티스토리 뷰
Paper/Verification
[Paper 리뷰] SSPS: Self-Supervised Positive Sampling for Robust Self-Supervised Speaker Verification
feVeRin 2025. 9. 4. 17:01반응형
SSPS: Self-Supervised Positive Sampling for Robust Self-Supervised Speaker Verification
- Speaker Verification에서 Self-Supervised Learning은 동일한 speaker의 anchor-positive pair만을 사용함
- SSPS
- 주어진 anchor에 대해 latent space에서 clustering assignment와 memory queue를 적용
- 동일한 speaker지만 서로 다른 recording condition을 가지는 appropriate positive를 find
- 논문 (INTERSPEECH 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Speaker Verification (SV)는 주어진 speech sample이 claimed identity와 match 하는지를 판별함
- 이때 SV system은 intra-speaker similarity를 maximize 하고 inter-speaker similarity는 minimize 하는 representation space를 정의할 수 있어야 함
- 대표적으로 ECAPA-TDNN은 supervised manner로 speech sample과 해당 identity를 associate 함
- BUT, 해당 방식은 large-scale labeled dataset에 상당히 의존적임
- 한편으로 input data로부터 informative representation을 추출하는 Self-Supervised Learning (SSL)을 활용하면 labeled dataset에 대한 의존성을 해결할 수 있음
- 이때 SSL framework는 동일한 input data의 서로 다른 view에서 derive 된 anchor와 positive sample을 사용함 - 특히 SV에서는 contrastive learning과 self-distillation이 주로 활용되고, 해당 방식들은 anchor/positive sample이 동일한 utterance에서 derive 된 동일한 speaker identity를 가지고 있다고 가정함
- 따라서 두 segment 간에 share 되는 encoding channel information을 avoid 하기 위해서는 data-augmentation이 필수적임 - BUT, data-augmentation 만으로는 SSL의 same-utterance positive sampling을 mitigate 할 수 없음
- Recording에서 발생하는 channel characteristic이 speaker representation에 condition 되어 intra-speaker variance를 증가시키기 때문
- 이때 SV system은 intra-speaker similarity를 maximize 하고 inter-speaker similarity는 minimize 하는 representation space를 정의할 수 있어야 함
-> 그래서 SSL 기반 SV의 positive sampling을 개선한 SSPS를 제안
- SSPS
- Anchor와 동일한 utterance에서 positive sample을 select 하지 않고, SSL을 통해 progressively acquire 한 knowledge를 활용하여 distinct utterance에서 pseudo-positive를 identify
- 이를 통해 동일한 speaker identity와 다양한 recording condition을 matching 하여 robust speaker representation을 학습
< Overall of SSPS >
- 기존 anchor-positive selection의 speaker identity 문제를 개선한 Self-Supervised Positive Sampling method
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 SV 성능을 달성
2. Method
- SSL Frameworks
- Self-supervised training framework에서는 unlabeled audio sample로부터 embedding pair를 생성하기 위해 joint-embedding architecture를 활용함
- $\mathcal{I}\equiv \{1,...,N\}$의 index를 가지는 size $N$의 training set이 있다고 하자
- 그러면 각 iteration마다 $\mathcal{B}\subseteq \mathcal{I}$ batch index와 함께 $B$ utterance가 select 됨
- 주어진 utterance $u_{i}\in\{u_{i}\}_{i\in\mathcal{B}}$에서는 2개의 segment $\mathbf{x}_{i}$ (anchor)와 $\mathbf{x}'_{i}$ (positive)가 randomly extract 됨
- 이후 random data-augmentation이 적용되고 mel-scaled spectrogram이 input feature로 사용됨
- 이때 architecture는 projector $g_{\phi}$가 있는 encoder $f_{\theta}$, projector $g_{\phi '}$이 있는 encoder $f_{\theta '}$의 2가지 branch로 구성됨
- Encoder $f_{\theta},f_{\theta '}$은 $\mathbf{x}_{i},\mathbf{x}'_{i}$를 $D_{repr}$ dimension을 가지는 representation $\mathbf{y}_{i},\mathbf{y}'_{i}$로 mapping 함
- Projector $g_{\phi}, g_{\phi '}$은 $\mathbf{y}_{i},\mathbf{y}'_{i}$를 $D_{emb}$ dimension의 embedding $\mathbf{z}_{i},\mathbf{z}'_{i}$로 transform 함
