티스토리 뷰
Paper/Neural Codec
[Paper 리뷰] Scaling Transformers for Low-Bitrate High-Quality Speech Coding
feVeRin 2026. 1. 29. 13:20반응형
Scaling Transformers for Low-Bitrate High-Quality Speech Coding
- 기존의 speech tokenization model은 대부분 strong inductive bias를 가지는 component를 사용한 low parameter-count architecture에 집중함
- TAAE
- Large parameter-count를 가지는 Transformer architecture를 사용하여 tokenization model을 scaling
- Finite Scalar Quantization-based bottleneck을 도입해 low bit-rate의 speech quality를 향상
- 논문 (ICLR 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- SoundStream과 같은 Neural Audio Codec (NAC)는 AudioLM, VALL-E 등의 generative model에서 주로 활용됨
- 이때 해당 speech generation pipeline에서 codec model이 차지하는 비중은 상당히 작음
- 즉, overall computational burden에 영향을 주지 않으면서 codec model의 size를 scaling 할 수 있음 - BUT, 기존의 NAC model은 대부분 covolutional/recurrent architecture를 활용하므로 scaling의 한계가 있음
- 이를 위해 Transformer와 같은 architecture를 고려할 수 있음 - 추가적으로 NAC model의 Residual Vector Quantizaiton (RVQ)는 token distribution learning을 어렵게 하고 bias에 취약하게 만듦
- 이때 해당 speech generation pipeline에서 codec model이 차지하는 비중은 상당히 작음
-> 그래서 codec model을 large parameter로 scaling 한 TAAE를 제안
- Transformer Audio AutoEncoder (TAAE)
- Transformer를 기반으로 codec architecture를 1B parameter range로 scaling
- RVQ를 개선하기 위해 Finite Scalar Quantizaiton (FSQ)에서 derive된 quantization scheme을 채택하고 FSQ를 low-order residual로 deompose하는 post-hoc method를 도입
< Overall of TAAE >
- Transformer와 FSQ를 활용하여 scaling된 neural codec
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 성능을 달성
2. Method
- Encoder and Decoder
- TAAE의 encoder-decoder structure는 standard Transformer architecture를 따름
- Stacked Transformer block은 layer norm을 포함한 self-attention과 feed-forward block으로 구성됨
- Self-attention의 경우 QK-norm을 사용하고 feed-forward block의 경우 SiLU activation을 포함한 gated MLP를 가지는 reverse bottleneck으로 구성됨 - 특히 각 encoder/decoder block에서는 strided convolution과 transposed convolution을 사용하여 최소한의 further resampling만 수행함
- 이를 통해 아주 작은 dimension의 embedding을 Transformer에 전달하는 것을 방지하고 sequence length를 limit 할 수 있음
- 추가적으로 ViT architecture를 따라 encoder 이전에 signal을 sequence-wise patching 함
- Encoder/decoder의 input/output에는 dense 1D convolutional block이 사용됨
