티스토리 뷰
Paper/ETC
[Paper 리뷰] EDM2: Analyzing and Improving the Training Dynamics of Diffusion Models
feVeRin 2025. 12. 18. 14:02반응형
EDM2: Analyzing and Improving the Training Dynamics of Diffusion Models
- Diffusion model은 data-driven image synthesis에서 우수한 성능을 보임
- EDM2
- Diffusion model architecture에 대한 uneven, inefficient training의 원인을 파악
- Activation, weight, update magnitude를 expectation에 대해 preserve 하도록 network layer를 redesign
- 추가적으로 training 이후 Exponential Moving Average parameter를 post-hoc setting
- 논문 (CVPR 2024) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Denoise Diffusion Model은 high-quality image synthesis를 지원함
- 이때 diffusion model은 pure noise를 iterative image denoising을 통해 새로운 image로 변환함
- 각 denoising step은 self-attention layer를 가지는 U-Net architecture를 통해 수행됨 - BUT, diffusion model training은 stochastic loss function으로 인한 어려움이 있음
- Final image quality는 sampling chain을 통해 predict 되는 faint image detail을 통해 결정되기 때문
- Network는 다양한 noise level, Gaussian noise realization, conditioning input 등을 고려해야 하기 때문
- 이때 diffusion model은 pure noise를 iterative image denoising을 통해 새로운 image로 변환함

-> 그래서 diffusion model의 predictable, even parameter update를 위한 training dynamics를 조사
- EDM2
- Weight, activation, gradient, weight update에 대한 expected magnitude를 활용
- 추가적으로 training 이후 Exponential Moving Average (EMA) paramter를 post-hoc setting
< Overall of EDM2 >
- 효과적인 diffusion model training을 위한 training dynamics 분석
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 성능을 달성
2. Improving the Training Dynamics
- 논문은 score network의 training dynamics에서 발생하는 imbalance의 영향을 분석하고 완화하는 것을 목표로 함
- 먼저 논문은 EDM을 따라 U-Net, self-attention layer로 구성된 ADM network를 채택하고 constant learning rate과 32 deterministic 2nd order sampling step을 사용함
- Evaluation은 ImageNet $512\times 512$ dataset을 사용함

- Preliminary Changes
- Baseline ($\texttt{Config A}$)
- Original EDM configuration과 달리 output channel을 $4$로 늘림
- 추가적으로 training dataset을 ImageNet-512의 $64\times 64\times 4$ latent representation으로 replace 하고 zero mean, standard deviation $\sigma_{data}=0.5$로 globally standardize 함
- 이때 baseline의 FID는 $8.00$으로 얻어짐
