티스토리 뷰
Paper/Representation
[Paper 리뷰] DinoSR: Self-Distillation and Online Clustering for Self-Supervised Speech Representation Learning
feVeRin 2025. 8. 31. 08:41반응형
DinoSR: Self-Distillation and Online Clustering for Self-Supervised Speech Representation Learning
- Speech를 위한 strong representation learning model이 필요함
- DinoSR
- Masked language modeling, self-distillation, online clustering을 combine
- Teacher network를 사용하여 input audio에서 contextualized embedding을 추출하고, embedding에 online clustering을 적용하고, discretized token을 통해 student network를 guide
- 논문 (NeurIPS 2023) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Self-supervised speech representation learning은 speech recognition, translation 등의 다양한 downstream task에서 우수한 성능을 달성함
- 먼저 Masked Language Modeling (MLM)은 unmasked context를 기반으로 masked part를 predict 함
- Data2Vec과 같은 self-distillation representation learning의 경우
- Student를 guide 하는 teacher를 training 하는데 필요한 labeled data의 의존성을 줄일 수 있음
- 이때 model은 data augmentation이나 masking을 통해 augment 된 unlabled data의 paired relation을 사용하여 training 됨
- 한편으로 $k$-means와 같은 clustering algorithm은 vector quantization에서 주로 활용됨
- 대표적으로 Wav2Vec 2.0은 clustering을 information bottleneck으로 사용하여 ideal representation을 얻음
-> 그래서 앞선 method들을 complement 한 strong representation learning model인 DinoSR을 제안
- DinoSR
- Teacher network를 사용해 input audio에서 contextualized embedding을 추출
- 해당 embedding에 online clustering을 적용해 machine-discovered phone inventory를 생성
- 최종적으로 discretized token을 사용하여 student network를 guide
< Overall of DinoSR >
- Self-distillation과 Online clustering을 combine 한 self-supervised learning model
- 결과적으로 다양한 downstream task에 대해 기존보다 우수한 성능을 달성
2. Method
- Self-Distillation Paradigm
- DinoSR은 student network $\theta_{student}$를 teacher network $\theta_{teacher}$의 guide를 따라 training 하는 것을 목표로 함
- Teacher, student는 모두 동일한 $K$-layer Transformer architecture를 사용함
- Self-distillation framework에서 teacher network는 training 시작 시에 randomly initialize 된 student network의 simple copy와 같음 - 한편으로 trivial solution $\theta_{student}=\theta_{teacher}$를 방지하기 위해, framework training 시에는 각 model이 동일한 input data에 대해 서로 다른 view를 생성해야 함
- 이를 위해 논문은 Data2Vec을 따라 input masking을 사용함
- 그러면 input speech는 student model을 위해 partially mask 되어 masked representation $\mathbf{z}_{t}^{K}\in\mathbb{R}^{D}$를 생성함
- $t=1,...,T$ : sequence length - Teacher model의 input은 unmask 되고, 이때 output representation은 $\tilde{\mathbf{z}}_{t}^{K}$와 같음
- Parameter update policy의 경우, student network는 gardient descent로 update 되는 반면 teacher model은 Exponential Moving Average (EMA)를 통해 student network parameter를 tracking 하여 update 됨:
(Eq. 1) $\theta_{teacher}\leftarrow \lambda\theta_{teacher}+(1-\lambda)\theta_{student}$
- $\lambda$ : decay rate
- Teacher, student는 모두 동일한 $K$-layer Transformer architecture를 사용함
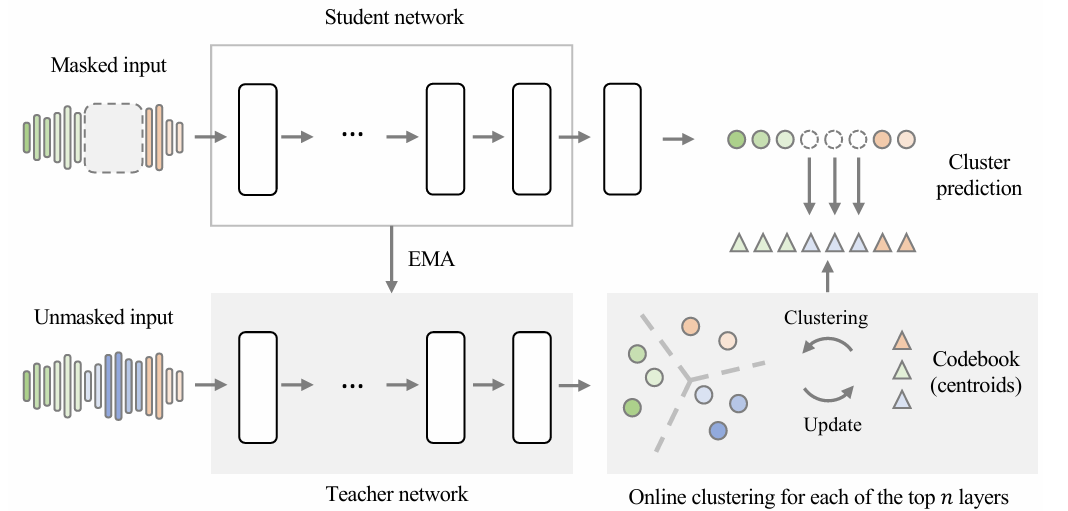
- Self-Supervised Learning with DinoSR
- Acoustic Unit Discovery with Online Clustering
- 논문은 teacher에 online acoustic unit discovery system을 적용하여 contextualized representation을 제공함
- 이때 MFCC나 pre-trained representation에 대해 $k$-means clustering을 적용하는 기존 approach와는 달리, 논문의 unit discovery system은 teacher model이 student와 함께 evolve 하므로 fix 되지 않음
- 이를 해결하기 위해, DinoSR은 teacher network의 multiple layer에서 online clustering을 수행함
- 먼저 top $N$ layer 내 teacher model의 $k$-th layer (i.e., $k\in (K-N,K]$)에 대해 codebook $\mathbf{E}^{k}=\{ \mathbf{e}_{1}^{k},...,\mathbf{e}_{V}^{k}\}$를 도입함
- $V$는 codeword 수, $\mathbf{e}_{i}^{k}\in\mathbb{R}^{D}$ - 그러면 codebook은 다음과 같이 update 됨:
- 각 codebook entry $v$에 대해, codebook을 따라 $v$의 current representation에 closest 한 teacher output frame의 set $\tilde{\mathbf{Z}}_{v}^{k}$를 생성함:
(Eq. 2) $\tilde{\mathbf{Z}}_{v}^{k}=\left\{\tilde{\mathbf{z}}_{t}^{k}\left| v=\arg\min_{i\in V} \left|\left| \tilde{\mathbf{z}}_{t}^{k}-\mathbf{e}_{i}^{k}\right|\right|_{2}\right.\right\}$
- Set index $v$는 student model training을 위한 pseudo-label로 사용됨 - 이후 각 codeword는 EMA를 사용하여 embedding의 weighted sum으로 update 됨:
(Eq. 3) $\mathbf{s}_{v}^{k}\leftarrow \tau\mathbf{s}_{v}^{k}+(1-\tau)\sum\tilde{\mathbf{Z}}_{v}^{k}$
$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, n_{v}^{k}\leftarrow\tau n_{v}^{k}+(1-\tau)\left|\tilde{\mathbf{Z}}_{v}^{k}\right|$
$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, \mathbf{e}_{v}^{k}\leftarrow \frac{\mathbf{s}_{v}^{k}}{n_{v}^{k}}$
- 각 codebook entry $v$에 대해, codebook을 따라 $v$의 current representation에 closest 한 teacher output frame의 set $\tilde{\mathbf{Z}}_{v}^{k}$를 생성함:
- 각 codeword $\mathbf{e}_{v}^{k}$에 대해, first term $\mathbf{s}_{v}^{k}$는 all neighboring teacher representation의 sum (i.e., (Eq. 2)의 $\tilde{\mathbf{Z}}_{v}^{k}$)를 track 하고, second term $n_{v}^{k}$는 neighbor의 amount를 track 함
- 두 term 모두 decay rate $\tau$를 사용하여 EMA로 approximate 되므로 neighbor set의 moving average인 codeword $\mathbf{e}_{v}^{k}$를 얻을 수 있음
- 실제로 $t\in M$인 frame의 subset에서 online clustering을 수행하면 computation을 reduce 할 수 있음 - Initialization의 경우, $\mathbf{s}_{v}^{k}$는 $\mathbf{e}_{v}^{k}$로 $n_{v}^{k}$는 $1$로 설정함
- 두 term 모두 decay rate $\tau$를 사용하여 EMA로 approximate 되므로 neighbor set의 moving average인 codeword $\mathbf{e}_{v}^{k}$를 얻을 수 있음
- 논문은 codeword를 neighboring representation을 통해 정의하므로 codeword를 teacher model에서 discover 된 acoustic unit으로 취급할 수 있고, student network training에 사용할 수 있음
- 이때 clustering process는 end-to-end fashion으로 frame의 context에 따라 discrete label을 생성함
- 논문은 teacher에 online acoustic unit discovery system을 적용하여 contextualized representation을 제공함
- Online Clustering vs. Vector Quantization
- VQ-Wav2Vec와 같은 Vector Quantization (VQ) method는 embedding space를 discretize 하여 model의 dimensionality를 reduce 하고 downstream task의 성능을 향상함
- 특히 discretized representation은 model-discovered acoustic unit으로 취급할 수 있음 - 한편으로 DinoSR의 online clustering은 VQ와 유사하지만, gradient-free embedding space에서 pseudo-label로 사용할 수 있는 acoustic unit을 추출함
- 이를 통해 computational cost를 reduce 하고, VQ의 non-differentiable nature로 인한 estimation 과정 (straight-through gradient estimation)을 bypass 하고, code-collapse 문제를 mitigate 할 수 있음
- VQ-Wav2Vec와 같은 Vector Quantization (VQ) method는 embedding space를 discretize 하여 model의 dimensionality를 reduce 하고 downstream task의 성능을 향상함
- Self-Supervised Learning via Cluster Prediction
- Training objective는 student model $\mathbf{z}_{t}^{K}$의 각 output frame에 대해, teacher model의 codeword index $v$를 모든 targeted layer에서 predict 하는 것과 같음 ($\tilde{\mathbf{z}}_{t}^{k}\in\tilde{\mathbf{Z}}_{v}^{k}$):
(Eq. 4) $ \sum_{t\in M}\sum_{k\in(K-N,K]}\log p_{\phi_{k}}\left(v|\mathbf{z}_{t}^{K}\right)$
- $M$ : all masked timestep의 set, $\phi_{k}$ : 각 target layer $k$에 대해 Softmax activation을 가지는 $\mathbb{R}^{D\times V}$의 linear projection으로 구성된 prediction head - 여기서 prediction head는 student model의 last layer $K$에 위치하고, target layer $k$와는 무관함
- Training objective는 student model $\mathbf{z}_{t}^{K}$의 각 output frame에 대해, teacher model의 codeword index $v$를 모든 targeted layer에서 predict 하는 것과 같음 ($\tilde{\mathbf{z}}_{t}^{k}\in\tilde{\mathbf{Z}}_{v}^{k}$):