- 해당 block은 Transformer 내에서 사용되는 embedding dimension과 input/output patch와 bottleneck의 latent representation에서 사용되는 required dimension 사이를 mapping 함 - 결과적으로 TAAE는 해당 Transformer block을 extensive use 하여 model size를 scaling 함
- Stacked Transformer block은 layer norm을 포함한 self-attention과 feed-forward block으로 구성됨
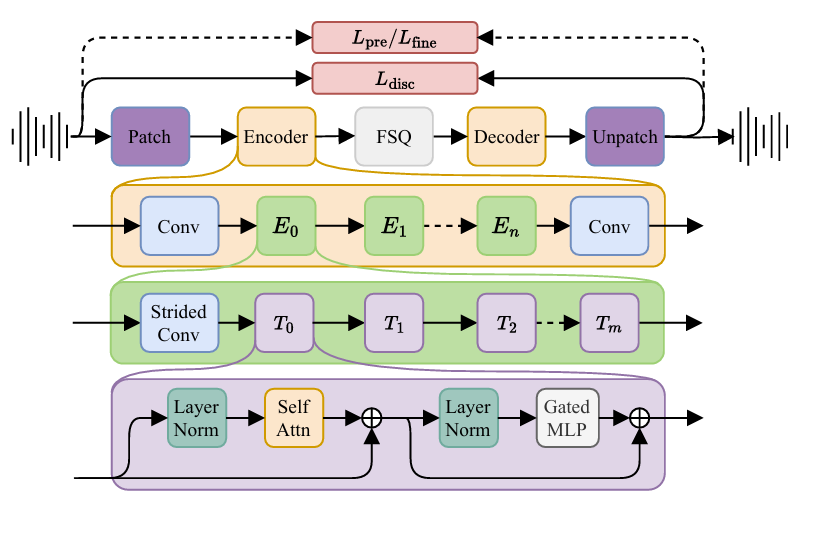
- Discrete Bottleneck
- 논문은 FSQ를 활용하여 기존 RVQ quantization의 문제를 해결함
- FSQ는 latent representation을 low-dimensional space로 project 한 다음, 해당 space의 각 dimension을 regular interval로 scalar quantizing 하여 token sequence를 derive 함
- 여기서 quantized level의 각 combination은 unique integer value에 mapping 되어 tokenization을 수행함 - Fixed level 수 $L$와 임의의 scalar $x$에 대해, scalar quantizer function $Q_{L}$은:
(Eq. 1) $ Q_{L}(x)=\frac{2}{L-1}\left\lfloor (L-1)\frac{\tanh x+1}{2}+\frac{1}{2}\right\rfloor-1$
- 해당 scalar quantization function은 latent vector element $\mathbf{z}$에 적용되어 quantized latent를 생성함 - Scalar quantizer를 training 하기 위해 논문은 hybrid approach를 도입함
- 먼저 uniform noise를 add 하여 explicit quantization 없이 quantization effect를 emulate 함:
(Eq. 2) $Q_{L}(x)\approx \tanh x+\frac{\mathcal{U}\{-1,1\}}{L-1}$ - 추가적으로 straight-through gradient estimation을 고려할 수 있음
- 결과적으로 논문은 해당 noise-based, straight-through estimation을 random mixing 하여 사용함
- 먼저 uniform noise를 add 하여 explicit quantization 없이 quantization effect를 emulate 함:
- FSQ는 latent representation을 low-dimensional space로 project 한 다음, 해당 space의 각 dimension을 regular interval로 scalar quantizing 하여 token sequence를 derive 함
- Post-Training Bottleneck Modification
- FSQ formulation은 discrete token의 수와 range에 따라 reconstruction quality를 adjust 할 수 있는 post-training possibility를 가지고 있음
- 이를 위해 uniform noise로 FSQ bottleneck을 training 하여 regularization이 training 이후에도 FSQ의 각 dimension에 대한 level 수를 modify 할 수 있도록 함
- 기본적으로 FSQ는 time-step 당 하나의 token을 생성하지만, 필요한 경우 single token을 multiple token으로 post-hoc decompose 할 수 있음
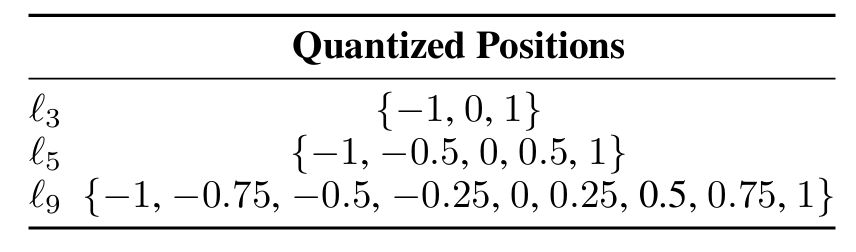
- 따라서 논문은 hierarchical residual decomposition을 고려함 - Residual FSQ는 single quantizer로 training 된 bottleneck에 post-hoc 될 수 있지만, $L=2^{n}+1, \,\, n\in \mathbb{Z}^{+}$을 만족하는 level 수만 가능함
- 여기서 level sequence는 $\{-1,0,1\}\,\, (L=3)$ level에서 시작하여 half way point에서 interval을 continually subdividing 하여 얻을 수 있음
