티스토리 뷰
Paper/TTS
[Paper 리뷰] InstantSpeech: Instant Synchronous Text-to-Speech Synthesis for LLM-driven Voice Chatbots
feVeRin 2025. 5. 20. 17:49반응형
InstantSpeech: Instant Synchronous Text-to-Speech Synthesis for LLM-driven Voice Chatbots
- Large Language Model과 pair 된 text-to-speech model은 entire sentence가 생성될 때까지 synthesis를 수행하지 않으므로 response latency가 증가함
- InstantSpeech
- Causal Transformer-based acoustic model과 causal convolution-based vocoder를 combine 한 fully-parallel architecture를 활용
- Limited lookahead 내에서 speech quality를 향상하기 위해 knowledge distillation을 적용
- 논문 (ICASSP 2025) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Large Language Model (LLM)을 기반으로 한 chatbot은 speech를 통해 user와 interaction 함
-> 그래서 fully-parallel low-latency TTS model인 InstantSpeech를 제안
- InstantSpeech
- Entire sentence를 wait 하지 않고 LLM이 initial few word를 생성한 직후에 synthesis를 initiate
- Causal Transformer-based acoustic model과 causal convolution-based vocoder를 사용하여 fully-parallel architecture를 구성
- 추가적으로 knowledge distillation을 적용하여 naturalness를 향상
< Overall of InstantSpeech >
- Fully-parallel architecture에 기반한 low-latency TTS model
- 결과적으로 다양한 LLM에 대해 low response latency와 high-quality synthesis를 달성
2. Method
- Model Overview
- InstantSpeech의 acoustic model은 FastPitch를 기반으로 2개의 causal Feed-Forward Transformer (cFFT) stack으로 구성됨
- 이때 cFFT의 attention block은 intentionally mask 되어 각 word의 timestep이 previous word와 specified lookahead word에만 attend 되도록 함
- 이를 통해 word에 대한 encoder input symbol은 prior word와 predefined lookahead word에만 attend 됨
- Decoder의 경우 symbol 대신 frame을 사용하여 동작함 - 추가적으로 각 cFFT의 post attention position-wise convolutional feed-forward layer는 future dependency를 remove 하기 위해 causal convolution으로 replace 됨
- 이를 통해 word에 대한 encoder input symbol은 prior word와 predefined lookahead word에만 attend 됨
- Pitch $\rho$, energy $\epsilon$, duration $\delta$ predictor는 causal convolution에 기반하여 구성되고, training loss $\mathcal{L}$은 FastPitch를 따름:
(Eq. 1) $\mathcal{L}=\mathcal{L}_{MSE}\left(\text{Mel},\hat{\text{Mel}}\right)+ \mathcal{L}_{MSE}\left(\delta,\hat{\delta}\right)+ \mathcal{L}_{MSE}\left(\rho,\hat{\rho}\right)+\mathcal{L}_{MSE}\left(\epsilon,\hat{\epsilon}\right)$ - Vocoder는 HiFi-GAN의 causal variant로써, Multi-Receptive field Fusion (MRF) block의 모든 convolution을 causal 하게 구성하고 nearest neighbour interpolation을 upsampling으로 사용함