- Representation은 speaker verification을 위해 사용되고 embedding은 loss $\mathcal{L}$을 compute 하기 위해 사용됨
- Batch를 $\mathbf{X}=\{\mathbf{x}_{i}\}_{i\in \mathcal{B}}, \mathbf{Y}=\{\mathbf{y}_{i}\}_{i\in \mathcal{B}}, \mathbf{Z}=\{ \mathbf{z}_{i}\}_{i\in\mathcal{B}}$, 다른 branch의 counterpart는 $\mathbf{X}',\mathbf{Y}',\mathbf{Z}'$라 하자
- SimCLR와 같은 SSL framework는 branch 간 weight가 identical 한 symmetrical joint-embedding architecture를 사용함
- DINO와 같은 assymetrical architecture는 하나의 branch를 student로 다른 하나는 teacher로 사용함
- 이때 teacher의 gradient는 compute 되지 않고, student weight의 Exponential Moving Average (EMA)를 통해 update 됨 ($m\in[0,1)$ : momentum coefficient)
- $\mathcal{I}\equiv \{1,...,N\}$의 index를 가지는 size $N$의 training set이 있다고 하자
- SimCLR
- SimCLR는 contrastive learning을 통해 anchor-positive pair 간의 similarity를 maximize 하는 것을 목표로 함
- 이때 positive sample은 anchor와 동일한 utterance에서 derive 되고, negative sample은 다른 speaker identity를 가져야 함 - 여기서 $\mathcal{L}_{SimCLR}$는:
(Eq. 1) $ \mathcal{L}_{SimCLR}=-\frac{1}{B}\sum_{i\in\mathcal{B}}\log \frac{\exp(\text{sim}(\mathbf{z}_{i},\mathbf{z}'_{i})/\tau)}{\sum_{j\in\mathcal{B}}\exp( \text{sim}(\mathbf{z}_{i},\mathbf{z}'_{i})/\tau)}$
- $\text{sim}(\mathbf{a},\mathbf{b})$ : cosine-similarity, $\tau$ : temperature
- SimCLR는 contrastive learning을 통해 anchor-positive pair 간의 similarity를 maximize 하는 것을 목표로 함
- DINO
- DINO는 student가 teacher output을 predict 하도록 training 되는 self-distillation framework를 활용함
- Teacher weight는 student weight의 EMA로 update 됨 - 이때 다양한 length의 augmented utterance set을 고려하여 4개의 short (local) segment와 2개의 long (global) segment를 생성함
- 모든 input은 student를 통해 처리되지만 global view는 teacher를 통해 처리됨 - Student, teacher projector는 temperature-softmax를 통해 normalize 된 embedding을 output 함
- Teacher embedding에 centering과 sharpening을 적용하여 uniform distribution으로의 collapse를 방지함 - 그러면 $\mathcal{L}_{DINO}$는:
(Eq. 2) $\mathcal{L}_{DINO}=\frac{1}{B}\sum_{i\in \mathcal{B}}\sum_{t=1}^{2}\sum_{s=1,s\neq t}^{2+4}H \left(\frac{\mathbf{z}'_{i,t}-\mathbf{c}}{\tau_{t}},\frac{\mathbf{z}_{i,s}}{\tau_{s}}\right)$
- $H(\mathbf{a},\mathbf{b})=-\text{softmax}(\mathbf{a})\log (\text{softmax}(\mathbf{b}))$
- $\mathbf{z}'_{i,t},\mathbf{z}_{i,s}$ : sample $i$의 $t$-th teacher, $s$-th student embedding
- $\tau_{t},\tau_{s}$ : teahcer/student의 temperature, $\mathbf{c}$ : teacher output에 대한 running mean
- DINO는 student가 teacher output을 predict 하도록 training 되는 self-distillation framework를 활용함

- Self-Supervised Positive Sampling (SSPS)
- SSL framework의 성능은 anchor-positive pair에 따라 달라짐
- 일반적인 SSL framework는 주어진 anchor에 대해 positive를 생성하기 위해 data-augmentation을 사용함
- BUT, standard data-augmentation은 동일한 speaker의 sample에 대한 acoustic diversity를 효과적으로 represent 하지 못함 - 이로 인해 SV task에서 SSL model은 anchor-positive pair가 동일한 utterance로부터 derive 되므로 channel-related information을 encoding 하는데 취약함
- 따라서 SSPS는 동일한 utterance의 여러 recording condition으로부터 positive를 sampling 하는 것을 목표로 함
- 먼저 same-utterance positive sampling group utterance는 유사한 channel characteristic을 가진다고 가정함
- $pos(i)$를 utterance $u_{pos(i)}$의 index라고 하면, training utterance $u_{i}\,\,(i\in\mathcal{B})$가 주어졌을 때 anchor가 sampling 됨
- 이때 standard SSL approach는 동일한 utterance ($pos(i)=i$)에서 positive를 생성하는 반면, SSPS는 clustering assignment를 기반으로 latent space에서 다른 utterance ($pos(i)\neq i$)의 pseudo-positive를 생성함
