티스토리 뷰
Paper/TTS
[Paper 리뷰] ContextSpeech: Expressive and Efficient Text-to-Speech for Paragraph Reading
feVeRin 2024. 6. 27. 10:52반응형
ContextSpeech: Expressive and Efficient Text-to-Speech for Paragraph Reading
- Text-to-Speech는 sentence에서는 우수한 성능을 보이고 있지만, paragraph/long-form reading에서는 어려움이 있음
- ContextSpeech
- Global text와 speech context를 sentence encoding에 incorporate 하는 memory-cached recurrence mechanism을 도입
- Hierarchically-structured textual semantics를 구성하여 global context enhancement의 scope를 향상
- 추가적으로 linearized self-attention을 채택해 efficiency를 개선
- 논문 (INTERSPEECH 2023) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Text-to-Speech (TTS) 모델은 우수한 sentence-level 합성 성능을 보이고 있지만, 여전히 news reading, audiobook과 같은 paragraph reading에서는 한계가 있음
- 일반적인 TTS 모델은 text를 sentence-level speech로 변환한 다음 paragraph reading을 위해 concatenate 하는 방식을 사용하므로, paragraph 내의 sentence 간의 global context를 capture 하지 못함
- 특히, paragraph 내의 sentence는 isolate되지 않고 speech/textual context와 관련하여 다양한 dependency를 가지므로, 단순 concatenation은 성능 저하로 이어짐 - 추가적으로 variable-length sentence를 가지는 corpus data로 인해 extra-long/short sentence에 대해서는 고품질의 합성을 유지하기가 어려움
- 결과적으로 sentence-level context를 활용한 음성 합성은 다음의 한계점을 가짐:
- Correlation between Adjacent Sentences
- Paragraph reading에서는 semantic information flowing을 통해 adjacent sentence들이 서로 영향을 받음
- 따라서 sentence-level synthesis는 context coherence가 부족하고 expressive reading이 어려움 - Efficiency or Consistency on Extra-Long Sentences
- Extra-long sentence를 합성하면 text와 speech 간의 bad alignment로 인해 high-latency가 발생함
- 이때 일반적으로 sentence는 segment로 분할된 다음, 개별적으로 합성되므로 prosody의 incosistent가 발생할 수 있음 - Quality on Extra-Short Sentences
- 1~2 word로 구성된 extra-short sentence에 대해서 기존 TTS 모델은 bad pronunciation을 보임
- Correlation between Adjacent Sentences
- 일반적인 TTS 모델은 text를 sentence-level speech로 변환한 다음 paragraph reading을 위해 concatenate 하는 방식을 사용하므로, paragraph 내의 sentence 간의 global context를 capture 하지 못함
-> 그래서 다양한 sentence들에 대한 global-level semantic dependency를 반영할 수 있는 paragraph TTS 모델인 ContextSpeech를 제안
- ContextSpeech
- Cross-sentence dependency를 preserve하기 위해 memory-cached recurrence mechanism을 도입해 cached hidden state를 기반으로 segment 간에 knowledge를 transfer 함
- 이때 backbone으로써 Conformer-based TTS 모델을 사용 - Context-aware TTS를 기반으로 text-based contextual encoder를 설계
