티스토리 뷰
Paper/TTS
[Paper 리뷰] CLAPSpeech: Learning Prosody from Text Context with Contrastive Language-Audio Pre-training
feVeRin 2024. 7. 27. 12:14반응형
CLAPSpeech: Learning Prosody form Text Context with Contrastive Language-Audio Pre-training
- Expressive text-to-speech를 위한 masked token reconstruction은 prosody를 효과적으로 모델링하는 것이 어려움
- CLAPSpeech
- 서로 다른 context에서 동일한 text token의 prosody variance를 explicitly learning 하는 cross-modal contrastive pre-training framework를 활용
- Encoder input과 contrastive loss를 설계하여 joint multi-modal space에서 text context와 해당 prosody pattern을 connect 함
- Multi-scale pre-training pipeline을 채택해 multiple level의 prosody pattern을 capture
- 논문 (ACL 2023) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Expressive text-to-speech (TTS)는 주로 FastSpeech2와 같은 external variation predictor (predictor-based, PB)나 Glow-TTS 같은 variational generative model (variation-based, VB)를 기반으로 prosody variance를 inject 함
- 한편으로 expressive TTS를 위해 masked language/acoustic model을 활용해 더 나은 text representation learning을 수행할 수도 있지만 다음의 단점을 가짐:
- Reconstruction loss로 prosody를 implicitly learning 하기 때문에 prosody modeling의 한계가 있음
- Pronunciation space와 prosody space를 decouple 하지 못함
- 특히 speech는 text context/speaker 같은 서로 다른 condition에서 동일한 token의 pitch/duration variance로 취급할 수 있음
- e.g.) 동일한 word "higher"에 대해 "higher up", "slightly higher"는 서로 다른 prosody를 가짐
- 한편으로 expressive TTS를 위해 masked language/acoustic model을 활용해 더 나은 text representation learning을 수행할 수도 있지만 다음의 단점을 가짐:
-> 그래서 text-speech joint multi-modal space에서 high-level prosody pattern과 text context를 connect 할 수 있는 CLAPSpeech를 제안
- CLAPSpeech
- Text context에서 prosody를 예측하는 text encoder와 selected token segment에서 ground-truth prosody를 추출하는 prosody encoder를 활용
- Phoneme, word level에서 각각 prosody information을 capture 하기 위해 2개의 CLAPSpeech model을 학습하는 multi-scale pre-training framework를 도입
- 추가적으로 pre-training stage 이후 CLAPSpeech는 모든 TTS model에 적용 가능한 plug-in text encoder로 취급되어 fine-grained prosody representation을 제공
< Overall of CLAPSpeech >
- Contrastive obejctive를 통해 prosody를 explicitly learning 하여 TTS의 prosody representation을 향상
- Front-end network architecture를 간단히 수정하여 쉽게 적용 가능
- 결과적으로 기존보다 뛰어난 음성 합성 품질을 달성
2. Method
- CLAPSpeech는 TTS에서 더 나은 prosody prediction이 가능한 text representation을 제공하기 위해 corss-modal contrastive learning을 도입함
