티스토리 뷰
Paper/TTS
[Paper 리뷰] EATS-Speech: Emotion-Adaptive Transformation and Priority Synthesis for Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech
feVeRin 2025. 8. 25. 17:01반응형
EATS-Speech: Emotion-Adaptive Transformation and Priority Synthesis for Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech
- 기존의 zero-shot Text-to-Speech는 emotion을 효과적으로 반영하지 못함
- EATS-Speech
- Speech를 non-emotion style, emotion, content로 decompose 하는 parallel pipeline을 활용
- LLM-based converter를 통해 reference speech에서 text-emotion mapping을 학습
- 논문 (INTERSPEECH 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech (TTS)는 speaker-specific training data 없이 다양한 style의 speech를 합성할 수 있음
- 이를 위해 zero-shot TTS model은 prosody, pitch와 같은 style attribute를 capture 할 수 있어야 함
- BUT, emotion 측면에서 zero-shot TTS model은 여전히 modeling의 한계가 있음 - 기존 zero-shot TTS에서는 emotion을 reference speech의 global representation에 embed 된 style attribute로 취급하므로 다음의 문제가 발생함:
- Emotion이 unified representation으로 modeling 되는 경우, 다른 style attribute에 의해 overshadow 될 수 있음
- 이 경우 emotion-specific feature를 non-empotional style component와 decoupling 하고 style attribute를 prioritize 해야 함 - Emotion은 text의 semantic content와 closely tie 되어 있으므로 emotionally inconsistent output이 생성됨
- 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 target text의 semantic expression에 adapt 할 수 있는 Large Language Model (LLM)을 고려할 수 있음
- Emotion이 unified representation으로 modeling 되는 경우, 다른 style attribute에 의해 overshadow 될 수 있음
- 이를 위해 zero-shot TTS model은 prosody, pitch와 같은 style attribute를 capture 할 수 있어야 함
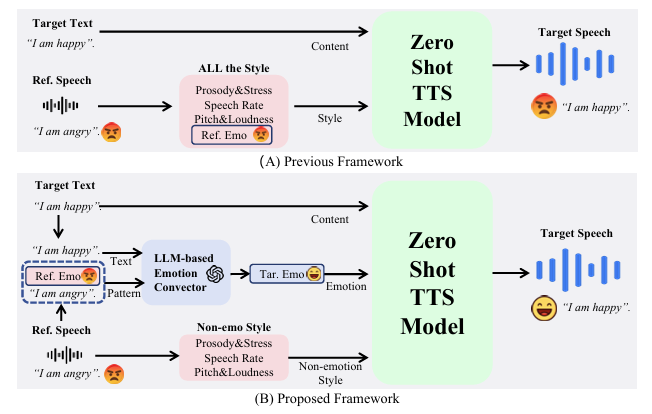
-> 그래서 기존 zero-shot TTS의 emotion 반영 문제를 해결한 EATS-Speech를 제안
- EATS-Speech
- Reference speech를 emotion representation과 non-emotion style attribute로 decompose
- 이후 emotion representation을 LLM-based emotion conversion model을 사용해 target text emotion과 match 하도록 transforming
< Overall of EATS-Speech >
- Emotion prioritization과 Emotion-aware LLM을 활용한 zero-shot TTS model
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 합성 품질을 달성
2. Method
- EATS-Speech는 emotion tokenizer가 포함된 disentangled speech synthesis framework를 기반으로 speech를 non-emotion style, emotion, content로 decoupling 함
- 여기서 non-emotion style은 speaking habit, timbre와 같은 speaker-specific characteristic을 represent 함
- Emotion brach의 경우, speaking speed, emotion expression 간의 intrinsic relationship을 고려하여 frame-level에서 fine-grained, duration-aware emotion attribute를 capture 함
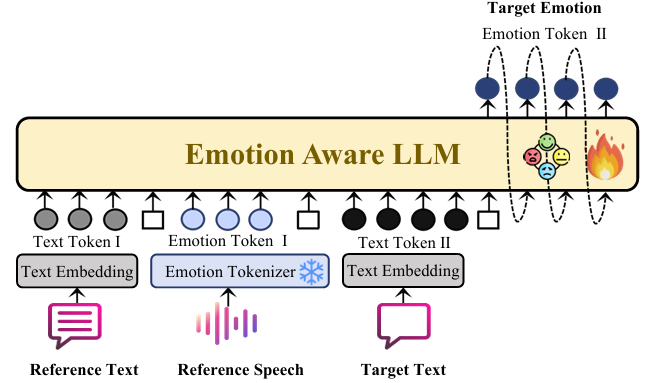
- Content branch의 경우, target text에서 directly derive 되어 accurate linguistic content generation을 보장함 - 특히 논문은 emotional consistency를 보장하기 위해 Emotion-Aware LLM을 emotion branch에 integrate 함
