티스토리 뷰
Paper/TTS
[Paper 리뷰] GenerTTS: Pronunciation Disentanglement for Timbre and Style Generalization in Cross-Lingual Text-to-Speech
feVeRin 2024. 11. 9. 09:20반응형
GenerTTS: Pronunciation Disentanglement for Timbre and Style Generalization in Cross-Lingual Text-to-Speech
- Cross-lingual text-to-speech는 다음의 어려움이 있음
- Timbre, pronunciation은 서로 correlate 되어 있음
- Speech style에는 language-agnostic, language-specific part가 포함되어 있음 - GenerTTS
- Pronunciation/style과 timbre를 disentangle 하기 위해 HuBERT-based information bottleneck을 도입
- Language-specific information을 제거하기 위해 style, language 간의 mutual information을 최소화
- 논문 (INTERSPEECH 2023) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Cross-lingual timbre, style generalization text-to-speech (TTS)는 unseen target language의 style로 speech를 생성하는 것을 목표로 함
- BUT, cross-lingual generalizable TTS를 위해서는 pronunciation, timbre, style을 decoupling 해야 함
- Timbre, pronunciation은 highly correlate되어 있고, style과 pronunciation 역시 서로 mix 되어 있음 - 해당 문제를 해결하기 위해,
- 대표적으로 Domain Adversarial Training을 고려할 수 있음
- BUT, Gradient Reversal Layer (GRL)을 사용하여 network를 training 하는 것은 unstable 함 - Data Augmentation 방식은 data construction process가 복잡하고 품질 저하의 문제가 있음
- 대표적으로 Domain Adversarial Training을 고려할 수 있음
- 한편으로 Phonetic PosteriorGram (PPG), ASR bottleneck feature (ASR-BNF), Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) 기반의 speech representation을 고려할 수 있음
- 해당 representation은 speech를 pronunciation, timbre 등으로 disentangle 할 수 있다는 장점을 가짐
- 특히 HuBERT representation은 적절한 channel size와 layer를 선택하면 timbre information을 제거하면서 style, pronunciation information을 효과적으로 preserve 할 수 있음
- BUT, cross-lingual generalizable TTS를 위해서는 pronunciation, timbre, style을 decoupling 해야 함
-> 그래서 timbre, style, pronunciation을 효과적으로 disentangle 할 수 있는 GenerTTS를 제안
- GenerTTS
- Timbre를 style, pronunciation과 disentangle 하기 위해 HuBERT를 bottleneck feature로 적용
- 이를 통해 cross-lingual TTS에서 pronunciation robustness와 speaker similarity를 보장 - 이후 style, pronunciation을 disentangle 하기 위해 self-supervised presentation-based structure를 도입하여 fine-grained style을 modeling
- 추가적으로 Mutual Information (MI) minimization constraint에 기반한 style adaptor를 도입
- Timbre를 style, pronunciation과 disentangle 하기 위해 HuBERT를 bottleneck feature로 적용
< Overall of GenerTTS >
- HuBERT bottleneck과 SSL-based structure를 활용한 generalizable TTS model
- 결과적으로 효과적인 disentanglement를 보장하여 뛰어난 합성 품질을 달성
2. Method
- Self-Supervised Acoustic Feature : HuBERT
- HuBERT는 timbre와 다른 feature를 disentangle 하는 self-supervised representation learning model
- 먼저 acoustic unit discovery system을 통해 iterative training target으로 pseudo-label을 생성한 다음,
- BERT와 유사한 masking strategy를 pretraining에 적용하여 long-range temporal relationship을 학습함 - HuBERT pretraining은 다음의 3가지 iteration을 고려함
- 첫 번째 iteration의 경우 MFCC에 대한 $k$-means를 training target으로 하고, trained model output은 MFCC 보다 나은 representation을 expect 함
- 두 번째, 세 번째 iteration의 경우 previous iteration의 middle layer에 대한 $k$-means를 current iteration의 training target으로 사용함
- 해당 iteration을 통해 HuBERT는 pseudo-label보다 더 나은 continuous representation을 얻을 수 있음
- 기존에는 해당 continuous embedding을 discretize 하여 사용하지만, discretization은 prosodic information loss가 발생한다는 단점이 있음
- 따라서 논문은 continuous embedding을 채택해 pronunciation과 style을 retaining 하면서 timbre information 만을 제거함
- 즉, HuBERT를 GenerTTS의 bottleneck feature로 활용하여 timbre/style, timbre/pronunciation을 disentangle 함
- 먼저 acoustic unit discovery system을 통해 iterative training target으로 pseudo-label을 생성한 다음,