- Improved Baseline ($\texttt{Config B}$)
- Baseline의 성능을 최적화하기 위해 hyperparameter (learning rate, EMA length, training noise level distribution 등)을 tuning 함
- $32\times 32$ resolution에서는 self-attention을 disable 함 - 한편 EDM에서는 initialization 시 loss magnitude를 모든 noise level에서 $1.0$으로 standardize 하지만, training progress에서는 hold 되지 않음
- 이로 인해 gradient feedback의 magnitude가 noise level에 따라 달라짐
- 따라서 논문은 multi-task loss의 continuous generalization을 채택하여 noise level function으로 raw loss value를 track 하고, training loss를 해당 reciprocal로 scalining 함
- 결과적으로 $\texttt{Config B}$를 통해 FID는 $8.00$에서 $7.24$로 개선됨
- Baseline의 성능을 최적화하기 위해 hyperparameter (learning rate, EMA length, training noise level distribution 등)을 tuning 함
- Architectural Streamlining ($\texttt{Config C}$)
- 모든 convolutional, linear layer에서 additive bias를 remove 하고 network의 data offset capability를 보장하기 위해 additional constant $1$ channel을 network input에 concatentate 함
- 추가적으로 He uniform을 통해 weight를 initialize 하고 positional encoding scheme을 standard Fourier feature로 replace 하고, group normalization layer에서 mean subtraction과 learned scaling을 제거하여 simplify 함
- 한편 training 과정에서 key/query vector의 magnitude growth로 인해 attention map에서 brittle, spiky configuration이 나타날 수 있음
- 이를 해결하기 위해 vector를 normalize 한 다음 dot product 하는 Cosine Attention을 도입함
- 결과적으로 $\texttt{Config C}$를 통해 FID는 $7.24$에서 $6.96$으로 개선됨
- 모든 convolutional, linear layer에서 additive bias를 remove 하고 network의 data offset capability를 보장하기 위해 additional constant $1$ channel을 network input에 concatentate 함
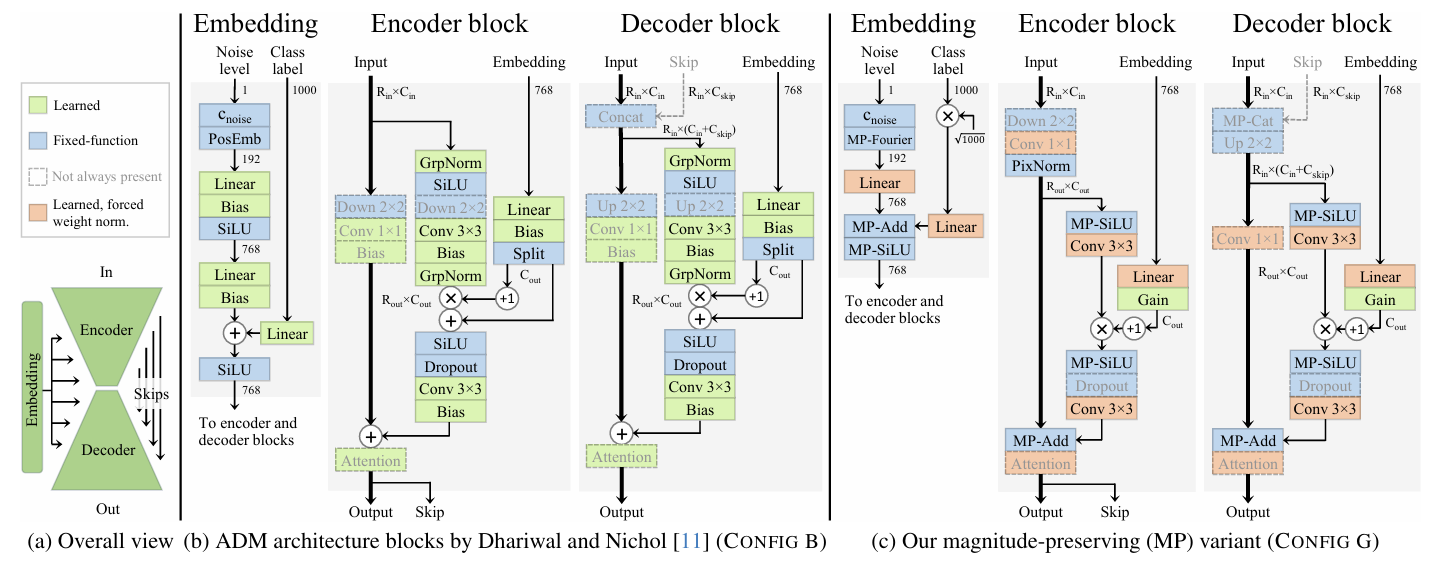
- Standardizing Activation Magnitudes
- $\texttt{Config C}$의 simplified architecture를 기반으로 activation magnitude 문제를 분석해 보면
- 아래 그림과 같이 $\texttt{Config C}$의 training에서 각 block 내의 activation magnitude는 uncontrollably grow 함
- 특히 training 마지막에서도 growth는 tapering off 되거나 stabilize 되지 않음
- 이는 ADM network가 구조적으로 encoder/decoder/self-attention block의 residual structure로 인해 normalization이 없는 long signal path를 포함하고 있기 때문
- 해당 path는 residual branch를 통해 contribution을 accumulate 하고 repeated convolution을 통해 activation을 amplify 하여, network을 unoptimal state에 keeping 함
