티스토리 뷰
Paper/Verification
[Paper 리뷰] ParaNoise-SV: Integrated Approach for Noise-Robust Speaker Verification with Parallel Joint Learning of Speech Enhancement and Noise Extraction
feVeRin 2025. 9. 18. 17:01반응형
ParaNoise-SV: Integrated Approach for Noise-Robust Speaker Verification with Parallel Joint Learning of Speech Enhancement and Noise Extraction
- 기존의 speaker verification model은 noise-robustness 측면에서 한계가 있음
- ParaNoise-SV
- Noise Extraction network와 Speech Enhancement network를 combine 한 dual U-Net을 활용
- Noise Extraction U-Net은 noise를 explicitly modeling 하고 Speech Enhancement U-Net은 parallel connection을 통한 guidance를 활용하여 speaker-relevant feature를 preserve
- 논문 (INTERSPEECH 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Speaker Verification (SV)는 주어진 speech가 target speaker와 match 하는지를 verify 함
- 기존 SV system은 real-world environment의 noise를 mitigate 하기 위해 separately trained Speech Enhancement (SE) model을 주로 활용함
- BUT, speaker-specific information을 degrade 하여 verification accuracy가 저하됨 - 이를 해결하기 위해서는 SE, SV system을 jointly learning 해야 함
- SV의 경우 U-Net-based approach, Self-Supervised Learning (SSL)-based approach를 고려할 수 있지만, large parameter size로 인한 한계가 있음
- 한편으로 SE 측면에서는 dual-stream model을 활용하면 더 나은 enhancement를 달성할 수 있음
- 기존 SV system은 real-world environment의 noise를 mitigate 하기 위해 separately trained Speech Enhancement (SE) model을 주로 활용함
-> 그래서 SV, SE network를 combine 하여 noise-robustness를 향상한 ParaNoise-SV를 제안
- ParaNoise-SV
- U-Net을 기반으로 Noise Extraction (NE) network와 Speech Enhancement (SE) network를 jointly training
- Parallel connection을 통해 network를 inter-connect 하여 noise-relevant feature가 speaker-relevant feature를 preserving 하면서 speech를 refine 하도록 유도
< Overall of ParaNoise-SV >
- NE, SE network를 jointly training 한 noise-robust SV model
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 verification 성능을 달성
2. Method
- Overview of ParaNoise-SV
- ParaNoise-SV는 NE, SE, SV를 dual encoder-decoder structure를 사용하여 integrate 함
- 특히 simultaneous NE, SE를 위해 SE-ResNet이 포함된 dual U-Net을 활용하고, speaker-relevant information을 preserving 하면서 balanced separation을 보장하기 위해 parallel connection을 도입함
- 이때 NE network는 noise를 isolate 하고 SE network는 각 encoding stage에서 parallel connection을 통해 dynamic noise suppression을 수행함 - 추가적으로 논문은 extracted noise를 feature level에서 활용하여 contamination을 방지함
- Speaker embedding extraction 시에는 ERes2NetV2가 사용되고, channel adaptation block은 skip connection을 통해 U-Net feature를 integrate 함
- 특히 simultaneous NE, SE를 위해 SE-ResNet이 포함된 dual U-Net을 활용하고, speaker-relevant information을 preserving 하면서 balanced separation을 보장하기 위해 parallel connection을 도입함

- Parallel Connections of Dual U-Nets
- Input spectrogram은 instance normalization을 사용해 normalize 되고 initial convolutional layer를 통해 process 되어 noise/speech feature map $N_{E,0}, S_{E,0}$을 생성함
- 각 encoder는 SE-ResNet을 사용하여 depth $L=4$의 hierarchical representation을 추출함
- NE network는 (Eq. 1)의 encoder block $e_{N}$을 통해 noise representation을 encode 하고 noise feature를 refine 함:
(Eq. 1) $ N_{E,i}=e^{i}_{N}(N_{E,i-1}),\,\,\,i=1,...,L$ - (Eq. 2)의 deepest encoded feature는 decoding operation $d_{N}$을 initialize 하고 skip connection은 (Eq. 3)의 noise extraction을 aid 함:
(Eq. 2) $N_{D,0}=N_{E,L}$
(Eq. 3) $N_{D,i}=d_{N}^{i}(N_{D,i-1},N_{E,L-i}),\,\,\,i=1,...,L$ - (Eq. 4)에서 transposed convolutional layer는 estimated noise spectrogram $\hat{N}$을 생성함:
(Eq. 4) $\hat{N}=\text{ConvTranspose}(N_{D,L},N_{E,0})$
- NE network는 (Eq. 1)의 encoder block $e_{N}$을 통해 noise representation을 encode 하고 noise feature를 refine 함:
- SE network는 parallel connection을 incorporate 함:
(Eq. 5) $S_{E,i}=e_{S}^{i}(S_{E,i-1},N_{E,i-1}),\,\,\,i=1,...,L$
(Eq. 6) $S_{D,0}=S_{E,L}$
- Information은 2개의 parallel network 간에 flow 되고, noise feature는 각 encoder block $e_{S}$에서 integrate 됨 - Encoded speech feature는 (Eq. 7)과 같이 skip connection과 함께 decode 되고 final transposed convolutional layer output은 (Eq. 8)과 같이 enhanced speech spectrogram $\hat{S}$를 output 함:
(Eq. 7) $S_{D,i}=d_{S}^{i}(S_{D,i-1},S_{E,L-i}),\,\,\,i=1,...,L$
(Eq. 8) $\hat{S}=\text{ConvTranspose}(S_{D,L},S_{E,0})$ - 결과적으로 SE network는 NE network로부터 noise information을 활용하여 speaker detail을 preserve 하고 noise suppression을 개선함
- 각 encoder는 SE-ResNet을 사용하여 depth $L=4$의 hierarchical representation을 추출함

