티스토리 뷰
Paper/Representation
[Paper 리뷰] HuBERT-AGG: Aggregated Representation Distillation of Hidden-Unit BERT for Robust Speech Recognition
feVeRin 2025. 9. 6. 08:07반응형
HuBERT-AGG: Aggregated Representation Distillation of Hidden-Unit BERT for Robust Speech Recognition
- Automatic Speech Recognition을 위한 Self-Supervised Learning은 noise robustness 측면에서 한계가 있음
- HuBERT-AGG
- Aggregated layer-wise representation을 distill 하여 noise-invariant SSL representation을 학습
- 특히 labeled data의 small portion을 활용해 pre-trained vanilla HuBERT의 모든 hidden state에 대한 weighted sum을 compute 하는 aggregator를 도입
- 논문 (ICASSP 2023) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Wav2Vec 2.0, W2V-BERT, HuBERT와 같은 Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) method는 Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR)과 같은 다양한 downstream task에서 우수한 성능을 보이고 있음
- 특히 HuBERT는 MFCC 또는 latent embedding을 clustering 하여 pseudo-label을 얻고, randomly masked frame을 classify 하는 방식으로 iteratively optimize 됨
- BUT, 대부분의 SSL method는 noise robustness 측면에서 한계가 있음
- 이를 위해 Speech Enhancement (SE) module을 integrate 하거나 cacaded framework를 고려할 수 있지만, noise-robust ASR system의 complexity를 증가시킴
-> 그래서 noise-robust ASR을 위한 SSL representation인 HuBERT-AGG를 제안
- HuBERT-AGG
- Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) criterion을 사용하여 vanilla HuBERT를 fine-tuning 하고,pre-trained HuBERT의 multiple hidden state에 대한 weighted sum을 compute 하는 aggregator를 도입
- Original-noisy speech pair와 aggregator에 대한 knowledge distillation을 수행
< Overall of HuBERT-AGG >
- Aggregator와 knowledge distillation을 활용한 noise-robust HuBERT representation
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 ASR 성능을 달성
2. Method
- HuBERT
- HuBERT는 BERT-like prediction loss에 aligned target label을 제공하는 offline clustering step을 활용함
- 이때 HuBERT는 masked region에 대해서만 prediction loss를 적용하여 model이 continuous input에 대한 combined acoustic, language model을 학습하도록 force 함
- 구조적으로 HuBERT backbone는 identical HuBERT block으로 구성된 BERT mask predictor와 convolutional waveform encoder를 사용함
- Convolutional encoder를 통해 encode 된 speech embedding sequence $X=[x_{1},...,x_{T}]$가 주어지면
- HuBERT의 mask predictor는 masked version $\tilde{X}$를 input으로 사용하여 각 time step $t$에서 target codeword에 대한 distribution을 predict 함