- 아래 그림과 같이 CLAPSpeech는 text encoder, prosody encoder로 구성되고, joint prosody space에서 text token과 speech segment를 connect 하는 것을 목표로 함
- 이를 통해 text encoder는 text context를 효과적으로 처리하고, prosody encoder는 timbre와 같은 other variable을 제거함으로써 speech segment에서 high-level prosody pattern을 추출할 수 있음 - Multi-scale contrastive pre-training framework의 경우, CLAPSpeech가 phoneme/word-level 모두에서 prosody를 capture 할 수 있도록 함
- 이후 얻어진 pre-trained text encoder를 TTS model에 plug-in 하여 prosody prediction을 개선할 수 있음
- 아래 그림과 같이 CLAPSpeech는 text encoder, prosody encoder로 구성되고, joint prosody space에서 text token과 speech segment를 connect 하는 것을 목표로 함

- Text Encoder and Prosody Encoder
- 동일한 pronounceable token의 prosody는 text context에 따라 다르므로, CLAPSpeech는 text context와 high-level prosody pattern 간의 correlation을 모델링하는 것을 목표로 함
- 이를 위해 text/prosody encoder를 설계하여 text-speech multi-modal prosody embedding space를 구성 - 먼저 text encoder는 input text의 phoneme과 Byte Pair Encoding (BPE)를 input으로 활용함
- 해당 phoneme/BPE sequence는 phonological habit과 semantic information과 관련된 prosodic pattern을 추출하는데 도움을 줌
- 구조적으로 text encoder는 Feed-Forward Transformer (FFT) block을 기반으로 함
- 이때 phoneme/BPE sequence를 개별적으로 처리하기 위해 2개의 independent FFT block을 활용
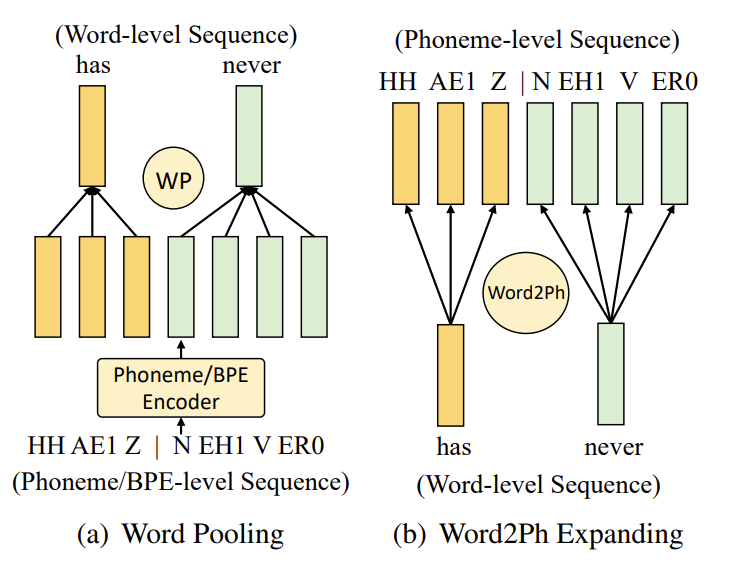
- 결과적으로 phoneme FFT block은 phonetic space에서 phonological habit을 모델링하고, BPE FFT block은 semantic information을 추출 - 이후 word-level pooling (WP)을 사용하여 BPE encoding을 word-level로 encoding 한 다음, word2ph operation을 통해 phoneme-level로 expand 함
- WP operation은 word boundary에 따라 각 word 내부의 phoneme hidden state를 average 하고
- Word2Ph operation은 word boundary 내의 각 phoneme에 대해 word hidden state를 repeate 함 - Phoneme sequence와 BPE sequence가 fuse 되면, additional FFT block을 사용하여 aligned phoneme과 BPE encoding을 fuse 하여 final phoneme-level text encoding을 얻음
- 이때 phoneme/BPE sequence를 개별적으로 처리하기 위해 2개의 independent FFT block을 활용
- Pre-training phase에서는 phoneme-level text encoding에서 indexing을 수행하여 selected token encoding을 얻은 다음, multi-modal embedding space에서 linearly project 함
- Prosody encoder는 selected token의 ground-truth speech segment에서 prosody pattern을 추출하는 것을 목표로 함
- 이를 위해 input speech feature로써 word boundary를 기준으로 mel-spectrogram을 clipping 하여 사용하고, prosody encoder는 input mel-spectrogram을 global encoding으로 처리하여 token encoding과 connect 함