- SSL-based TTS System
- GenerTTS는 Phoneme to HuBERT (P2H) encoder와 HuBERT to Mel-spectrogram (H2M) decoder로 구성됨
- 먼저 P2H encoder는 text encoder로써 input phoneme sequence에서 HuBERT embedding을 예측함
- H2M decoder는 timbre adaptation을 수행하기 위해, HuBERT를 input으로 하여 speaker embedding condition에 따라 다양한 mel-spectrogram을 생성함
- 최종적으로 waveform은 predicted mel-spectrogram으로부터 neural vocoder를 통해 합성됨
- 논문에서는 MelGAN을 채택
- 먼저 P2H encoder는 text encoder로써 input phoneme sequence에서 HuBERT embedding을 예측함
- P2H Encoder
- P2H encoder는 style, pronunciation information을 제공함
- 구조적으로는 phoneme encoder, pitch/energy predictor, length regulator (LR)이 있는 duration predictor, HuBERT decoder로 구성됨
- 추가적으로 fine-grained style을 modeling 하기 위한 style adaptor를 적용 - 해당 P2H는 self-attention과 lightweight convolution에 기반한 Parallel Tacotron을 기반으로 함
- 즉, P2H encoder에서 phoneme encoder는 phoneme sequence에서 latent representation을 학습한 다음, 해당 representation을 duration predictor에 전달하여 phoneme duration을 예측함
- Duration information에 따라 LR은 phoneme encoder output을 target frame sequence length로 upsampling 함
- 이때 Parallel Tacotron과 마찬가지로 P2H encoder에는 iterative loss가 적용됨
- 한편으로 논문은 mel-spectrogram을 directly predict 하지 않고 upsampled phoneme encoder output에서 target HuBERT embedding을 예측하는 decoder를 도입함
- 해당 HuBERT decoder는 fully-connected layer가 있는 3개의 lightweight convolution (LConv1) block을 가짐
- LConv1 block은 Gated Linear Unit (GLU), lightweight convolution (LConv), feed-forward (FF) layer, 2개의 residual connection, layer normalization으로 구성됨
- 추가적으로 model stability를 높이고 prosody information을 explicitly modeling 하기 위해 pitch predictor와 energy predictor를 도입함
- 이를 통해 speech waveform에서 pitch/energy를 추출하여 phoneme duration에 따라 phoneme-level feature에 mapping 함
- H2M Decoder
- H2M decoder는 HuBERT에서 mel-spectrogram을 예측하고 synthesis speech에 대한 timbre information을 지원함
- 구조적으로는 fully-connected layer가 있는 3-layer LConv2 block으로 구성되고 80-dimensional mel-spectrogram을 output 함 - High timbre adaptation을 위해 LConv2 block은 AdaSpeech와 같이 LConv1 block의 layer normalization을 conditional layer normalization으로 대체하여 speaker embedding에 따라 condition 됨
- 추가적으로 H2M training에서는 teacher-forcing을 적용하여,
- Training 중에는 ground-truth HuBERT embedding을 H2M decoder input으로 사용
- Inference 시에는 predicted HuBERT를 사용 - Iterative loss는 predicted mel-spectrogram과 ground-truth mel-spectrogram에도 적용됨
- H2M decoder는 HuBERT에서 mel-spectrogram을 예측하고 synthesis speech에 대한 timbre information을 지원함
- Cross-Lingual Style Adaptor
- 논문의 style adaptor는 mel-spectrogram aligner (Mel aligner), style encoder, style predictor, mutual information constraint가 있는 language embedding으로 구성됨
- 먼저 style encoder를 사용하여 phoneme-level spectrogram에서 fine-grained style embedding을 modeling 하고 이를 phoneme encoder output과 concatenate 함
- 이때 mel aligner는 phoneme duration information에 따라 frame-level mel-spectrogram을 phoneme-level spectrogram으로 mapping 하는 데 사용됨
- Pitch, energy 같은 variance feature는 style과 closely relate 되어 있으므로 pitch/energy predictor에 style embedding을 추가함
- Cross-lingual style transfer의 경우 inference 시에 reference 된 mel-spectrogram의 language와 spoken content는 style encoder input과 inconsistent 함
- 따라서 논문은 style predictor를 도입하여 text-related information을 통해 style ID에 따라 fine-grained style을 예측함
- Training 시 style encoder output은 stop gradient 이후의 style predictor에 대한 prediction target으로 사용됨
- Inference 시 style encoder는 target style ID와 input phoneme sequence에 따라 style을 예측함
- 추가적으로 cross-lingual style transfer는 synthesis speech가 target language의 native pronunciation을 유지하면서 high style similarity를 가지도록 요구함
- 따라서 style transfer에서 nativeness를 개선하기 위해, 논문은 language-specific information을 style embedding과 더욱 decouple 함
- 즉, language ID에서 language embedding을 modeling 하고 language embedding과 style embedding 간의 MI를 minimize 함
- 이때 high-dimensional space에서 MI를 추정하는 것은 어려우므로, variational Contrastive Log-ratio Upper Bound (vCLUB)으로 측정된 MI의 upper limit를 사용

3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : Mandarin (zh-CN), English (en-US) speech dataset
- Comparisons : Parallel Tacotron, M3-TTS
- Results
- 전체적으로 GenerTTS가 가장 우수한 성능을 보임

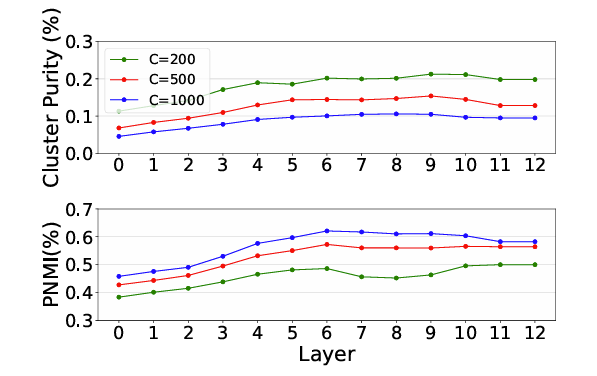
- HuBERT Analysis
- HuBERT의 13 layer에 대한 $k$-means feature를 얻어 Cluster Purity와 Phone-Normalized Mutual Information (PNMI)를 비교해 보면
- 9-th layer에서 얻어진 embedding이 가장 높은 pronunciation relationship을 보임
- 추가적으로 speaker similarity 측면에서 HuBERT embedding은 높은 similarity를 보임
- 즉, HuBERT embedding에는 timbre-related information이 거의 존재하지 않음

- $F0$ 측면에서도 HuBERT embedding은 style, pronunciation 등의 factor는 유지하면서 timbre를 효과적으로 제거하는 것으로 나타남

반응형
'Paper > TTS' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