- 특정 수의 level $L$에 해당하는 position을 포함하는 set을 $\ell_{L}$이라고 하면, 각 larger set은 previous set의 superset $\ell_{2^{n}+1}\supset \ell_{2^{n-1}+1}$에 해당함
- 그러면 progressively halved smaller $\ell_{3}$ set의 Minkowski sum을 통해 특정 수의 set을 얻을 수 있음
- e.g.) $\ell_{3}+\frac{\ell_{3}}{2}\supset \ell_{5},\ell_{3}+\frac{\ell_{3}}{2}+\frac{\ell_{3}}{4}\supset \ell_{9}$ - 이를 기반으로 post-hoc residual quantization은 주어진 latent $\mathbf{x}$에 대한 residual quantizer의 standard formulation으로 수행됨:
(Eq. 3) $\hat{\mathbf{z}}=\sum_{k=0}^{K}q_{k}$
$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\mathbf{q}_{0}=\kappa_{0}(\mathbf{z})$
$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\mathbf{q}_{k}=\kappa_{k}\left(\mathbf{z}-\sum_{i=0}^{k-1}\mathbf{q}_{i}\right)$
- $q_{k}$ : quantizer output - $\kappa_{k}$는 level $L=2^{n}+1, \,\, n\in \mathbb{Z}^{+}$에 따라 정의된 quantizer function $Q_{2n+1}$으로써:
(Eq. 4) $\kappa_{k}(\mathbf{z})=\frac{Q_{2n+1}((2n)^{k}\mathbf{z})}{(2n)^{k}}$
- 결과적으로 해당 formulation을 통해 residual formulation 없이도 quantized latent $\hat{\mathbf{z}}$가 seen quantized level set에 속한다는 것을 보장할 수 있음
- Calculating FSQ Bits-per-Second
- 앞선 post-hoc modification strategy를 활용하면 동일한 resolution level에서도 bits-per-second rate를 다양하게 조절할 수 있음
- 먼저 $n$ residual level을 가지는 decomposition에 대해, bits-per-second (bps)는:
(Eq. 5) $\text{bps}=f_{r}\sum_{i=0}^{n}\lceil \log_{2}(k_{i})\rceil$
- $f_{r}$ : latent rate, $k_{i}$ : residual decomposition의 각 stage에 대한 codebook size - 이때 codebook size는:
(Eq. 6) $k=L^{d}$
- $L$ : residual stage의 FSQ level 수, $d$ : FSQ dimension - Training 시 $L=17, d=6$, 25Hz frame rate의 FSQ bottleneck이 있으면 bps는 $25\times \lceil\log_{2}(17^{6})\rceil=625$로 얻어짐
- 해당 codebook을 5-level의 2-stage residual formulation으로 partition 하면 bps는 $25\times 2\times \lceil \log_{2}(5^{6})\rceil$이 됨
- 먼저 $n$ residual level을 가지는 decomposition에 대해, bits-per-second (bps)는:
- Discriminator
- 논문은 EnCodec을 따라 여러 resolution의 multiple complex STFT discriminator를 도입하고 다음과 같이 수정함:
- Channel 수를 늘리고 parameter count를 scaling 함
- Unevenly spaced STFT resolution을 채택하여 discriminator의 systemic bias를 완화함
- Convolutional network 이전에 complex STFT의 magnitude를 scaling 하여 signal의 noise-floor에 대한 late-training bias를 해결함
- Training Objectives
- Model training은 pre-training과 fine-tuning의 2-stage로 진행됨