- 특히 BERT-based embedding, pre-defined statistical information 등에 대한 text-based feature를 input으로 사용하고 phoneme embedding과 통합해 one-to-many mapping 문제를 해결 - Memory와 computation cost를 줄이기 위해, memory reused framework에서 permute-based relative position encoding과 linearized self-attention을 결합
- 이를 통해 softmax self-attention으로 발생하는 quadratic complexity를 완화
- Cross-sentence dependency를 preserve하기 위해 memory-cached recurrence mechanism을 도입해 cached hidden state를 기반으로 segment 간에 knowledge를 transfer 함
< Overall of ContextSpeech >
- 다양한 sentence에 걸쳐 global-level semantic dependency를 반영하는 pragraph TTS 모델
- 결과적으로 효율적인 추론 latency를 달성하면서 variable-length의 sentence로 이루어진 paragraph에 대해서 뛰어난 합성 성능을 달성
2. Method
- ConformerTTS with Memory Reuse
- Backbone Model
- ContextSpeech는 FastSpeech2와 유사한 framework를 기반으로 encoder/decoder에 Conformer Block (CB)를 채택한 ConformerTTS를 기반으로 함
- 이때 CB는 Convolution Module (ConvM)과 Multi-Head Self-Attention (MHSA)를 통합하여 local correlation과 global interaction을 모델링함 - 다음으로 adjacent hidden state 간의 correlation을 encoding 하기 위해 self-attention 다음에 Convolution-based Feed-Forward Network (ConvFFN)이 추가됨
- 구체적으로 ConvM은 convolutional feed-forward module, GLU, depthwise convolution module, 다른 convolutional feed-forward module의 4-stacked component로 구성됨
- $N$을 encoder/decoder의 CB stack 수라고 하면, $n$-th CB의 input feature는 $H_{t}^{n}=[h_{t,1},...,h_{t,L}]$로 represent 됨
- 여기서 $t$는 current sequence index, $L$은 sequence length
- ContextSpeech는 FastSpeech2와 유사한 framework를 기반으로 encoder/decoder에 Conformer Block (CB)를 채택한 ConformerTTS를 기반으로 함
- Segment-level Memory Reuse
- 논문은 아래 그림의 (b)와 같이, 각 layer에서 previous segment의 hidden state를 cache 하고 contextual information을 involving 하기 위해 current segment와 reuse 하는 방식을 도입함
- 이때 previous segment는 fixed-length로 구성되고 current segment는 complete sentence로 사용됨 - 이를 통해 ContextSpeech는 text, speech 모두에서 intact semantic과 acoustic information을 retain 할 수 있음
- 이때 MHSA의 input feature를 reuse 하는 대신, ConvM의 concatenation point 주변의 contextual information을 capture 할 수 있도록 CB의 input feature를 cache 함
- 그러면 $n<N$일 때 $n$-th block의 output이 $(n+1)$-th block의 input이 되므로 hidden state는 (Eq. 1)과 같이 represent 됨:
(Eq. 1) $H_{t}^{n+1}=[\mathrm{SG}(H_{t-1}^{n+1})\circ \mathrm{ConformerBlock}(H_{t}^{n})]$
- $\mathrm{SG}(\cdot)$ : stop-gradient operation
- $[A\circ B]$ : length-dimension에 대한 hidden sequence $A, B$의 concatenation
- 논문은 아래 그림의 (b)와 같이, 각 layer에서 previous segment의 hidden state를 cache 하고 contextual information을 involving 하기 위해 current segment와 reuse 하는 방식을 도입함