- 이때 codeword distribution은 다음과 같이 parameterize 됨:
(Eq. 1) $p(c|\tilde{X},t)=\frac{\exp\left(\text{sim}\left(\phi(\tilde{X})_{t}\mathbf{W},\mathbf{e}_{c}\right)/\tau \right)}{ \sum_{c'=1}^{C}\exp\left(\text{sim}\left(\phi(\tilde{X})_{t}\mathbf{W},\mathbf{e}_{c'}\right)/\tau\right)}$
- $C$ : total codeword 수, $\mathbf{e}_{c}$ : codeword $c$의 embedding
- $\mathbf{W}$ : projection matrix, $\phi(\tilde{X})_{t}$ : step $t$의 output feature sequence
- $\text{sim}(\cdot,\cdot)$ : cosine-similarity, $\tau$ : scaling parameter - $z_{t}\in[C]$를 $C$-class categorical variable, $X$에 대한 discrete target sequence를 $Z=[z_{1},z_{2},...,z_{T}]$라 했을 때, HuBERT의 masked region에 대한 prediction loss는:
(Eq. 2) $\mathcal{L}_{m}(\tilde{X})=\sum_{t\in M}\log p\left(z_{t}|\tilde{X},t\right)$
- $M\subset \{1,...,T\}$ : $X$의 masked time step - HuBERT는 clustered codeword의 assignment를 iteratively refine 함
- First iteration에서는 training data의 MFCC feature를 clustering 하여 codeword를 assign 하고
- 이후에는 previous iteration에서 생성된 latent representation을 clustering 하여 codeword를 assign 함

- HuBERT-NIT
- 먼저 논문은 original-noisy speech pair를 사용하여 HuBERT에 noise-invariant training을 incorporate 하는 HuBERT-NIT를 고려함
- Original speech를 $X$, encoded noisy speech를 $\hat{X}$라고 하자
- 논문은 original speech encoding $\phi^{l}(X)$ 기반의 pre-trained vanilla HuBERT와, masked noisy speech encoding $\phi_{NIT}^{l}(\hat{X})$ 기반의 HuBERT-NIT가 생성한 encoding 간의 $L2$, cosine distance를 penalize 함 - 해당 regularization term은 layer-wise manner로 적용됨:
(Eq. 3) $ \mathcal{L}_{d}\left(\phi^{l}(X),\phi_{NIT}^{l}(\hat{X})\right)=\left|\left| \phi^{l}(X)-\phi^{l}_{NIT}(\hat{X})\right|\right|^{2}-\frac{\phi^{l}(X)\cdot \phi_{NIT}^{l}(X)}{ \left|\left| \phi^{l}(X)\right|\right|\cdot \left|\left| \phi_{NIT}^{l}(\hat{X})\right|\right|}$
(Eq. 4) $\mathcal{L}_{d\text{-}NIT}=\sum_{l=1}^{L}\mathcal{L}_{d}\left(\phi^{l}(X),\phi_{NIT}^{l}(\hat{X})\right)$
- $L$ : encoder layer 수
- HuBERT-NIT를 training 할 때 vanilla HuBERT의 parameter는 freeze 됨 - HuBERT-NIT의 output distribution $\hat{O}$는 vanilla HuBERT output $O$에 대한 Kullback-Leibler Divergence (KLD)를 통해 supervise 됨:
(Eq. 5) $\mathcal{L}_{KLD}=\sum_{t=1}^{T}O_{t}\left(\log O_{t}-\log \hat{O}_{t}\right)$ - 결과적으로 HuBERT-NIT의 final loss는 $\mathcal{L}_{d\text{-}NIT}, \mathcal{L}_{KLD}$의 weighted sum으로 얻어짐:
(Eq. 6) $\mathcal{L}_{NIT}=\lambda_{1}\mathcal{L}_{d\text{-}NIT}+\lambda_{2}\mathcal{L}_{KLD}$
- Original speech를 $X$, encoded noisy speech를 $\hat{X}$라고 하자
- HuBERT-AGG
- HuBERT-AGG는 ASR task에 exclusively optimize 된 aggregated representation을 distilling 함으로써 learned noise-invariant representation을 개선함
- 이를 위해 pre-trained HuBERT의 encoder layer에 대한 weighted-sum을 compute 하는 aggregator가 도입됨
- 먼저 distillation을 위한 aggregator는 CTC criterion을 따라 training 되어 ASR task를 위한 aggregated representation을 추출함
- Pre-trained vanilla HuBERT의 $L$ layer representation을 $\mathbf{H}=[\mathbf{h}_{1},\mathbf{h}_{2},...,\mathbf{h}_{L}]$, aggregator를 vector $\mathbf{a}=[a_{1},a_{2},...,a_{L}]$이라고 하자
- $a_{l}$ : weighted-sum을 위한 $\mathbf{h}_{l}$의 해당 weight - 그러면 aggregated representation은 $\bar{\mathbf{h}}=\mathbf{aH}^{\top}$과 같음
- 따라서 $\mathcal{L}_{d\text{-}NIT}$를 modify 하고 $\bar{\mathbf{h}}$를 HuBERT-AGG last encoder layer의 target으로 사용할 수 있음:
(Eq. 7) $\mathcal{L}_{d\text{-}AGG}=\sum_{l=1}^{L-1}\mathcal{L}_{d}\left( \phi^{l}(X),\phi_{AGG}^{l}(\hat{X})\right)+\left|\left| \bar{\mathbf{h}}-\phi_{AGG}^{l}(\hat{X})\right|\right|^{2} - \frac{\bar{\mathbf{h}}\cdot \phi_{AGG}^{l}(X)}{\left|\left|\bar{\mathbf{h}}\right|\right|\cdot \left|\left| \phi^{l}_{AGG}(\hat{X})\right|\right|}$
- Pre-trained vanilla HuBERT의 $L$ layer representation을 $\mathbf{H}=[\mathbf{h}_{1},\mathbf{h}_{2},...,\mathbf{h}_{L}]$, aggregator를 vector $\mathbf{a}=[a_{1},a_{2},...,a_{L}]$이라고 하자
- 추가적으로 HuBERT-AGG last layer는 aggregated representation을 통해 supervise 되므로 (Eq. 2)의 $\mathcal{L}_{KLD}$를 original HuBERT loss로 replace 해야 함
- 결과적으로 HuBERT-AGG의 final loss는:
(Eq. 8) $\mathcal{L}_{AGG}=\lambda_{1}\mathcal{L}_{d\text{-}NIT}+\lambda_{2}\mathcal{L}_{m}$
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : LibriLight, LibriSpeech + MUSAN
- Comparisons : HuBERT
- Results
- 전체적으로 HuBERT-AGG을 활용하면 WER을 개선할 수 있음
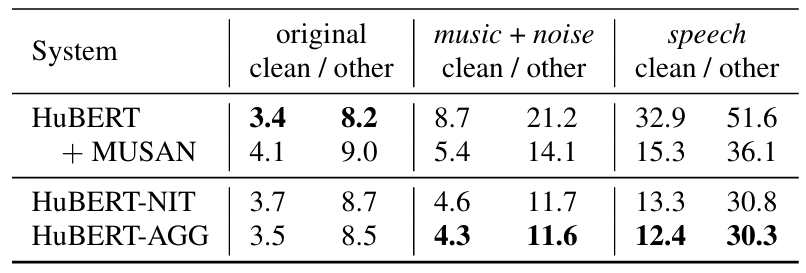
- Investigating Choice for $D_{AGG}$
- Aggregator를 training 하는데 필요한 data 양은 ASR 성능에 큰 영향을 주지 않음

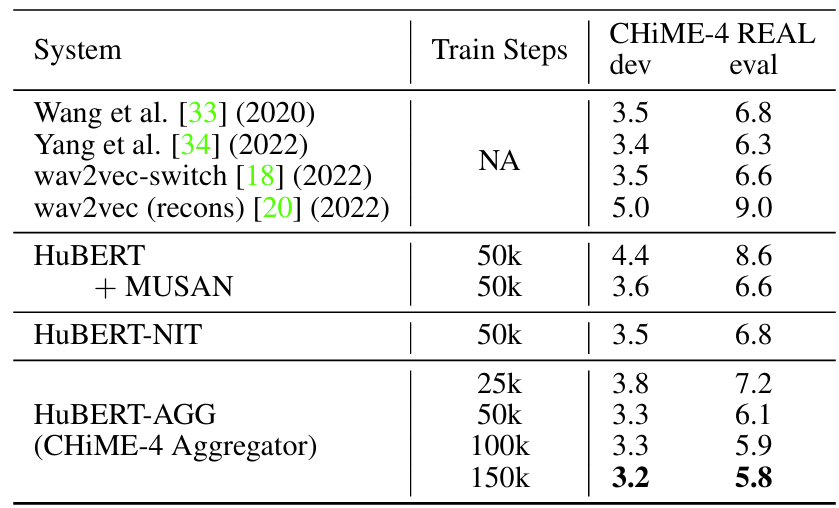
- Results on Real-World Noisy Speech
- Noisy speech에 대해서도 HuBERT-AGG는 우수한 성능을 보임
반응형
'Paper > Representation' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