- Clipped speech segment에는 contextual information leaking이 없고 selected token에 대한 local prosody information만 포함됨 - Contrastive learning으로 인해 global prosody encoding은 phonetic/speaker space에서 disentagle 될 수 있음:
- Positive sample, negative sample이 동일한 pronounceable token에 속하므로 phonetic information이 제거됨
- Prosody encoder는 training 중에 output feature에서 prosody information을 최대화하기 위해 spekaer information을 filter out 함
- 해당 방식을 통해 context-aware text encoding과 context-unaware mel-encoding을 connect 할 수 있음
- 즉, prosody encoder는 speech segment에서 high-level prosody information을 추출하는 방법을 학습하고, text encoder는 text context를 활용하여 prosody encoder가 추출한 prosody를 예측함 - 구조적으로 prosody encoder backbone은 ResNet-50을 기반으로 다음의 수정 사항을 반영함:
- Mel-spectrogram을 처리하기 위해 layer normalization을 가지는 1D convolution을 사용하여 fundamental residual block을 구축
- Dynamic length의 speech segment를 처리하기 위해, attentive pooling layer를 사용하여 ResNet의 output feature map을 aggregate
- 이를 위해 input speech feature로써 word boundary를 기준으로 mel-spectrogram을 clipping 하여 사용하고, prosody encoder는 input mel-spectrogram을 global encoding으로 처리하여 token encoding과 connect 함

- Multi-Scale Contrastive Pre-Training
- CLAPSpeech는 서로 다른 context하에서 prosody variance를 모델링하는 것을 목표로 함
- 따라서 contrastive pre-training을 위한 mini-batch를 구성하기 위해, 논문은 text token을 randmoly select 한 다음 selected token을 포함하는 $N$개의 text-speech pair의 batch를 sampling 함
- 이때 phoneme/word-level에서 prosody variance를 더 잘 추출하기 위해 multi-scale constrastive training framework를 도입함
- 구체적으로 논문은 phoneme-level, word-level text token 각각에 대해 2개의 CLAPSpeech model을 학습
- 먼저 phoneme-level CLAPSpeech의 training process에서 selected phoneme token이 포함된 text context를 $X_{text}$라고하자
- 그러면 phoneme token의 speech segment는 $X_{speech} \in \mathbb{R}^{T\times F}$이고 $X_{text},X_{speech}$를 통해 $N$개의 text-speech pair의 batch를 나타낼 수 있음
- $F$ : mel-bin 수, $T$ : time-bin 수 - 이후 text와 speech는 각각 text encoder $f_{text}(\cdot)$과 prosody encoder $f_{speech}(\cdot)$으로 전달됨
- Text encoder $f_{text}(X_{text})$의 output은 input text에 대한 phoneme-level encoding이므로, 이를 indexing 하여 phoneme-level token encoding $f_{text}(X_{text})_{i_{ph}}$를 얻을 수 있음
- $i_{ph}$ : phoneme-level text sequence에서 phoneme token의 index - 한편으로 output speech encoding $f_{speech}(X_{speech})$는 input speech segment의 global representation과 같음
