티스토리 뷰
Paper/ASR
[Paper 리뷰] Listen Like a Teacher: Mitigating Whisper Hallucinations using Adaptive Layer Attention and Knowledge Distillation
feVeRin 2026. 2. 3. 10:30반응형
Listen Like a Teacher: Mitigating Whisper Hallucinations using Adaptive Layer Attention and Knowledge Distillation
- Whisper는 noisy acoustic condition에서 hallucination의 문제가 있음
- ALA & MOKD
- Adaptive Layer Attention (ALA)를 사용해 Whisper encoder의 robustness를 향상
- Multi-Objective Knowledge Distillation (MOKD) framework를 기반으로 hallucination을 suppress
- 논문 (AAAI 2026) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- 최근 Whisper와 같은 Transformer-based encoder-decoder architecture는 Automatic Speech Recognition에서 우수한 성능을 보이고 있음
- BUT, Whisper-style model은 noisy/non-speech segment에 대해 hallucination이 발생함
- 특히 hallucination은 noisy input condition에서 encoder/decoder의 internal representation이 misalign 되는 경우 자주 발생함 - 이를 방지하기 위해 Voice Activity Detection, post-processing, data augmentation 등을 고려할 수 있지만, latent representation 문제를 근본적으로 해결할 수 없음
- BUT, Whisper-style model은 noisy/non-speech segment에 대해 hallucination이 발생함
-> 그래서 Whisper의 hallucination 문제를 개선하기 위해 ALA와 MOKD를 활용한 2-stage framework를 제안
- ALA & MOKD
- Adaptive Layer Attention (ALA)는 Transformer encoder의 hierarchical representation을 활용하는 dynamic fusion mechanism으로써, noisy condition에서 encoder의 robustness를 향상함
- Multi-Objective Knowledge Distillation (MOKD)는 ALA-augmented encoder-decoder model을 teacher로 사용하여 noisy condition에서 decoder behavior를 supervise함
< Overall of This Paper >
- ALA와 MOKD를 활용하여 Whisper의 hallucination을 개선한 ASR framework
- 결과적으로 기존보다 우수한 ASR 성능을 달성
2. Method
- Stage-1의 Adaptive Layer Attention (ALA)는 encoder representation을 향상하고, Stage-2의 Multi-Objective Knowledge Distillation (MOKD)는 noisy condition에서 decoder hallucination을 mitigate 함

- Adaptive Layer Attention
- Whisper와 같은 Transformer-based ASR model은 raw audio를 linguistic representation으로 progressively abstract 하는 deep encoder stack을 활용함
- BUT, noisy condition에서 특정 encoder layer가 distorted/redudant signal을 capture 하여 decoder로 전달하는 경우 ASR 성능이 저하될 수 있음
- 따라서 논문은 ALA를 사용하여 structurally similar encoder layer의 representation을 adaptively fuse 하여 robust, context-aware acoustic modeling을 지원함