- 먼저 논문은 direct adversarial classifier loss를 remove 하고 $N$ individual discriminator를 포함한 multi-discriminator의 $M$ per-layer feature에 대한 normalized feature-matching $L1$ loss를 사용함:
(Eq. 7) $ \mathcal{L}_{disc}(\mathbf{x},\hat{\mathbf{x}})=\frac{1}{MN}\sum_{m=1}^{M}\sum_{n=1}^{N} \frac{||D_{n}^{m}(\mathbf{x})-D_{n}^{m}(\hat{\mathbf{x}})||_{1}}{\text{mean}(||D_{n}^{m}(\mathbf{x})||_{1})}$
- $D_{n}^{m}$ : $n$-th individual discriminator의 $m$-th layer output, $\mathbf{x}$ : target signal, $\hat{\mathbf{x}}$ : reconstructed signal - Pre-training stage에서는 $L1$ reconstruction loss와 $L1$ STFT loss를 combine 하여 사용함:
(Eq. 8) $\mathcal{L}_{pre}(\mathbf{x},\hat{\mathbf{x}})=\mathcal{L}_{disc}(\mathbf{x},\hat{\mathbf{x}}) + \gamma^{k}L_{1}(\mathbf{x},\hat{\mathbf{x}})+\gamma^{k}L_{1}(|\mathbf{X}|,|\hat{\mathbf{X}}|)$
- $\gamma$ : exponential decay coefficient, $k$ : training step, $\mathbf{X},\hat{\mathbf{X}}$ : 각각 target, reconstructed signal의 STFT bin - Fine-tuning stage에서는 pre-trained WavLM-Large model 기반의 perceptual loss를 도입함
- 해당 perceptual loss는 (Eq. 7)의 discriminator feature-matching loss와 유사하게 target/reconstructed example의 layer feature에 대한 $L1$ loss로 얻어짐:
(Eq. 9) $\mathcal{L}_{perc}(\mathbf{x},\hat{\mathbf{x}})=\frac{1}{M}\sum_{m=1}^{M}\frac{|| C^{m}(\mathbf{x})-C^{m}(\hat{\mathbf{x}})||_{1}}{\text{mean}(||C^{m}(\mathbf{x})||_{1})}$
- $C_{m}$ : model의 $m$-th layer - 그러면 fine-tuning에 대한 overall loss는:
(Eq. 10) $\mathcal{L}_{fine}(\mathbf{x},\hat{\mathbf{x}})=\mathcal{L}_{disc}(\mathbf{x},\hat{\mathbf{x}})+\mathcal{L}_{perc}(\mathbf{x},\hat{\mathbf{x}})$
- 해당 perceptual loss는 (Eq. 7)의 discriminator feature-matching loss와 유사하게 target/reconstructed example의 layer feature에 대한 $L1$ loss로 얻어짐:
- 먼저 논문은 direct adversarial classifier loss를 remove 하고 $N$ individual discriminator를 포함한 multi-discriminator의 $M$ per-layer feature에 대한 normalized feature-matching $L1$ loss를 사용함:
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : LibriLight, MLS
- Comparisons : DAC, EnCodec, SpeechTokenizer, SemantiCodec, Mimi
- Results
- 전체적으로 TAAE의 성능이 가장 우수함
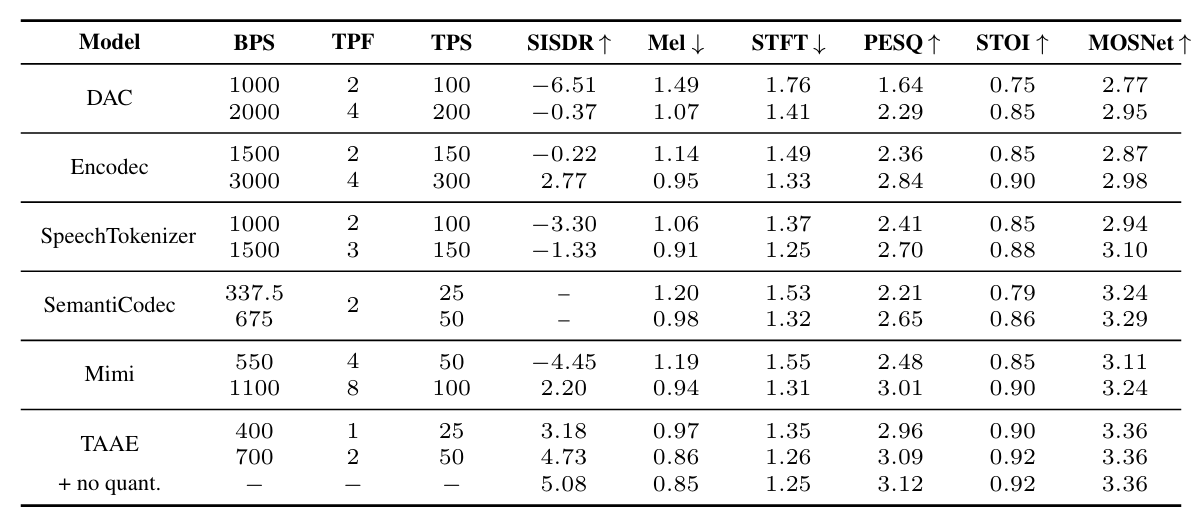
- MUSHRA test에서도 ground-truth 수준의 성능을 달성함

반응형
'Paper > Neural Codec' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

