티스토리 뷰
Paper/Representation
[Paper 리뷰] DiceHuBERT: Distilling HuBERT with a Self-Supervised Learning Objective
feVeRin 2025. 8. 28. 17:05반응형
DiceHuBERT: Distilling HuBERT with a Self-Supervised Learning Objective
- Compact Self-Supervised Learning-based speech foundation model이 필요함
- DiceHuBERT
- HuBERT의 iterative self-distillation mechanism을 활용하여 original model을 student model로 directly replace
- HuBERT pre-training과 동일한 objective를 사용해 additional module, architectural constraint를 eliminate
- 논문 (INTERSPEECH 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Self-Supervised Learning (SSL)-based speech foundation model은 다양한 speech task에서 활용되고 있지만, 상당한 model size로 인해 mobile applicaiton에는 부적합함
- 이를 해결하기 위해 DPHuBERT, FitHuBERT, ARMHuBERT 등과 같이 Knowledge Distillation을 활용하여 model size를 effectively compress 할 수 있음
- 특히 해당 방식들은 일반적으로 teacher model과 student model 간의 layer-wise feature를 aligning 하여 knowledge를 distilling 함
- BUT, original SSL objective를 overlook 하고 student에 architectural constraint를 impose 할 수 있음
-> 그래서 original SSL objective를 활용한 distilled SSL model인 DiceHuBERT를 제안
- DiceHuBERT
- Teacher model과 동일한 SSL objective를 사용하고, teacher model feature의 $k$-means centroid에서 생성된 target을 활용하여 knowledge distillation을 수행
- 특히 HuBERT pre-training의 iterative self-distillation을 활용하여 knowledge를 progressively distill
< Overall of DiceHuBERT >
- Teacher model의 SSL objective를 활용하여 additional constraint 없이 distill 된 SSL model
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 성능을 달성
2. Preliminaries
- Prior HuBERT Distillation
- FitHuBERT, ARMHuBERT, DistilHuBERT 등의 기존 방식은 pre-trained second-iteration HuBERT model을 teacher model로 사용하여 student model로 layer-wise feature distillation을 수행함
- 특히 student model은 teacher와 동일한 수의 layer를 가지고 layer output 간의 direct distillation을 지원함
- Distillation objective는 teacher, student feature 간의 Mean Squared Error (MSE)로 정의됨 - 이때 student $S$의 feature dimension $D^{S}$를 teacher $T$의 feature dimension $D^{T}$와 align 하기 위해 linear projection layer $W_{(l)}\in\mathbb{R}^{D^{S}\times D^{T}}$가 적용됨:
(Eq. 1) $ \mathcal{L}_{feat}=\sum_{l\in \{1,...,L\}}\alpha_{(l)}\text{MSE}\left( H^{T}_{(l)},H^{S}_{(l)}W_{(l)}\right)$
- $H_{(l)}$ : $l$-th layer의 feature form
- $\alpha_{(l)}$ : 각 layer loss에 대한 weight
- 특히 student model은 teacher와 동일한 수의 layer를 가지고 layer output 간의 direct distillation을 지원함
- HuBERT Pre-Training
- HuBERT는 masked token prediction task에 기반한 SSL speech representation model로써, pre-training process는 $N$ iteration으로 수행됨
- 여기서 각 iteration은 distinct target을 가지지만, input feature의 target인 randomly masked timestamp를 predict 하는 동일한 learning obejctive를 사용함
- 즉, SSL loss는 masked timestamp에 대해 compute 된 cross-entropy loss로 정의됨:
(Eq. 2) $\mathcal{L}_{SSL}=-\sum_{t\in M}\log p\left(z_{t}|\tilde{X},t\right)$
- $M$ : masked timestamp set, $\tilde{X}$ : speech utterance $X=[x_{1},...,x_{T}]$에 $M$을 적용하여 얻어진 masked input, $z_{t}$ : timestamp $t$의 target class - 한편으로 target은 $k$-means clustering을 통해 generate 됨
