaneously learning 해야 함
- 먼저 $\mathbf{y}_{t}$는 Student Encoder의 final layer $\mathbf{x}_{t}$로부터 reconstruct 됨
- $\mathbf{q}_{l},\mathbf{q}_{p}$의 경우 $\mathbf{y}_{l},\mathbf{y}_{p}$의 deepest layer인 student layer $\mathbf{x}_{l},\mathbf{x}_{p}$를 통해 reconstruct 됨
- $\mathbf{x}_{l}=6, \mathbf{x}_{p}=9$ - 추가적으로 논문은 $\mathbf{x}_{l},\mathbf{x}_{p}$를 mapping 하기 위한 2개의 predictor $\text{Pred}_{l}, \text{Pred}_{p}$를 도입함
- 그러면 mapping vector $\mathbf{x}'_{l},\mathbf{x}'_{p}$는 다음과 같이 represent 됨:
(Eq. 7) $ \left\{\begin{matrix}
\mathbf{x}'_{l}=\text{Pool}(\text{Pred}_{l}(\mathbf{x}_{l})) \\
\mathbf{x}'_{p}=\text{Pred}_{p}(\mathbf{x}_{p})
\end{matrix}\right.$
- $\text{Pred}_{l}, \text{Pred}_{p}$는 각각 2개의 Transformer layer, 1개의 linear layer로 구성됨 - $\mathbf{x}'_{l},\mathbf{x}'_{p}$를 얻은 다음, reconstruction을 위해 Contrastive loss를 도입함
- Contrastive loss를 활용하면 $\mathbf{x}'_{l},\mathbf{x}'_{p}$의 feature dimension distribution을 $\mathbf{q}_{l},\mathbf{q}_{p}$에 align 하여 Student branch에 incorporate 할 수 있음
- 여기서 Contrastive loss는:
(Eq. 8) $\mathcal{L}_{ctr}=-\log \frac{\exp(\text{Sim}(\mathbf{x}',\mathbf{q})/\kappa)}{ \sum_{\hat{\mathbf{q}}\sim\mathbf{Q}}\exp(\text{Sim}(\mathbf{x}',\hat{\mathbf{q}})/\kappa)}$
- $\text{Sim}$ : cosine similarity, $\kappa=0.1$ : non-negative temperature, $\mathbf{Q}$ : negative examples
- 이때 논문은 intra-utterance의 other masked frame을 negative로 선택함
- 결과적으로 quantization learning loss는:
(Eq. 9) $\mathcal{L}_{qt}=\mathcal{L}_{ctr}+\mathcal{L}_{km}$ - Shallow decoupling scenario에서 total loss는 다음과 같이 얻어짐:
(Eq. 10) $\mathcal{L}_{sc}=(1-\gamma_{1}-\gamma_{2})\mathcal{L}_{sl1}+\gamma_{1}\mathcal{L}_{qt}^{l}+\gamma_{2}\mathcal{L}_{qt}^{p}$
- $\gamma_{1}=0.1, \gamma_{2}=0.2$ : hyperparameter
- DQ-Data2Vec은 3가지 target speech representation $\mathbf{y}_{t}, \mathbf{q}_{l},\mathbf{q}_{p}$를 가지므로 Student branch는 해당 representation을 simultaneously learning 해야 함
- Deep Decoupling
- Unlabeled data를 사용한 language, phoneme quantization의 shallow decoupling은 weak constraint에 해당하므로, labeled data를 도입하면 더 나은 성능을 달성할 수 있음
- 즉, language label과 non-target high-resource language의 text label을 활용하는 deep coupling을 고려함
- Deep coupling scenario에서는 student layer output $\mathbf{x}$와 quantized vector $\mathbf{q}$를 $1:1$ ratio로 mix 하여 unified representation $\mathbf{u}$를 생성함
- Phoneme unified representation $\mathbf{u}_{p}$의 경우 각 utterance 내에서 $\mathbf{x}_{p}$ frame $50\%$를 randomly mask 하고 $\mathbf{q}_{p}$ frame으로 replace 함
- Language unified representation $\mathbf{u}_{l}$은 frame-level replacement 대신 batch 내에서 utterance-level replacement를 수행함
- 결과적으로 unified representation $\mathbf{u}_{l},\mathbf{u}_{p}$는:
(Eq. 11) $\left\{\begin{matrix}
\mathbf{u}_{l}=\text{Mix}\left(\text{Pool}(\mathbf{x}_{l}),\mathbf{q}_{l}\right)=\text{Pool}(\mathbf{x}_{l})*\mathbf{M}_{l}+\mathbf{q}_{l}*(1-\mathbf{M}_{l}) \\
\mathbf{u}_{p}=\text{Mix}(\mathbf{x}_{p},\mathbf{q}_{p})=\mathbf{x}_{p}*\mathbf{M}_{p}+\mathbf{q}_{p}*(1-\mathbf{M}_{p})
\end{matrix}\right.$
- $\mathbf{M}_{l}\in\mathbb{R}^{1\times D}, \mathbf{M}_{p}\in\mathbb{R}^{T\times D}$ : binary mask matrix
- $\mathbf{x}_{l}, \mathbf{x}_{p}$는 masked, unmasked frame을 가짐 - 이후 Cross Entropy (CE)와 CTC loss를 사용하여 model을 supervise 함:
(Eq. 12) $\mathcal{L}_{ce}=\text{CrossEntropy}(\mathbf{u}_{l},\mathbf{Y}_{l})$
(Eq. 13) $\mathcal{L}_{ctc}=\left\{\begin{matrix}
\text{CTC}(\mathbf{u}_{p},\mathbf{Y}_{p}), & \text{if}\,\,\mathbf{Y}_{p}\in\mathbb{H} \\
0, & \text{otherwise} \\
\end{matrix}\right.$
- $\mathbf{Y}_{l}, \mathbf{Y}_{p}$ : language, phoneme text label
- $\mathbb{H}$ : non-target high-resource language
- 해당 mixture는 quantized representation의 quality를 directly/indirectly enhance 함
- Direct enhance의 경우 $\mathbf{q}_{l},\mathbf{q}_{p}$의 gradient backpropagation을 통해 quantizer를 optimize 함
- Indirect enhance의 경우 $\mathbf{x}_{l},\mathbf{x}_{p}$로부터 얻어진 gradient를 사용하여 Student를 optimize 한 다음, EMA를 통해 Teacher를 update 하여 $\mathbf{y}_{l},\mathbf{y}_{p}$에 대한 clustering을 지원함
- BUT, quantizer가 shallow decoupling과 동일한 design을 사용하는 경우 $\mathbf{q}_{l},\mathbf{q}_{p}$의 gradient는 EMA에 의해 stop 되어 temporal convolution block만 update 될 수 있음
- 이를 해결하기 위해 논문은 larger kernel size를 가지는 convolution block을 도입하여 $\mathbf{y}_{l}, \mathbf{y}_{p}$의 language/phoneme information을 further emphasize 함 - 결과적으로 deep decoupling scenario의 total loss는:
(Eq. 14) $\mathcal{L}_{dc}=\mathcal{L}_{sc}+\gamma_{3}(\mathcal{L}_{ce}+\mathcal{L}_{ctc})$
- $\gamma_{3}=0.1$
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : CommonVoice
- Comparisons : XLSR, Wav2Vec 2.0, Data2Vec