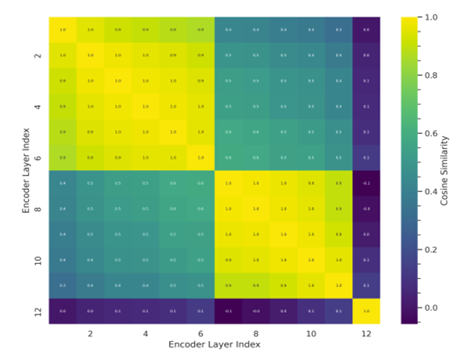
- Inter-Layer Similarity Analysis
- 먼저 noise condition 하에서 모든 encoder layer output 간의 cosine-similarity를 비교해 보면:
- Layer $L1$-$L6$은 high mutual similarity를 가지고, low-level acoustic feature block을 구성함
- Layer $L7$-$L11$은 higher-level semantic abstraction을 가지는 block을 구성함
- Layer $L12$는 다른 layer와 달리 noise에 overfitting 되어 있을 가능성이 크고, decoder input에 대한 specialized optimization을 reflect 함
- 이를 기반으로 $L12$와 같은 noisy/uninformative layer를 decoder에 전달하지 않고도 useful abstraction을 retaining 하는 selective fusion strategy를 고려할 수 있음
- 먼저 noise condition 하에서 모든 encoder layer output 간의 cosine-similarity를 비교해 보면:
- Adaptive Fusion via Block-wise Attention
- Encoder가 모든 $L$ layer에서 $E=\{e_{1},e_{2},...,e_{L}\}$와 같이 hidden state를 생성한다고 하자
- 그러면 encoder layer output 간의 pairwise cosine-similarity를 compute 하고 high inter-layer similarity를 가지는 layer에 대한 $K$ coherent block $\{B_{1},B_{2},...,B_{K}\}$를 구성할 수 있음:
- Mean Block Representation
- 먼저 각 block $B_{k}$에 대해, 해당 block의 모든 hidden state에 mean pooling을 적용하여 block-level representation $r_{k}$를 얻음:
(Eq. 1) $ r_{k}=\frac{1}{|B_{k}|}\sum_{l\in B_{k}}e_{l}$
- 이때 (Eq. 1)은 block-wise embedding set $R=\{r_{1},r_{2},...,r_{K}\}$를 생성함 - Positional Encoding
- Temporal structure를 maintain 하기 위해 mean block representation에 positional encoding을 적용함:
(Eq. 2) $Z=\text{PosEnc}(R)$
- (Eq. 2)로 얻어진 $Z$는 Multi-Head Attention (MHA)로 전달됨 - Adaptive Multi-Head Attention and Final Projection
- 각 token에 대해 final encoder layer의 hidden state를 query로 사용하여 MHA를 통해 block representation $Z$에 attend 함:
(Eq. 3) $h_{t}=\text{MHA}(q_{t},Z,Z)$
- 여기서 $q_{t}$는 position $t$의 final encoder layer에 대한 projected hidden state
- 이후 attention output은 project 되고 original query에 residually add 된 다음, normalize 되어 resulting sequence $H=\{h_{1},h_{2},...,h_{T}\}$를 생성함
- Mean Block Representation
- Multi-Objective Knowledge Distillation
- Encoder에 ALA를 적용한 다음, 논문은 student-teacher Knowledge Distillation (KD)를 활용하여 decoder의 robustness를 향상함
- 이때 clean-teacher model로 noisy-student model을 guide 하여 encoder/decoder representation을 align 함
- Distillation framework는 encoder/decoder representation alignment를 위해 multiple obejctive를 사용함:
- 먼저 $(x^{T},y^{T}), (x^{S},y^{S})$를 각각 clean-teacher, noisy-student의 input/output pair라고 하자
- 그러면 $e^{T}_{t}, e^{T}_{s}$는 timestep $t$의 encoder hidden state, $d_{t}^{T}, d_{t}^{S}$는 timestep $t$의 decoder hidden state와 같음
- 특히 student model은 다음 4가지의 objective를 사용하여 optimize 됨:
- Encoder Cosine-Similarity Loss
- Last layer에서 cosine-similarity를 사용하여 teacher/student encoder representation 간의 alignment를 encourage 하면:
(Eq. 4) $ \mathcal{L}_{Enc\text{_}Cos}=\sum_{t=1}^{T}\left(1-\cos\left(e^{T}_{t},e_{t}^{S}\right)\right)$ - Decoder Cosine-Similarity Loss
- Decoder level에서 context-embedding space를 match 하기 위해 decoder의 last layer에 cosine-similarity를 적용하면:
(Eq. 5) $ \mathcal{L}_{Dec\text{_}Cos}=\sum_{t=1}^{T}\left(1-\cos\left(d^{T}_{t},d_{t}^{S}\right)\right)$ - Decoder Mean Squared Error (MSE) Loss
- Teacher/student cross-attention map에 대한 MSE loss는:
(Eq. 6) $\mathcal{L}_{Dec\text{_}MSE}=\sum_{t=1}^{T}\left|\left| d_{t}^{T}-d_{t}^{S}\right|\right|_{2}^{2}$ - Cross-Entropy (CE) Loss
- Predicted token probability와 ground-truth transcript 간의 CE loss는:
(Eq. 7) $\mathcal{L}_{CE}=-\sum_{t=1}^{T}\log P_{S}(y_{t})$
- Encoder Cosine-Similarity Loss
- 결과적으로 얻어지는 Total Knowledge Distillation Loss는:
(Eq. 8) $\mathcal{L}_{total}=\lambda_{1}\mathcal{L}_{Enc\text{_}Cos}+\lambda_{2}\mathcal{L}_{Dec\text{_}Cos}+\lambda_{3}\mathcal{L}_{Dec\text{_}MSE} + \lambda_{4}\mathcal{L}_{CE}$
- $\lambda_{1}=0.8, \lambda_{2}=\lambda_{3}=\lambda_{4}=1.0$
- 해당 MOKD setting은 student model이 teacher output을 mimic 하고 encoder/decoder space에서 deeper structural similarity를 capture 하도록 보장함
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : Kathbath, CommonVoice, LibriSpeech, DEMAND
- Comparisons : Whisper
- Results
- Whisper encoder에 ALA를 적용하면 더 나은 성능을 얻을 수 있음
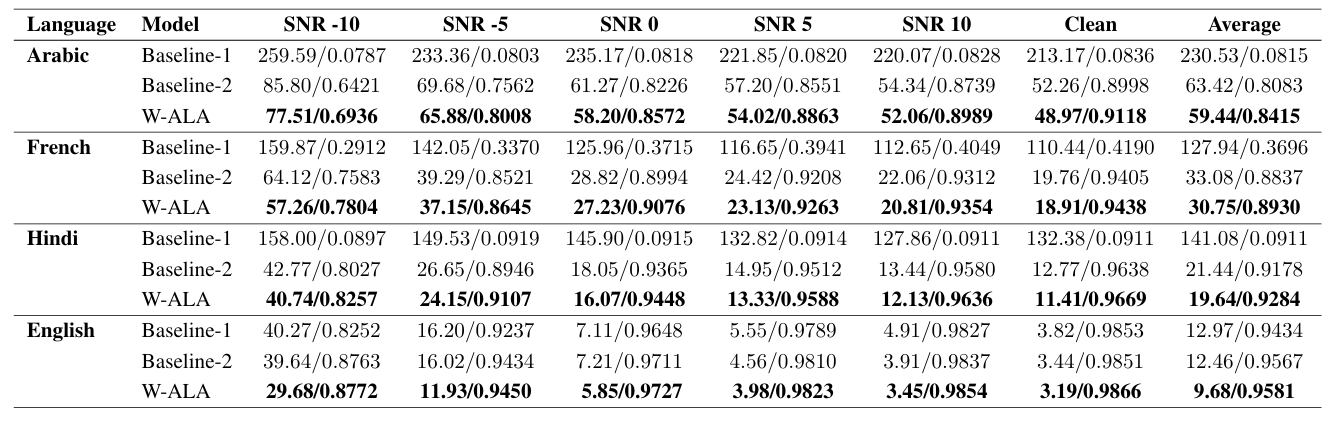
- Efficiency 측면에서 ALA는 minimal overhead를 가짐

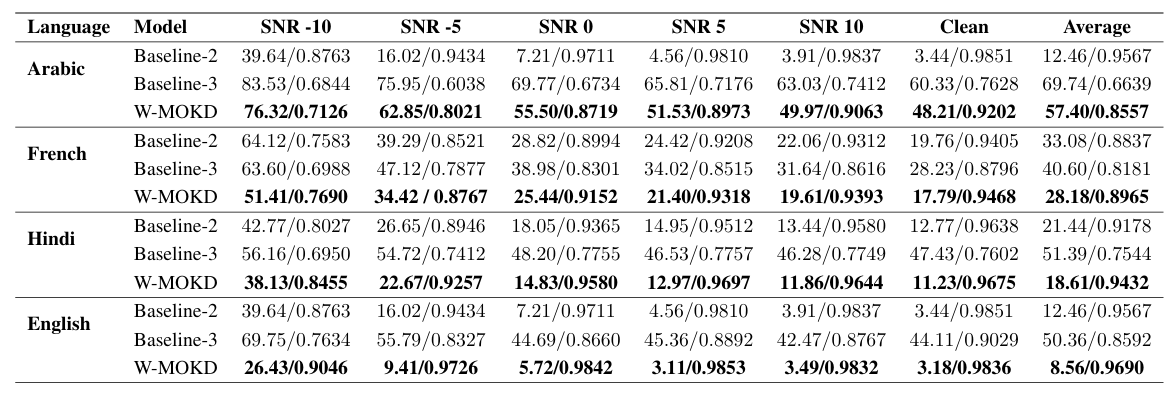
- MOKD 역시 Whisper의 ASR 성능을 개선함
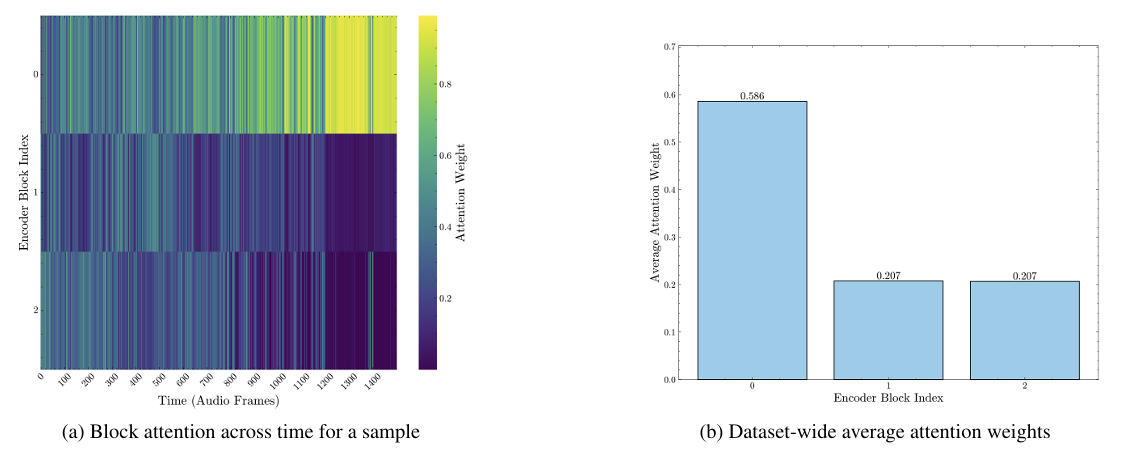
- Encoder Block Robustness
- ALA는 robust encoder feature를 dynamically emphasising 함
- Ablation Study
- MHA mean으로 layer fusing을 수행하는 경우 최적의 성능을 달성할 수 있음

- 각 loss component 역시 성능 향상에 유효함

반응형
'Paper > ASR' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