- 단순하게 해당 path에 group normalization을 적용하는 것을 고려할 수 있지만, StyleGAN과 같이 excessive normalization은 network의 성능을 저하시키고, 각 layer가 학습을 bypass 하도록 유도할 수 있음
- 따라서 논문은 data-dependent normalization의 영향력을 줄이기 위해, individual layer와 pathway가 expectation을 기반으로 activation magnitude를 preserve 하도록 함
- 아래 그림과 같이 $\texttt{Config C}$의 training에서 각 block 내의 activation magnitude는 uncontrollably grow 함
- Magnitude-Preserving Learned Layers ($\texttt{Config D}$)
- Expected activation mangitude를 preserve 하기 위해 논문은 각 layer output을 activation magnitude의 expected scaling으로 divide 함
- 여기서 incoming activation에 agnostic 한 scheme을 찾기 위해 다음의 statistical assumption을 고려함:
- 먼저 pixel과 feature map이 mutually uncorrelate 되어 있고 equal standard deviation $\sigma_{act}$를 가진다고 가정하자
- 여기서 fully-connected, convolutional layer는 하나의 output channel 마다 stacked unit으로 구성된다고 볼 수 있음 - 각 unit은 output element를 생성하기 위해 input activation의 일부 subset에 weight vector $\mathbf{w}_{i}\in\mathbb{R}^{n}$의 dot product를 apply 할 수 있음
- 그러면 해당 가정 하에서 $i$-th channel의 output feature standard deviation은 $||\mathbf{w}_{i}||_{2}\sigma_{act}$가 되고, 논문은 input activation magnitude를 restore 하기 위해 $||\mathbf{w}_{i}||_{2}$를 channel-wise로 divide 함
- 먼저 pixel과 feature map이 mutually uncorrelate 되어 있고 equal standard deviation $\sigma_{act}$를 가진다고 가정하자
- $\texttt{Config D}$의 해당 modification을 통해 아래 그림의 3행과 같이 magnitude drift를 eliminate 할 수 있고, FID를 $6.96$에서 $3.75$로 향상할 수 있음
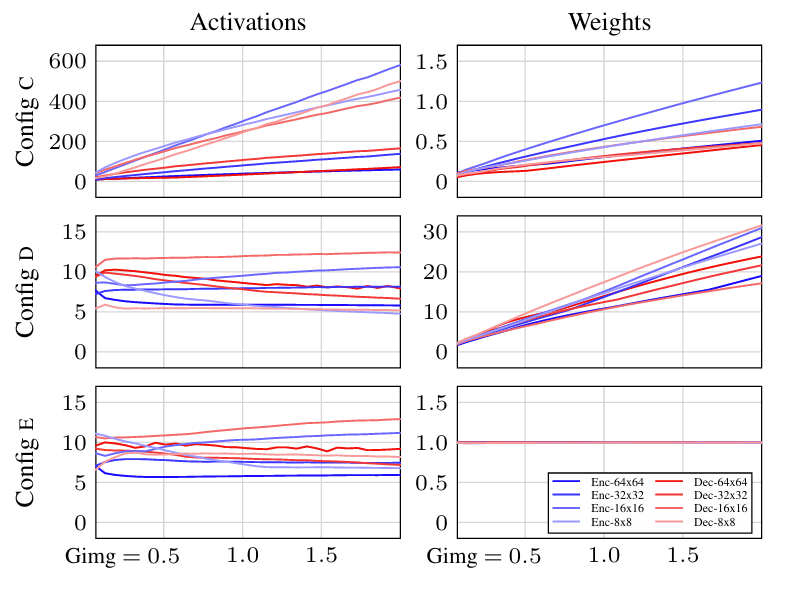
- Standardizing Weights and Updates
- 위 그림에서 $\texttt{Config D}$는 network weight가 grow 하는 경향이 있음
- Weight를 normalize 하는 경우, loss gradient가 weight vector에 perpendicular 하도록 강제되기 때문
- 따라서 논문은 해당 learning rate를 explicit control 할 수 있는 방법을 고려함
- Weight를 normalize 하는 경우, loss gradient가 weight vector에 perpendicular 하도록 강제되기 때문
- Controlling Effective Learning Rate ($\texttt{Config E}$)
- 논문은 forced weight normalization을 통해 weight growth 문제를 해결함
- 여기서 각 training step 이전에 모든 weight vector $\mathbf{w}_{i}$를 unit variance로 explicitly normalize 함 - 특히 training 시에는 standard weight normalization을 사용하여 training gradient를 $\mathbf{w}_{i}$가 있는 unit-magnitude hypersphere의 tangent plane으로 project 함