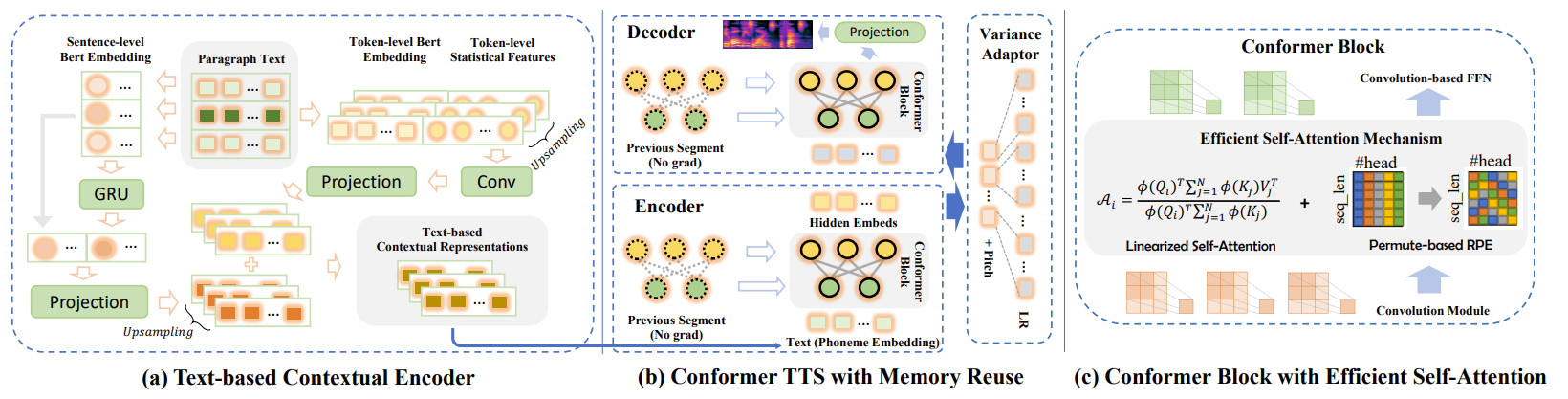
- Text-based Contextual Encoder
- Context가 다르면 동일한 sentence라도 prosody가 달라져야 함
- 특히 external linguistic이나 semantic feature를 반영해 contextual information을 모델링하면 품질을 향상할 수 있음
- 따라서 ContextSpeech는 paragraph reading의 expressiveness를 향상하기 위해 text-based contextual encoder를 도입함 - Pre-defined context range $c$가 있는 paragraph가 주어지면, contextual encoder는 다음의 process를 따라 2가지의 contextual representation을 추출함
- Token-based Contextual Representation
- Current sentence는 token-level BERT embedding (TBE)와 token-level statistical feature (TSF)를 추출하는 데 사용됨
- Concatenation 이후 TBE, TSF는 upsampling 되고, convolution/projection layer를 거쳐 phoneme-level feature와 align 됨 - Sentence-based Contextual Representation
- Input paragraph의 각 sentence에 대해 sentence-level BERT embedding을 추출하여 GRU를 통해 paragraph-level contextual representation (PCR)을 구성함
- 이후 PCR과 current sentence embedding 간의 concatentation을 projection layer로 전달하고, phoneme-level로 upsampling 함
- Token-based Contextual Representation
- 한편으로 TSF는 아래 표와 같음
- $k,s,p$ : 각각 token, sentence, paragraph
- $i_{k,s}$ : sentence에서 current token의 index, $n_{s,p}$ : original paragraph text의 sentence 수
- $\max(n_{k,s})$ : training data에 대한 sentence의 최대 token 수 - 앞선 과정으로 생성된 token-based, sentence-based contextual embedding은 current sentence의 phoneme embedding에 추가됨
- 결과적으로 contextual encoder는 paragraph-level statistical feature를 통합하여 current phoneme horizon을 global paragraph context로 broad 하고,
- Enhanced hierarchical contextual feature를 embedding 한 phoneme을 통해 expressiveness를 개선함
- 특히 external linguistic이나 semantic feature를 반영해 contextual information을 모델링하면 품질을 향상할 수 있음
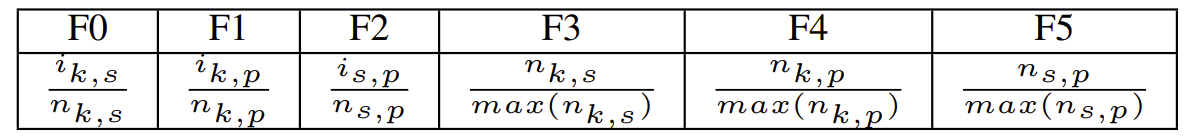
- Efficient Self-Attention Mechanism
- Self-attention module은 quadratic time/memory complexity로 인해 model efficiency를 저해하므로, 논문은 long-form input을 효율적으로 처리하기 위해 다음의 linearized self-attention을 도입함
- Linearized Self-Attention
- $X\in\mathbb{R}^{L\times d}$를 self-attention module의 input이라고 하고, $Q=W_{q}\cdot X, K=W_{k}\cdot X, V=W_{v}\cdot X$를 $X$에 대한 linear transformation이라고 하자
- 그러면 canonical softmax-based self-attention mechanism은 $\mathcal{A}(Q,K,V)=\mathrm{softmax}(QK^{T}/\sqrt{d})V$와 같이 정의됨
- 이때 time/memory complexity는 input length에 따라 quadratic 하게 증가함 - 여기서 attention matrix는 (Eq. 2)와 같이 matrix $Q$와 $K$의 $i$-th/$j$-th row인 $Q_{i}, K_{j}$의 similarity function으로 generalize 될 수 있음:
(Eq. 2) $\mathcal{A}(Q_{i},K,V)=\frac{\sum_{j=1}^{L}\mathrm{sim}(Q_{i},K_{j})V_{j}}{\sum_{j=1}^{L}\mathrm{sim}(Q_{i},K_{j})}$
- Similarity function은 non-negative인 다른 attention function이 될 수 있음 - Qualified kernel function $\phi(x)$가 주어지면 generalized row-wise attention matrix는 (Eq. 3)과 같이 re-written 됨:
(Eq. 3) $\mathcal{A}(Q_{i},K,V)=\frac{\sum_{j=1}^{L} \phi(Q_{i})^{T}\phi(K_{j})V_{j}}{\sum_{j=1}^{L}\phi(Q_{i})^{T}\phi(K_{j})}$ - 이때 matrix mulitplication의 특성에 따라 $\phi(Q_{i})^{T}$는 (Eq. 4)와 같이 summation formula이 taken out 되고, 결과적으로 summation formula를 pre-compute 해 각 query에 reuse 할 수 있음:
(Eq. 4) $=\left(\phi(Q_{i})^{T}\sum_{j=1}^{L}\phi(K_{j})V_{j}\right) / \left(\phi(Q_{i})^{T}\sum_{j=1}^{L}\phi(K_{j})\right)$
- Permute-based Relative Position Encoding
- Linearized self-attention에 relative positional information에 대한 awareness를 반영하기 위해, permute-based relative encoding을 채택함
- 그러면 (Eq. 2)의 $\mathrm{sim}(Q_{i},K_{j})$는 (Eq. 5)와 같이 permute-based format으로 convert 됨:
(Eq. 5) $\mathrm{sim}_{p}(Q_{i},K_{j})=\left(r_{i}P_{B}^{i}\phi(Q_{i})\right)^{T}\left(r^{-j}P_{B}^{j}\phi(K_{j})\right)$
- $r$ : sequence length가 증가함에 따라 exploding 하는 것을 방지하기 위해 1로 설정됨 - Permutation $B : \{1,2,...,d\}\rightarrow \{1,2,...,d\}$는 randomly generate 됨
- $d$ : query/key의 dimension
- 여기서 first $\{1,2,...,d\}$와 second $\{1,2,...,d\}$는 order가 다른 index collection으로 처리될 수 있음 - $P_{B}$는 $B$의 permutation matrix로써, $B(i)=j$이면 $P_{B, ij}=1$이고 그렇지 않으면 $P_{B,ij}=0$
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : Chinese Speech Dataset
- Comparisons : DelightfulTTS
- Results
- Quality on Paragraph Reading
- MOS 측면에서 ContextSpeech는 ground-truth recording 수준의 MOS를 달성함
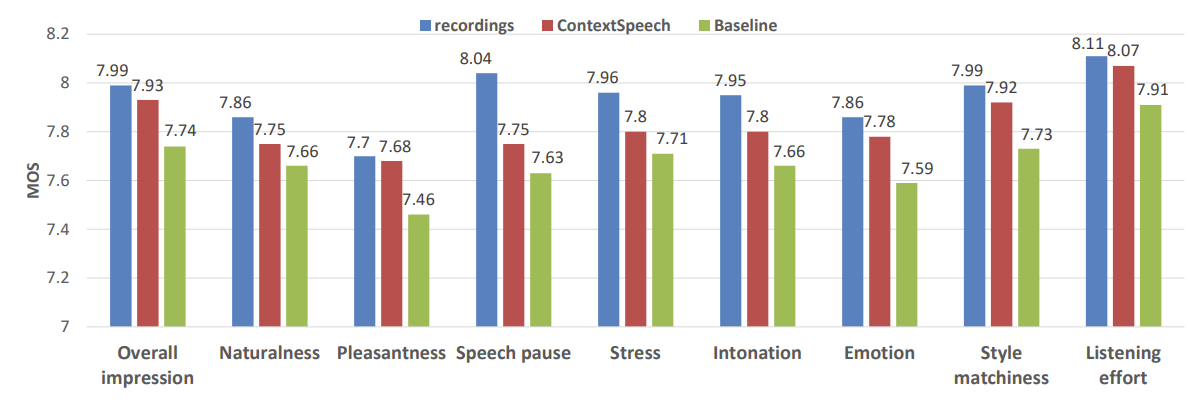
- Prosody 측면에서도 ContextSpeech는 우수한 성능을 보임

- Robustness on Extra-Short Sentence
- 일반적인 TTS 모델에서 extra-short sentence (1~2 word)는 bad pronunciation이나 low speech rate와 같은 robustness 문제가 있음
- Mel-spectrogram 측면에서 이를 확인해 보면, ContextSpeech는 complete formant를 명확하게 생성하는 것으로 나타남

- Efficiency on Extra-Long Sentences
- 한편으로 extra-long sentence에 대해 ContextSpeech는 baseline보다 훨씬 빠른 latency를 달성함

- 추가적으로 extra-long sentence에 대해서도 기존보다 뛰어난 합성 성능을 보임

- Ablation Study
- Ablation Study 측면에서 Memory Recurrence (MR), Text-based Contextual Encoder (TCE), Efficient Self-Attention (ESA)를 각각 제거하는 경우 성능 저하가 발생함
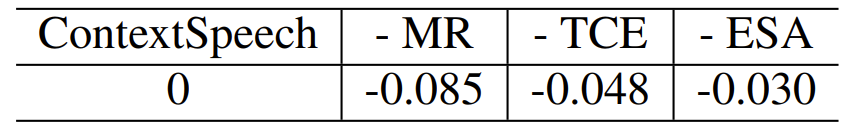
반응형
'Paper > TTS' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