- 일반적인 SSL framework는 주어진 anchor에 대해 positive를 생성하기 위해 data-augmentation을 사용함
- Framework
- Unaltered audio pattern을 capture 하기 위해, 논문은 longer audio segment와 data-augmentation 없이 $u_{i}$에서 sampling 한 reference segment $\hat{\mathbf{x}}_{i}$를 도입함
- 추가적으로 framework에 다음 2개의 memory queue가 적용됨:
- Reference representation $\{\hat{\mathbf{y}}_{i}\}_{i\in \mathcal{I}}$를 store 하기 위한 size $(| \hat{\mathbf{Q}}|,D_{repr})$의 $\hat{\mathbf{Q}}$
- Positive embedding $\{ \mathbf{z}'_{i}\}_{i\in\mathcal{I}}$를 store 하기 위한 size $(|\mathbf{Q}'|,D_{emb})$의 $\mathbf{Q}'$
- SSPS는 pre-defined standard SSL training epoch 이후 enable 되고, $\mathbf{Q}'$에서 pseudo-positive embedding을 sampling 하여 $\mathbf{z}'$를 $\mathbf{q}'_{pos(i)}$로 replace 함
- Pseudo-Positives Sampling
- 각 SSPS epoch beginnig에서 reference representation $\hat{\mathbf{Q}}$에 대해 $k$-means clustering을 수행하여 utterance를 $K$ cluster로 grouping 함
- SSL representation이 improve 됨에 따라 assignment는 progressively refine 됨 - $c_{i}$를 $i$-th utterance의 cluster index, $\mathbf{m}_{k}$를 $k$-th cluster의 centroid라 했을 때, SSPS는 pseudo-positive를 sampling 하는 cluster $\hat{c}_{i}$를 결정하기 위해 다음의 2가지 방법을 고려함
- Same-Cluster Sampling
- Anchor cluster의 utterance는 $K$가 train set의 speaker identity 수와 가까울 때 CA-DINO와 유사한 pseudo-positive로 취급할 수 있음:
(Eq. 3) $\hat{c}_{i}=c_{i}$
- Anchor cluster의 utterance는 $K$가 train set의 speaker identity 수와 가까울 때 CA-DINO와 유사한 pseudo-positive로 취급할 수 있음:
- Neighboring-Clusters Sampling
- Channel-related information이 speaker-related information 보다 먼저 modeling 된다고 가정하면, neighboring cluster의 utterance도 larger $K$를 select 했을 때 pseudo-positive로 볼 수 있음:
(Eq. 4) $ \hat{c}_{i}=\text{sample}(\mathcal{C}_{c_{i}})$
- $\text{sample}(S)$ : $S$의 uniform random selection - $\mathcal{C}_{k}$는 $k$-th cluster의 $M$ nearest cluster를 구성함:
(Eq. 5) $\mathcal{C}_{k}\triangleq\text{top}_{j\neq k}M\left(\{ \text{sim}(\mathbf{m}_{k},\mathbf{m}_{j})\},\forall j\in [1,K]\right)$
- $\text{top} M(S)$ : $S$의 largest $M$ value에 대한 index를 descending order로 return 하는 역할
- Channel-related information이 speaker-related information 보다 먼저 modeling 된다고 가정하면, neighboring cluster의 utterance도 larger $K$를 select 했을 때 pseudo-positive로 볼 수 있음:
- 결과적으로 SSPS는 $\hat{c}_{i}$를 따라 $i$-th sample에 대해 pseudo-positive를 select 함:
(Eq. 6) $pos(i)=\text{sample}(\mathcal{S}_{\hat{c}_{i}})$
- $\mathcal{S}_{c}\triangleq\{i\in\mathcal{I}\,\,\text{s.t.}\,\, c_{i}=c\}$ : 주어진 cluster의 training sample index
- $\mathbf{q}'_{pos(i)}$가 $\mathbf{Q}'$에 존재하지 않으면 default SSL positive sampling이 수행됨
- 각 SSPS epoch beginnig에서 reference representation $\hat{\mathbf{Q}}$에 대해 $k$-means clustering을 수행하여 utterance를 $K$ cluster로 grouping 함
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : VoxCeleb2
- Comparisons : SimCLR, DINO
- Results
- SSPS를 ECAPA-TDNN에 적용하면 더 나은 SV 성능을 얻을 수 있음

- 다른 SSL method와 비교하여도 SSPS의 성능이 더 우수함

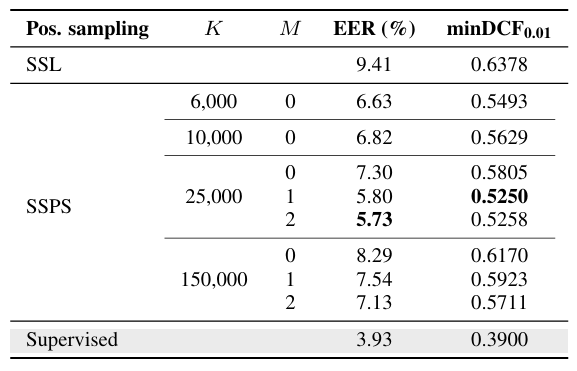
- Selection of SSPS Hyperparameters
- $K=25000, M=2$일 때 최적의 성능을 달성함
- Visualization of Speaker Representations
- $t$-SNE 측면에서 SSPS는 intra-class variance가 적고 서로 멀리 떨어진 cluster를 가짐

반응형
'Paper > Verification' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