- 이를 통해 Adam의 variance estimate는 실제 tangent plane step을 통해 compute 될 수 있고, gradient vector의 to-be erased normal component에 corrput 되지 않을 수 있음
- 특히 weight, gradient 간의 correlation이 없다고 하면 각 Adam step은 fixed proportion으로 gradient를 approximately replace 할 수 있음
- Learning rate를 control 할 때 constant learning rate는 convergence를 induce 하지 않으므로, 논문은 Inverse Square Root learning rate decay schedule $\alpha(t)=\alpha_{ref}/\sqrt{\max(t/t_{ref},1)}$을 채택함
- $t$ : current training iteration, $\alpha_{ref}, t_{ref}$ : hyperparameter - 결과적으로 $\texttt{Config E}$는 training 시 weight, activation magnitude를 successfully preserve 하여 FID를 $3.75$에서 $3.02$로 개선함
- 논문은 forced weight normalization을 통해 weight growth 문제를 해결함
- Removing Group Normalizations ($\texttt{Config F}$)
- Data-dependent group normalization layer를 remove 할 수 있음
- 이때 network는 어떤 normalization layer 없이도 sucessfully training 될 수 있지만, encoder main path에 weaker pixel normalization layer를 도입하면 더 나은 성능을 얻을 수 있음
- 특히 $\texttt{Config F}$는 $\texttt{Config D}$의 standardization에 대한 statistical assumption을 violate 하는 corrleation을 counteracte 해야 함
- 따라서 논문은 모든 group normalization을 remove 하고 $1/4$를 pixel normalization으로 replace 함
- 추가적으로 embedding network의 두 번째 linear layer와 network output의 non-linearity를 remove 하고 residual block의 resampling operation을 combine 함
- 결과적으로 FID는 $3.02$에서 $2.71$로 개선됨
- Magnitude-Preserving Fixed-Function Layers ($\texttt{Config G}$)
- Network에는 activation magnitude를 preserve 하지 않는 layer가 여전히 존재함
- 먼저 Fourier feature의 $\sin, \cos$ function은 unit variance를 가지지 않으므로 $\sqrt{2}$로 scaling 해야 함
- SiLU non-linearity는 compensate 되지 않으면 expected unit-variance distribution을 attenuate 함
- 따라서 논문은 output을 $\mathbb{E}_{x\sim \mathcal{N}(0,1)}[\text{silu}(x)^{2}]^{1/2}\approx 0.596$으로 divide 함 - Addition이나 concatenation을 통해 2개의 network branch가 join 되는 경우, 각 branch의 contribution에 따라 magnitude가 영향을 받을 수 있음
- 이를 위해 addition operation을 weighted sum으로 switch 하여 fixed residual path에는 $30\%$ weight, embedding에는 $50\%$ weight를 주고, 해당 weighted sum의 expected standard deviation을 활용함