- First iteration에서는 MFCC feature가 사용되고, 이후 $N$ iteration에서는 previous $N-1$th iteration model의 6-th layer hidden feature를 clustering input으로 사용하여 $N$-th model의 target을 generate 함
- 이때 각 following iteration은 previous iteration의 pre-trained feature를 사용하여 model training을 guide 하는 self-distillation process로 볼 수 있음
- 여기서 각 iteration은 distinct target을 가지지만, input feature의 target인 randomly masked timestamp를 predict 하는 동일한 learning obejctive를 사용함
3. Method
- DiceHuBERT는 $N$ (teacher) iteration에서 $N+1$ (student) iteration으로 transition 할 때, model size를 줄이기 위해 original SSL objective를 maintain 하는 HuBERT iterative self-distillation process를 활용함
- 특히 해당 approach는 additional distillation framework가 필요하지 않으므로 HuBERT의 pre-training framework를 directly reuse 할 수 있음
- 따라서 DiceHuBERT는 architecture-agnostic 하고 student model architecture selection에 대한 flexibility를 제공함 - Teacher model과 동일한 SSL objective를 사용하므로 앞선 (Eq. 1)의 MSE loss 보다 더 robust 한 representation을 학습할 수 있음
- 특히 해당 approach는 additional distillation framework가 필요하지 않으므로 HuBERT의 pre-training framework를 directly reuse 할 수 있음
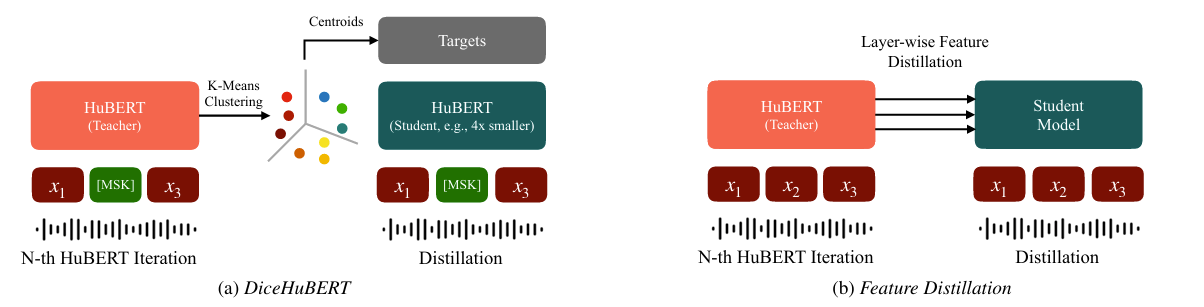
- Student Architecture
- 논문은 student architecture에 대해 feature dimension $D^{S}$, layer 수 $L$의 2가지 aspect를 고려함
- 특히 기존 HuBERT-base model을 modify 하여 HuBERT-shallow, HuBERT-narrow를 구축함
- HuBERT-shallow의 경우 layer 수를 reduce 하고, HuBERT-narrow의 경우 feature dimension과 intermediate feed-forward dimension을 reduce 함
- Target Labels
- 논문은 SSL objective를 위해 다음 2가지의 distinct target label을 고려함
- 먼저 hard label은 $N$-th iteration HuBERT model에서 intermediate feature의 $k$-means clustering을 통해 생성됨
- 해당 label은 one-hot encode 되고, (Eq. 2)의 cross-entropy loss를 적용할 수 있음 - Soft label은 각 feature와 $k$-means에 의해 생성된 모든 centroid 간의 distance로 얻어지고, softmax를 적용하여 각 cluster probability를 estimate 함
- 여기서 hard label은 해당 distance의 $\arg\min$을 통해 compute 됨
- 그러면 feature $H$에 대해, centroid $H_{i}$를 가지는 $i$-th cluster의 probability $p(i|H)$는:
(Eq. 3) $ p(i|H)=\frac{\exp\left(-\rho(H,H_{i})/\tau\right)}{\sum_{j=\{1,...,K\} } \exp\left(-\rho(H,H_{j})/\tau\right)}$
- $\rho(\cdot, \cdot)$ : representation 간의 $L2$ distance
- $K$ : cluster 수, $\tau$ : temperature - 결과적으로 soft label에 대한 SSL loss는 student model의 output class distribution과 teacher model의 soft label 간의 KL-divergence로 정의됨
- 먼저 hard label은 $N$-th iteration HuBERT model에서 intermediate feature의 $k$-means clustering을 통해 생성됨
4. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : LibriSpeech
- Comparisons : Wav2Vec 2.0, HuBERT, DistilHuBERT, FitHuBERT, DPHuBERT, ARMHuBERT, STaRHuBERT
- Results
- 전체적으로 DiceHuBERT의 성능이 가장 뛰어남

- Student Architecture
- HuBERT-base의 feature dimension $D_{base}$에 대해, $D^{S}=D_{base}/2$로 student를 설정했을 때 최고의 성능을 달성함

- Distillation Method
- $\mathcal{L}_{SSL}$을 사용했을 때 우수한 distillation 성능을 달성함
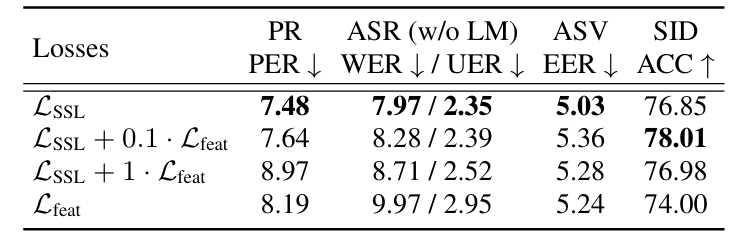
- Target Label
- $\tau=5$의 soft label을 사용하면 더 나은 성능을 달성할 수 있음

- Teachers
- Distillation을 통해 얻어진 student가 teacher 보다 더 나은 성능을 보임

반응형
'Paper > Representation' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