3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : LibriSpeech
- Comparisons : Wav2Vec 2.0, HuBERT, Data2Vec, ContentVec, WavLM
- Results
- 전체적으로 DinoSR은 뛰어난 speech recognition 성능을 보임
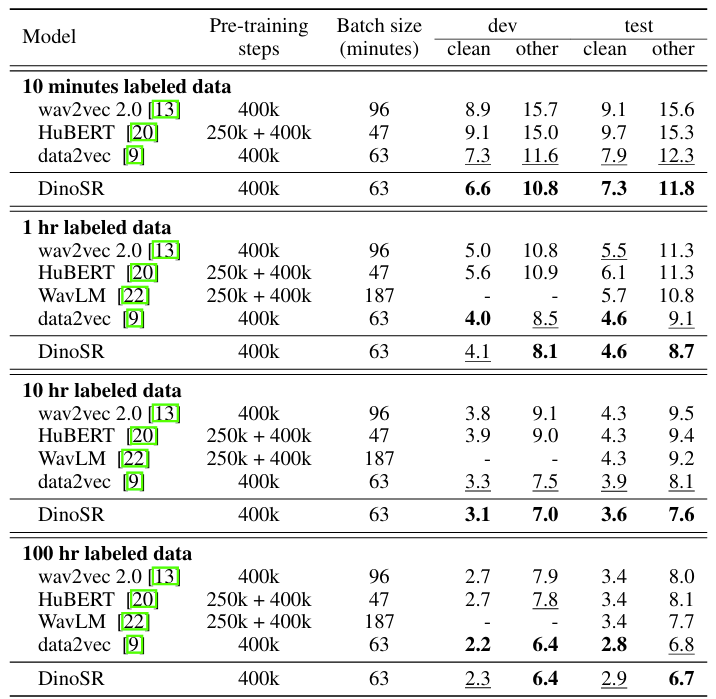
- 더 많은 processed audio를 사용할수록 WER을 향상할 수 있음