- SiLU non-linearity는 compensate 되지 않으면 expected unit-variance distribution을 attenuate 함
- Standardization 이후에는 activation을 learned amount로 scale 하는 specific place를 identify 해야 함:
- 먼저 desired output이 항상 unit-vairance를 가지는 것을 expect 할 수 없으므로 network의 가장 끝에 learned zero-initialized scalar gain을 추가함
- 각 residual block 내의 conditioning signal에도 유사한 learned gain을 적용함
- 해당 final configuration을 통해 FID는 $2.56$으로 향상될 수 있음
- 먼저 Fourier feature의 $\sin, \cos$ function은 unit variance를 가지지 않으므로 $\sqrt{2}$로 scaling 해야 함
3. Post-hoc EMA
- Image synthesis에서 model weight에 대한 Exponential Moving Average (EMA)는 큰 영향을 미침
- 따라서 논문은 EMA profile을 training 이전에 specify 하지 않고 post-hoc으로 choice 하는 방법을 고려함
- Power Function EMA Profile
- 기존의 EMA는 training parameter $\theta$와 network parameter의 running weighted average $\hat{\theta}_{\beta}$를 maintain 함
- 각 training step에서 average는 $ \hat{\theta}_{\beta}(t)=\beta\hat{\theta}_{\beta}(t-1)+(1-\beta)\theta(t)$로 update 됨
- $t$ : current training step, Decay rate는 $\beta$에 의해 결정됨 - 한편 논문은 exponential decay 대신 power function에 기반한 averaging profile을 사용함
- Long exponential EMA는 network parameter가 mostly random인 initial training stage에 non-negligible weight를 주는 경향이 있기 때문
- Average profile은 training time에 따라 automatically scale 될 수 있기 때문
- Power function을 사용하면 앞선 요구사항을 반영할 수 있고, 이때 time $t$에서의 averaged parameter를 다음과 같이 정의할 수 있음:
(Eq. 1) $\hat{\theta}_{\gamma}(t)=\frac{\int_{0}^{t}\tau^{\gamma}\theta(\tau)d\tau}{\int_{0}^{t}\tau^{\gamma}d\tau}=\frac{\gamma+1}{t^{\gamma+1}}\int_{0}^{t}\tau^{\gamma}\theta(\tau)d\tau$
- $\gamma$ : profile의 sharpness를 control 하는 역할
- (Eq. 1)에서 $\theta_{t=0}$의 weight는 always zero에 해당하고, resulting averaging profile 역시 scale-independent 함 - $\hat{\theta}_{\gamma}(t)$를 prcatically compute 하기 위해, 각 training step 이후에 다음과 같이 incremental update를 수행할 수 있음:
(Eq. 2) $\hat{\theta}_{\gamma}(t)=\beta_{\gamma}(t)\hat{\theta}_{\gamma}(t-1)+(1-\beta_{\gamma}(t))\theta(t)$
- $\beta_{\gamma}(t)=(1-1/t)^{\gamma+1}$
- (Eq. 2)는 기존 EMA와 유사하지만, $\beta$가 current training time에 따라 달라진다는 차이점이 있음 - Parameter $\gamma$는 averaging profile에 unintuitive effect를 제공함