- Text encoder $f_{text}(X_{text})$의 output은 input text에 대한 phoneme-level encoding이므로, 이를 indexing 하여 phoneme-level token encoding $f_{text}(X_{text})_{i_{ph}}$를 얻을 수 있음
- 최종적으로 output representation은 nomalize 된 다음, multi-modal embedding space로 linearly project 됨:
(Eq. 1) $T_{ph}=\text{L}_{text}(\text{LN}(f_{text}(X_{text})_{i_{ph}}))$
$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,S=\text{L}_{speech}(\text{LN}(f_{speech}(X_{speech})))$
- $T_{ph} \in \mathbb{R}^{N\times C}$ : phoneme token representation
- $S\in\mathbb{R}^{N\times C}$ : channel size $C$의 speech representation
- $\text{LN}$ : layer normalization, $\text{L}_{text},\text{L}_{speech}$ : linear projection
- 그러면 phoneme token의 speech segment는 $X_{speech} \in \mathbb{R}^{T\times F}$이고 $X_{text},X_{speech}$를 통해 $N$개의 text-speech pair의 batch를 나타낼 수 있음
- 위 과정을 통해 text, speech embedding은 comparable 하므로 CLAPSpeech는 batch 전체에서 $N\times N$개의 possible text-speech pairing 중에서 예측을 수행할 수 있음
- 구체적으로 text encoder와 prosody encoder는 batch의 $N$개의 real-pair에서 text/speech encoding의 cosine similarity를 최대화하면서, $N^{2}-N$개의 incorrect-pairing에 대한 cosine similarity를 최소화하도록 학습됨
- 그러면 해당 similarity score에 대한 symmetric cross-entropy loss는:
(Eq. 2) $\mathcal{L}_{ph}=0.5\times \left(l_{text}(\tau\cdot C_{ph})+l_{speech}(\tau\cdot C_{ph})\right)$
- $C_{ph} \in \mathbb{R}^{N\times N}$ : phoneme token embedding $T_{ph}$와 speech encoding $S$ 간의 cosine similarity matrix
- 즉, $C_{ph}=T_{ph}\cdot S^{\top}$, $\tau$ : learnable hyperparameter
- $l_{k} = \frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=0}^{N}\log \text{diag}(\text{softmax}(C))$ : $C$의 text/speech axis에 대한 cross-entropy function - Word-level CLAPSpeech도 비슷한 과정으로 training 할 수 있음
- 즉, word pooling을 사용하여 phoneme-level text encoding을 word-level로 변환하고, index 하여 word token embedding $T_{word}$를 얻은 다음
- (Eq. 2)와 유사하게 다음의 training loss를 적용함:
(Eq. 3) $\mathcal{L}_{word}=0.5\times \left(l_{text}(\tau\cdot C_{word})+l_{speech}(\tau\cdot C_{word})\right)$
- $C_{word}$ : word token encoding $T_{word}$와 speech encoding $S$ 간의 cosine similarity matrix
- 즉, word pooling을 사용하여 phoneme-level text encoding을 word-level로 변환하고, index 하여 word token embedding $T_{word}$를 얻은 다음
- CLAPSpeech Plugged in TTS Systems
- CLAPSpeech의 text encoder는 TTS task에 대한 rich prosody information이 포함된 text representation을 제공함