- Speaker Embedding Extraction
- Noisy speech에서는 spectral component가 missing/corrupt 되어 speaker verification이 어려울 수 있음
- 이때 multiple scale에서 information을 capture 하면 specific frequency가 degrade 되어도 speaker characteristic을 preserve 할 수 있음
- 따라서 논문은 multi-scale feature fusion과 channel expansion을 활용하는 ERes2NetV2를 통해 noisy environment에서의 verification 성능을 향상함
- 특히 SE network의 speech refinement capability를 fully exploit 하기 위해, 해당 decoder feature를 ERes2NetV2에 skip connection을 사용하여 integrate 함
- BUT, ERes2NetV2는 channel expansion으로 인해 dimension mismatch가 발생하므로, 논문은 multiple convolution layer로 구성된 channel adaptation을 SE decoder output에 적용함
- Speaker embedding extraction은 noise suprpession으로 인한 information loss를 minimize 하기 위해 2-stage process를 채택함
- 먼저 SE network의 deepest encoder feature는 initial pooled vector로 사용되고, fully-connected (FC) layer를 통과하여 initial embedding을 생성함
- 이후 SV network를 통해 further process 되고, ASP를 적용하고, refined feature를 initial pooled vector와 concatenate 하여 final FC layer로 전달함
- Final embedding은 SE encoder output을 사용하여 parallel connection을 통해 refine 된 다음, ERes2NetV2 output과의 multi-scale aggregation을 통해 얻어짐
- 해당 final embedding은 speaker verifcation을 위한 identity representation으로 사용됨

- Loss Functions
- 논문은 NE, SE, SV를 integrated framework에서 optimize 함
- 이때 loss function은:
(Eq. 9) $\mathcal{L}=\mathcal{L}_{n}+\mathcal{L}_{s}+\mathcal{L}_{C}+\mathcal{L}_{AP}+\mathcal{L}_{AAM}$
- $\mathcal{L}_{n}$ : noise extraction loss로써, $\hat{N}$과 original noise spectrogram 간의 Mean Squared Error (MSE) loss
- $\mathcal{L}_{s}$ : speech enhancement loss로써, $\hat{S}$와 clean speech spectrogram 간의 MSE loss - Initial embedding과 speaker label 간의 cross-entropy loss $\mathcal{L}_{C}$는 speaker embedding extraction을 위해 사용됨
- Angular Prototypical (AP) loss $\mathcal{L}_{AP}$와 Additive Angular Margin (AAM) loss $\mathcal{L}_{AAM}$은 final embedding을 optimize 하고 noise robustness를 향상함
- $\mathcal{L}_{AP}$는 same speaker의 final clean embedding과 noisy embedding을 align 하고 $\mathcal{L}_{AAM}$은 final speaker embedding을 speaker-wise prototype과 separate 함
- 이때 loss function은:
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : VoxCeleb1 + MUSAN
- Comparisons : VoiceID, NDML, ExU-Net, DiffSV 등

- Results
- 전체적으로 ParaNoise-SV의 성능이 가장 뛰어남
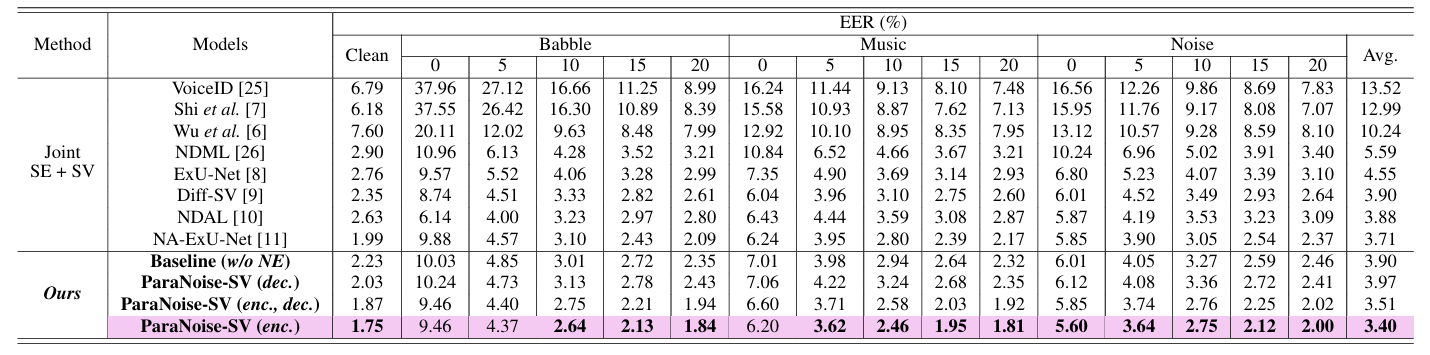
- Out-of-Domain noise source에 대해서도 우수한 성능을 보임

- ParaNoise-SV는 seen/unseen condition에 상관없이 안정적인 성능을 달성함


반응형
'Paper > Verification' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