- Acoustic Unit Discovery
- Acoustic unit discovery task에 대해서도 DinoSR은 가장 우수한 성능을 보임

- Downstream Evaluation
- SUPERB benchmark에 대해서도 DinoSR은 최고의 성능을 달성함

- Impact of Codebook Hyperparameter
- Codebook size $V$ 보다 layer 수 $N$을 변경하는 것이 WER에 더 민감함

- $0.9$ 이상의 codebook decay $\tau$는 불필요함

- Cluster Quality
- DinoSR은 높은 cluster quality를 가짐

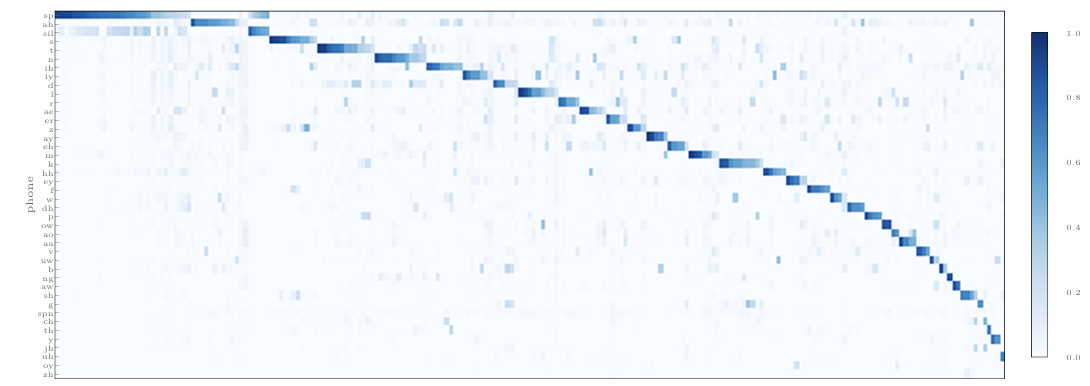
- Mapping Phones to Codewords
- Conditional probability $P(\text{phone}| \text{code})$를 확인해 보면, 각 codeword는 하나의 phone에만 concentrate 함
- Codeword는 phone distribution의 long-tail nature를 capture 함
반응형
'Paper > Representation' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