- Results
- 전체적으로 DQ-Data2Vec의 성능이 가장 뛰어남

- WER 측면에서도 우수한 성능을 보임
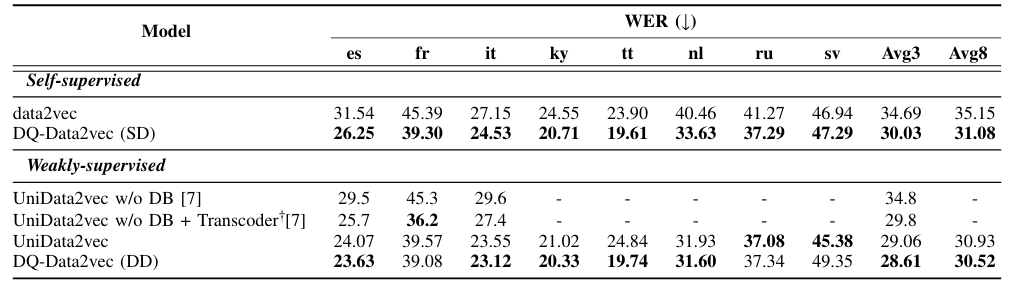
- Quantization Analysis
- Clustering 성능 측면에서도 DQ-Data2Vec이 더 뛰어남

- Conditional probability $P(lang|code)$의 learned codebook을 확인해 보면, shallow decoupling scenario에서 language quantizer는 distinct alignment path를 capture 함

- $P(phone|code)$의 경우, first row가 wide range를 차지함
- 이는 대부분의 active codeword가 silencing unit에 allocate 되었다는 것을 의미함

- DQ-Data2Vec은 multilingual mix dataset에서도 안정적인 성능을 보임
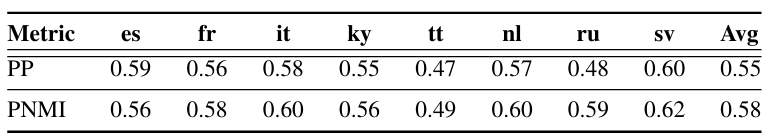
- Decoupling Quantization
- 각 quantizer design은 성능 향상에 유효함

반응형
'Paper > Representation' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