- Emotion-Aware LLM은 reference speech에서 추출한 emotion token, reference text의 content와 target text를 input으로 사용함
- 이를 위해 reference emotion-text pair에서 emotion-expression pattern을 학습하고, 해당 pattern을 target text로 transfer 하여 emotion-adaptive synthesis를 지원함
- 결과적으로 EATS-Speech framework는 Emotion Tokenizer, Emotion-Aware LLM을 중심으로 구성됨

- Disentangled Speech Synthesis with Emotion Tokenizer
- Emotion Tokenizer는 speech에서 emotion을 추출함
- 구조적으로는 pre-trained frame-level Emotion2Vec, emotion predictor, Residual Vector Quantization (RVQ) encoder로 구성됨
- Emotion Tokenizer의 training framework는 YourTTS를 따름
- 특히 emotion-prioritized speech synthesis를 위해 synthesis process를 parallel stream으로 transform 함 - 이때 speech는 non-emotion style, emotion, content의 3가지 component로 구성되고, speech duration은 emotional expression과 연관되어 있으므로 duration은 emotion brach에 allocate 됨
- Emotion branch에서 input speech는 Emotion2Vec module을 통해 process 되고, 이때 module은 50Hz에서 768 dimensionality로 frame-level emotional feature를 추출함
- 이후 feature는 emotion projector를 통해 512의 lower dimensionality로 project 된 다음, 3-bit RVQ encoder로 전달됨
- 여기서 1024 entry로 구성된 codebook은 각 RVQ encoding을 represent 함 - Non-emotion style branch에서 input speech는 먼저 mel-spectrogram으로 convert 됨
- 이후 fixed 512-dimensional style condition을 추출하기 위해 prompt encoder가 적용됨
- Utterance-level emotional classification에 기반한 Gradient reversal mechanism은 branch를 emotion-independent 하도록 보장함
- Style condition feature는 projector를 통해 8-class의 emotion category에 project 되어 emotion separation을 지원함 - Content branch에서는 input text가 text embedding layer에 전달됨
- 해당 embedding은 content condition으로 사용되고, normalized flow Transformer에 input 됨
- Multi-Reference Timbre Encoder (MRTE)는 text length를 emotion token length와 align 하기 위해 사용됨
- Emotion branch에서 input speech는 Emotion2Vec module을 통해 process 되고, 이때 module은 50Hz에서 768 dimensionality로 frame-level emotional feature를 추출함
- Emotion Tokenizer의 loss function $\mathcal{L}_{ET}$는:
(Eq. 1) $\mathcal{L}_{ET}=\mathcal{L}_{RVQ}+\mathcal{L}_{GR}+\mathcal{L}_{NF}+\mathcal{L}_{Vocoder}$ - 각 loss term은 다음과 같음:
- $\mathcal{L}_{RVQ}$는 RVQ reconstruction loss로써, Mean Squared Error (MSE)를 통해 compute 됨:
(Eq. 2) $\mathcal{L}_{RVQ}=\text{MSE}(\hat{e},e)$
- $\hat{e}$ : decoded emotion token, $e$ : original emotional feature - $\mathcal{L}_{GR}$는 gradient reversal loss로써, gradient reversal이 적용된 projected non-emotion style feature와 Emotion2Vec utterance classification 간의 cross-entropy loss와 같음:
(Eq. 3) $\mathcal{L}_{GR} =-\log P(\hat{y}|f_{style})$
- $\hat{y}$ : predicted emotion classification, $f_{style}$ : non-emotion style feature - $\mathcal{L}_{NF}$는 mel-spectrogram reconstruction loss로써, normalized flow Transformer가 predict한 mel-spectrogram과 emotion token에 해당하는 actual mel-spectrogram 간의 MSE로 얻어짐:
(Eq. 4) $\mathcal{L}_{NF} =\text{MSE}(\hat{m},m)$
- $\hat{m}$ : predicted mel-spectrogram, $m$ : ground-truth mel-spectrogram - $\mathcal{L}_{Vocoder}$는 vocoder loss로써, predicted speech에서 segment를 randomly crop하고 MSE를 통해 ground-truth speech segment와 comparing하여 얻어짐:
(Eq. 5) $\mathcal{L}_{Vocoder} =\text{MSE}(\hat{s}_{rand},s_{rand})$
- $\hat{s}_{rand}$ : randomly cropped predicted speech segment, $s_{rand}$ : ground-truth segment
- $\mathcal{L}_{RVQ}$는 RVQ reconstruction loss로써, Mean Squared Error (MSE)를 통해 compute 됨:
- Emotion-Aware LLM for Emotion Transformation
- Emotion-Aware LLM은 reference speech에서 추출된 emotion token, reference text, target text을 input으로 사용함
- 해당 module은 re-trained GPT-2 decoder-only Transformer를 기반으로 구축됨
- 먼저 pre-trained emotion tokenizer를 사용하여 reference emotion token을 추출한 다음, reference emotion token, reference text, target text를 exact dimension의 embedding space로 project 함
- 이때 speech sequence의 모든 stream은 개별적으로 process 된 다음 combine 됨
- Text와 emotion sequence는 서로 다른 learnable positional embedding으로 augment 됨 - 이후 embedding sequence는 causal Transformer layer stack을 통해 process 됨
- Emotion-Aware LLM은 autoregressive prediction을 사용하여 각 token을 sequentially generate 함
- 특히 emotional feature를 emphasize 하는 emotion token을 통해 generation process에서 semantic, emotional cue를 integrate 함 - Emotion-Aware LLM의 training은 2-step으로 구성됨
- 먼저 first step에서는 text-to-emotion token mapping을 학습하고, 이때 loss는:
(Eq. 6) $ \mathcal{L}_{step1}=-\sum_{t=1}^{T}\log P\left(\hat{e}_{t}|\mathbf{e}_{<t}, \mathbf{t}\right)$
- $\hat{e}_{t}$ : time step $t$의 predicted emotion token
- $\mathbf{e}_{<t}$ : previous emotion token, $\mathbf{t}$ : text sequence - 즉, model은 previous token과 text를 기반으로 next emotion token $\hat{e}_{t}$를 predict 함
- 먼저 first step에서는 text-to-emotion token mapping을 학습하고, 이때 loss는:
- Second step에서는 emotion transformation을 위해 reference emotion token $\mathbf{e}_{ref}$, reference text $\mathbf{t}_{ref}$, target text $\mathbf{t}_{target}$을 기반으로 target emotion token $\mathbf{e}_{ref}$를 생성함
- 해당 process는 autoregressive 하게 동작하고, 각 target emotion token은 sequentially generate 됨
- 그러면 해당 loss는:
(Eq. 7) $\mathcal{L}_{step2}=-\sum_{t=1}^{T}\log P\left(\hat{e}_{t}|\mathbf{e}_{<t}, \mathbf{e}_{ref},\mathbf{t}_{ref},\mathbf{t}_{target}\right)$
- 이를 통해 model은 reference speech의 emotional feature에서 target speech의 emotional feature로의 mapping을 target text에 따라 학습할 수 있음
- 해당 module은 re-trained GPT-2 decoder-only Transformer를 기반으로 구축됨
3. Experiments
- Settings
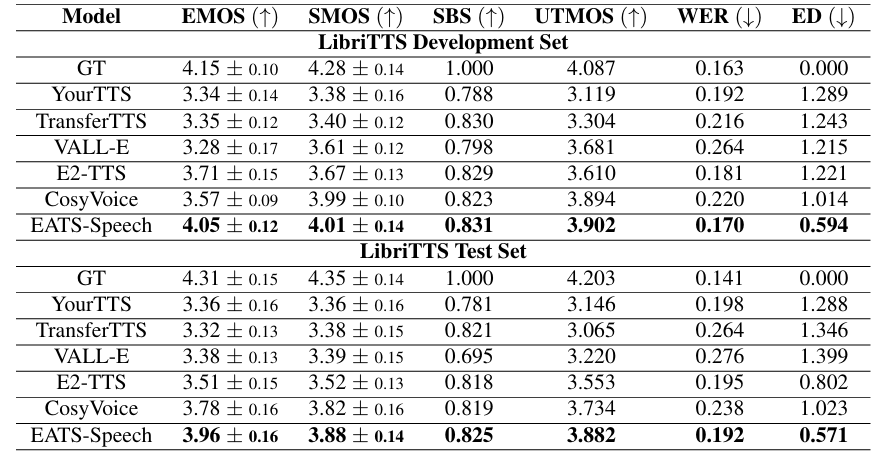
- Results
- 전체적으로 EATS-Speech의 성능이 가장 뛰어남
- Ablation Study
- 각 component를 제거하는 경우 성능 저하가 발생함

반응형
'Paper > TTS' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글