- 추가적으로 generated signal을 multiple sub-band로 decompose 하기 위해 Multi-Scale/Multi-Period Discriminator (MSD, MPD)로 optimize 되는 Pseudo-Quadrature Mirror Filter (PQMF)를 채택함
- PQMF, Sub-Band Discriminator (SBD)는 training 중에만 사용되어 sub-frequency domain에서 generator를 enhance 함 - 추론 시에는 모든 causal convolution layer의 input tail을 state $z$로 cache 함
- 해당 cached state는 next word를 synthesize 할 때 각 layer의 input head와 concatenate 됨
- 추가적으로 generated signal을 multiple sub-band로 decompose 하기 위해 Multi-Scale/Multi-Period Discriminator (MSD, MPD)로 optimize 되는 Pseudo-Quadrature Mirror Filter (PQMF)를 채택함
- 이때 cFFT의 attention block은 intentionally mask 되어 각 word의 timestep이 previous word와 specified lookahead word에만 attend 되도록 함

- [Algorithm 1]과 [Algorithm 2]는 training/inference에서 사용되는 encoder attention mask $M_{e}$와 decoder attention mask $M_{d}$를 구성하는 데 사용됨
- $N_{s}$는 각 word의 phonetic symbol 수, $N_{f}$는 각 word의 mel-frame 수를 의미함
- 특히 $N_{f}$는 $N_{s}$에 의해 각 symbol의 duration을 grouping 한 다음 summation 하여 compute 됨 - $\alpha$는 pre-defined lookahead word 수, $L_{e}, L_{d}$는 각각 $N_{s},N_{f}$를 sum 하여 얻어진 encoder, decoder length를 의미함
- $N_{s}$는 각 word의 phonetic symbol 수, $N_{f}$는 각 word의 mel-frame 수를 의미함

- Synchronous Text-to-Speech Synthesis
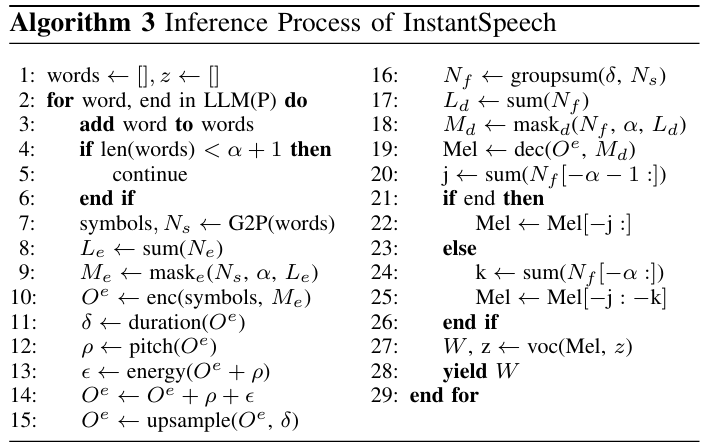
- [Algorithm 3]는 LLM의 text stream에 따라 waveform chunk $W$를 생성하는 inference process에 해당함
- 여기서 LLM이 주어진 input promp $P$에 대해 한번에 하나의 word를 생성한다고 하자
- LLM이 생성하는 word 수가 pre-defined lookahead $\alpha$를 exceed 하면 InstantSpeech는 synthesis를 수행함 - Accumulated word는 G2P module을 통해 처리되어 phonetic symbol과 $N_{s}$를 생성하고, encoder mask $M_{e}$를 생성하는 데 사용됨
- 특히 G2P는 Phonemizer를 활용하고, one-word lookahead 만으로도 current word에 대한 accurate phoneme을 생성할 수 있음 - 먼저 model은 masked encoder를 통해 linguistic feature $O^{e}$를 생성한 다음, pitch $\rho$, energy $\epsilon$, duration $\delta$를 생성함
- 이후 $\delta$를 기반으로 fused feature를 upsampling 함
- 다음으로 $\delta$를 $N_{s}$로 group 하고 각 group을 summation 하여 $N_{f}$를 생성함
- 이는 decoder mask $M_{d}$를 calculate 하는 데 사용됨 - Masked decoder는 current word와 lookahead word를 포함하는 mel을 생성함
- 만약 LLM이 finish 되지 않은 경우, current word의 mel-frame만 retain 하고 lookahead word는 discard 함 - 최종적으로 waveform chunk $W$는 mel과 previous iteration의 cached convolutional state $z$를 사용하여 causal vocoder를 통해 얻어짐
- 여기서 LLM이 주어진 input promp $P$에 대해 한번에 하나의 word를 생성한다고 하자
- Knowledge Distillation
- InstantSpeech는 limited lookahead로 인해 future context에 대한 unrestricted view를 가진 FastPitch에 비해 natural speech를 생성하기 어려움