- 따라서 relative standard deviation $\sigma_{rel}=(\gamma+1)^{1/2}(\gamma+2)^{-1}(\gamma+3)^{-1/2}$을 통해 profile을 parameterize 함
- 즉, $10\%$의 EMA length에 대해 $\sigma_{rel}=0.10$인 profile을 refer 함 ($\gamma \approx 6.94$)
- 각 training step에서 average는 $ \hat{\theta}_{\beta}(t)=\beta\hat{\theta}_{\beta}(t-1)+(1-\beta)\theta(t)$로 update 됨
- Synthesizing Novel EMA Profiles after Training
- 논문은 training 이후에 $\gamma, \sigma_{rel}$을 freely choice 하는 것을 목표로 함
- 이를 위해 $\gamma_{1}=16.97, \gamma_{2}=6.94$에 대응하는 $0.05, 0.10$의 $\sigma_{rel}$을 가지는 2개의 averaged parameter vector $\hat{\theta}_{\gamma_{1}},\hat{\theta}_{\gamma_{2}}$를 maintain 함
- 해당 averaged parameter vector는 training 시 save 되는 snapshot에 periodically store 됨 - Training 이후 EMA profile에 해당하는 approximate $\hat{\theta}$를 reconstruct 하기 위해:
- 먼저 stored $\hat{\theta}_{\gamma_{i}}$의 EMA profile과 desired EMA profile 간의 least-square optimal fit를 찾음
- 이후 stored $\hat{\theta}_{\gamma_{i}}$에 해당 linear combination을 적용함
- 이러한 post-hoc EMA reconstruction은 single stored $\hat{\theta}$로도 가능하지만, 2개의 stored $\hat{\theta}$를 사용하면 더 나은 accuracy를 달성할 수 있음
- 이를 위해 $\gamma_{1}=16.97, \gamma_{2}=6.94$에 대응하는 $0.05, 0.10$의 $\sigma_{rel}$을 가지는 2개의 averaged parameter vector $\hat{\theta}_{\gamma_{1}},\hat{\theta}_{\gamma_{2}}$를 maintain 함
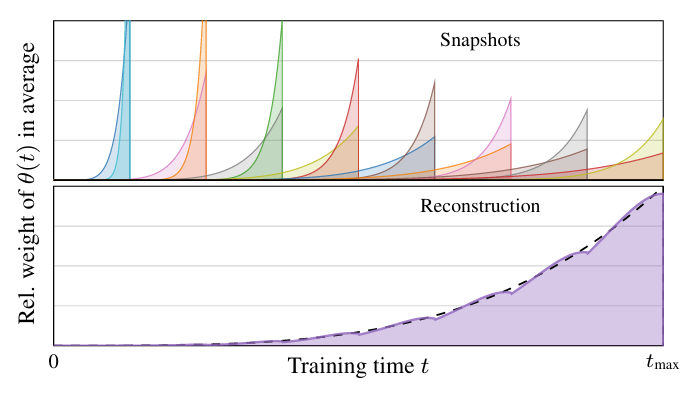
- Analysis
- Post-hoc EMA를 사용하여 EMA length에 따른 효과를 분석해 보면:
- 아래 그림과 같이 각 $\texttt{Config}$ 마다 최적의 EMA length는 다르게 나타남
- BUT, optimum의 narrowness는 각 weight tensor가 prefer 하는 EMA length에 대해 uniform 하게 나타남 - 추가적으로 EMA length는 training이 진행됨에 따라 longer EMA로 slowly shift 함
- 아래 그림과 같이 각 $\texttt{Config}$ 마다 최적의 EMA length는 다르게 나타남
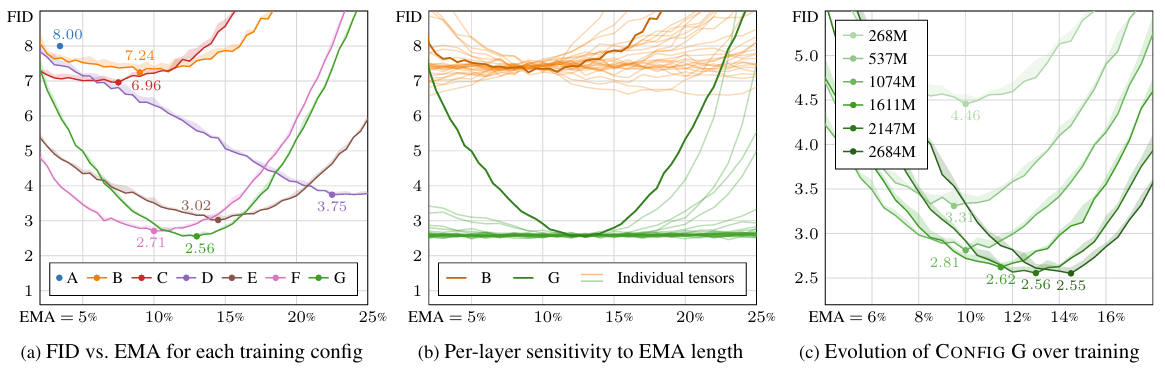
4. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : ImageNet
- Comparisons : EDM, ADM, VDM++, RIN
- Results
- 전체적으로 EDM2의 성능이 가장 우수함

- Optimal EMA length는 guidance strength에 크게 의존함
- 즉, vanilla/guidance 간의 discrepancy는 non-optimal EMA parameter로 인해 발생함

- EDM2는 latent diffusion 뿐만 아니라 RGB-space diffusion에서도 우수한 성능을 보임

반응형
'Paper > ETC' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