- 특히 생성된 text representation은 phoneme level에 위치하므로, input으로 phoneme sequence를 사용하는 대부분의 TTS model에 plug-in 할 수 있음
- Variation-based TTS model인 ProtaSpeech를 예로 들면,
- 아래 그림과 같이 CLAPSpeech의 pre-trained text encoder는 PortaSpeech의 phonetic encoder에 대한 auxiliary encoder의 역할을 수행함
- 이후 phonetic encoder와 CLAPSpeech text encoder의 phoneme-level output을 fuse 하여 처리함
- 이때 TTS system training 중에 CLAPSpeech text encoder의 parameter를 fix 하여 overfitting을 방지
- 비슷한 방식으로 prediction-based TTS system인 FastSpeech2에도 CLAPSpeech를 결합할 수 있음
- 추가적으로 품질 개선을 위해 multi-length adversarial training을 도입

3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset
- Pre-train : LibriSpeech, WenetSpeech
- Evaluation : LJSpeech, Biaobei, LibriTTS - Comparisons
- Prediction-based (PB) : FastSpeech2
- Variation-based (VB) : PortaSpeech
- Results
- 전체적인 성능 측면에서 CLAPSpeech가 가장 우수한 성능을 달성함
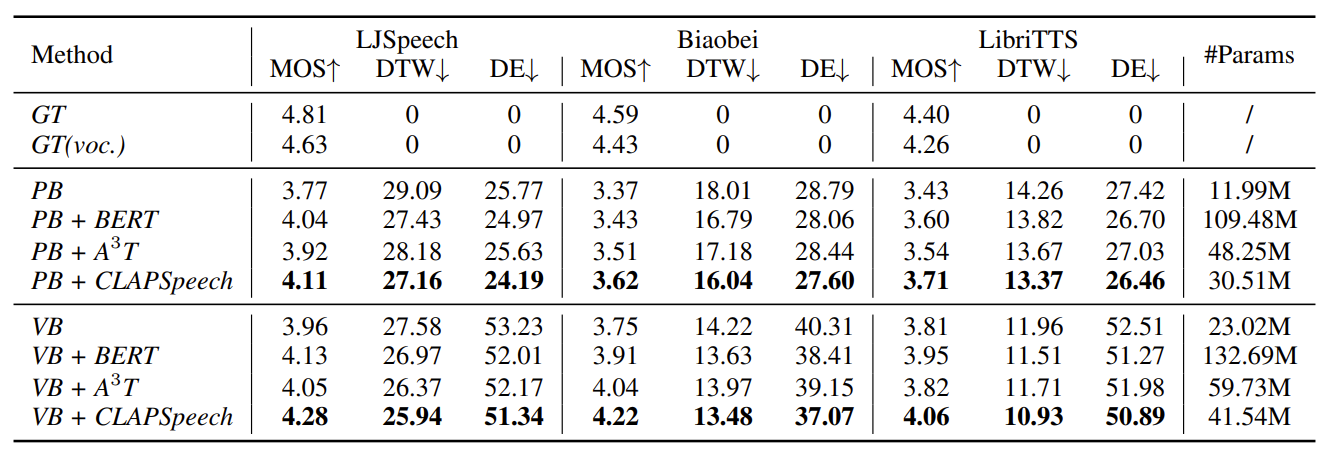
- Mel-spectrogram 측면에서도 CLAPSpeech는 realistic pitch contour를 생성할 수 있음

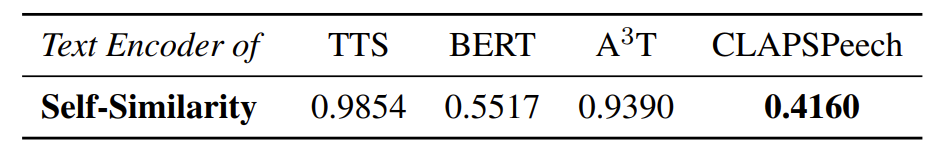
- Token Representation Self-Similarity
- Representation learning의 효과를 확인하기 위해, 다양한 context $T=[T_{1},...,T_{N}]$에서 select 된 token의 average similarity를 다음과 같이 정의:
(Eq. 4) $s(T)=\frac{1}{N(N-1)}\sum_{i=1}^{N}\sum_{j=1,j\neq i}^{N}\text{cosine}(T_{i},T_{j})$
- $T_{i},T_{j}$ : 서로 다른 text context에서 추출한 selected token encoding
- 낮은 $s(T)$는 selected token이 representation을 생성하는데 더 적은 기여를 한다는 것을 의미 - 결과적으로 해당 similarity score 측면에서 CLAPSpeech는 다른 representation 보다 우수한 결과를 달성함
- Representation learning의 효과를 확인하기 위해, 다양한 context $T=[T_{1},...,T_{N}]$에서 select 된 token의 average similarity를 다음과 같이 정의:
- 추가적으로 CLAPSpeech와 vanilla TTS text encoder에서 생성된 self-similarity matrix $M$을 시각화하면
- 여기서 $M_{i,j}=\text{cosine} (T_{i},T_{j})$
- CLAPSpeech는 아래 그림과 같은 self-similarity matrix를 얻을 수 있음

- Fine-grained Prosody Transfer
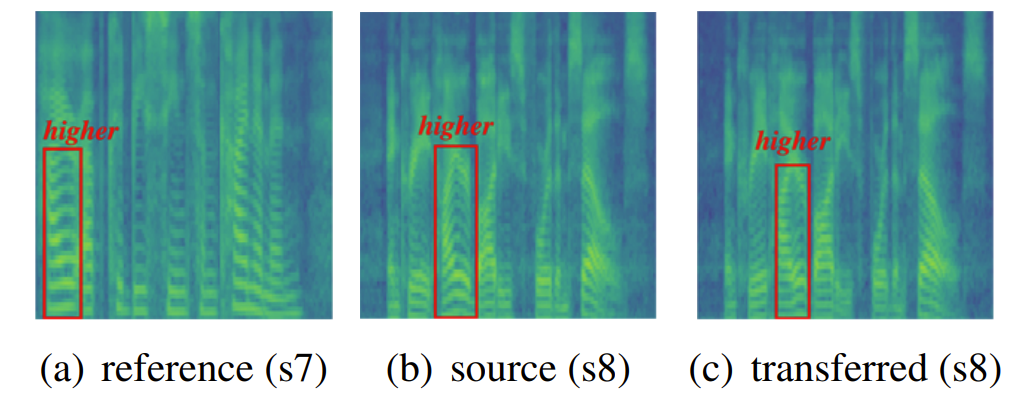
- CLAPSpeech의 text-speech joint multi-modal space는 high-level prosody pattern (pitch contour/duration information)을 나타냄
- 이를 위해 CLAPSpeech의 text encoder를 사용하여 아래 s7, s8의 text prosody encoding을 추출한 다음, s8의 "higher" text token encoding을 s7으로 transfer 함

- 결과적으로 아래 그림과 같이 s8의 "higher" prosody pattern은 s7로 succesfully transfer 됨
- Ablation Study
- CLAPSpeech의 각 component를 제거하는 경우 성능 저하가 발생함

반응형
'Paper > TTS' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