- 따라서 논문은 FastPitch를 knowledge distillation을 위한 teacher로 사용하여 soft label에 embed 된 richer feature representation을 학습하도록 함
- 이를 위해 논문은 Text-Audio Distillation (TA)와 Text-Only Distillation (TO)를 고려함:
- TA에서는 student가 ground-truth audio와 teacher의 soft label 모두에서 학습할 수 있도록 text-audio paired dataset이 필요함
- TO에서는 student가 teacher를 통해서만 학습하여 LLM이 생성한 text-only data로 distillation 함
- 특히 distillation은 student $s$와 teacher $t$의 identical alignment가 필요하므로 student decoder를 guide 하기 위해 다음의 strategy를 고려함:
- TA의 경우, teacher, student decoder를 모두 guide 하기 위해 ground-truth pitch, energy, duration을 사용함
- TO의 경우, student decoder를 guide 하기 위해 teacher가 predict 한 pitch, energy, duration을 사용함
- 추가적으로 distillation strategy의 경우:
- D1 : duration $\delta$, pitch $\rho$, energy $\epsilon$ predictor output과 함께 decoder output mel-spectrogram을 distill 함
- D2 : D1을 extend 하여 encoder output linguistic feature $O^{e}$를 distill 함
- D3 : 모든 $L$ intermediate layer output $I$를 distill 하여 D2를 extend 함
- 결과적으로 TO, TA의 loss function은:
(Eq. 2) $\mathcal{L}_{TO}=\mathcal{L}_{MSE}\left(\hat{\text{Mel}}_{t},\hat{\text{Mel}}_{s}\right)+\mathcal{L}_{MSE} \left(\hat{\delta}_{t},\hat{\delta}_{s}\right)+\mathcal{L}_{MSE}\left(\hat{\rho}_{t},\hat{\rho}_{s}\right)+\mathcal{L}_{MSE}\left(\hat{\epsilon}_{t},\hat{\epsilon}_{s}\right)$
$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,+\mathcal{L}_{MSE}\left(O^{e}_{t},O^{e}_{s}\right)+\gamma\cdot\sum_{l=1}^{L}\mathcal{L}_{MSE}\left(I_{t,l},I_{s,l}\right),$
$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, \mathcal{L}_{TA}=\lambda\cdot\mathcal{L}+(1-\lambda)\cdot\mathcal{L}_{TO}$
- $\gamma, \lambda$ : hyperparameter
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : LJSpeech, UltraChat
- Comparisons : FastPitch
- Results
- 전체적으로 InstantSpeech는 Look Ahead (LA)가 늘어날수록 MOS가 향상됨

- Performance of Distilled Models
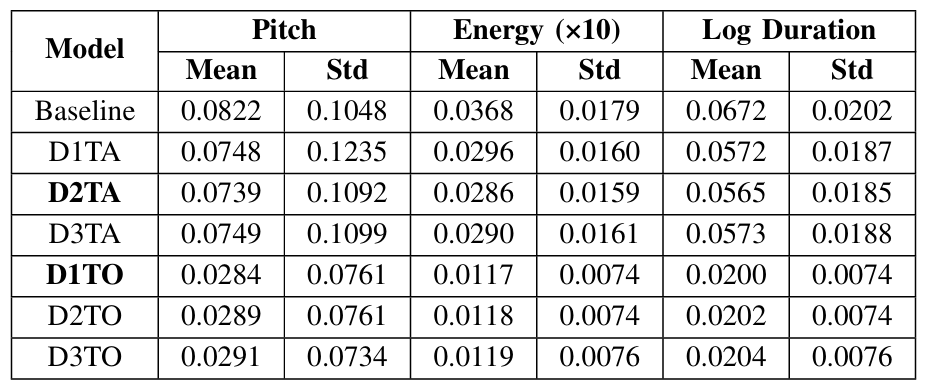
- Text-Audio (TA) Distillation의 경우 encoder output을 distill (D2TA)할 때 가장 낮은 MSE를 달성함
- Text-Only (TO) Distillation의 경우 basic distillation (D1TO)을 수행할 때 가장 낮은 MSE를 달성함
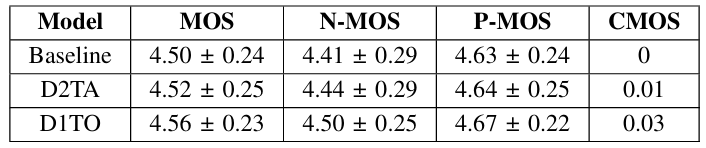
- MOS 측면에서 D2TA, D1TO 모두 baseline 보다 우수한 성능을 보임
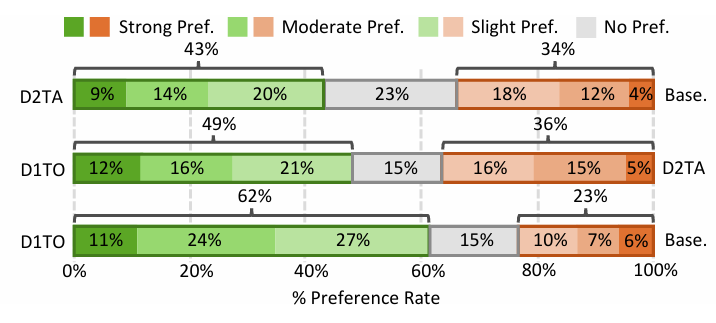
- Preference 측면에서도 D2TA, D1TO 모두 baseline 보다 더 선호됨
- Integration with Large Language Model
- Gemma2 (G), Llama3.1 (L), Mistral NeMo (M.N.)의 3가지 LLM에 대해,
- InstantSpeech (IS)는 FastPitch (FP) 보다 빠른 inference speed를 달성함

반응형
'Paper > TTS' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

