티스토리 뷰
Paper/Neural Codec
[Paper 리뷰] LMCodec: A Low Bitrate Speech Codec with Causal Transformer Models
feVeRin 2024. 5. 22. 11:06반응형
LMCodec: A Low Bitrate Speech Codec with Causal Transformer Models
- Neural codec은 낮은 bitrate로 고품질의 audio를 얻을 수 있어야 함
- LMCodec
- Backbone으로 residual vector quantization을 사용하여 audio를 coarse-to-fine token의 hierarchy로 encoding 하는 causal convolutional codec을 사용
- 이때 generative 방식으로 coarse-to-fine token을 예측하도록 Transformer language model을 training 하여 더 적은 수의 code를 transmission 할 수 있음
- Second Transformer의 경우, past transmitted code를 기반으로 next code의 uncertainty를 예측하고 conditional entropy coding을 수행하는 데 사용됨
- 논문 (ICASSP 2023) : Paper Link
1. Introduction
- Speech coding은 distortion을 최소화하면서 speech signal을 제한된 bit로 compress 하는 것을 목표로 함
- Opus, EVS와 같은 parametric codec은 Linear Predictive Coding (LPC), Code Excited Linear Prediction (CELP) 등의 psychoacoustic expertise를 활용했음
- 한편으로 최근의 neural network 기반의 data-driven coding 방식은 coarse-to-fine code에 대한 hierarchy를 구축하여 bitrate scalability와 뛰어난 compression 성능을 보임
- 대표적으로 SoundStream은 causal convolutional architecture와 residual vector quantizer를 활용해 3kbps에서 12kbps Opus 수준의 품질을 달성 - BUT, neural codec, parametric codec 모두 3kbps 보다 낮은 bitrate에서는 품질이 크게 저하됨
-> 그래서 매우 낮은 bitrate에서도 고품질의 coding이 가능한 LMCodec을 제안
- LMCodec
- SoundStream token에 autoregressive Transformer를 사용하여 coarse token distribution의 entropy를 모델링하고 coarse token에서 fine token을 예측함
- 추론 시에는 input waveform에서 SoundStream의 code를 추출하는 대신, 모든 code를 receiver에 send 하지 않고 entropy-coded coarse token만 전달함
- 결과적으로 receiver side에서는 generative language model을 사용하여 coarse token에서 fine token을 예측한 다음, SoundStream decoder로 audio를 reconstruct 함
- 여기서 coarse token으로부터 fine SoundStream token을 예측하기 위해 AudioLM을 활용
- 이때 LMCodec은 fully causal model로 구성되므로 online encoding/decoding이 가능함
- SoundStream token에 autoregressive Transformer를 사용하여 coarse token distribution의 entropy를 모델링하고 coarse token에서 fine token을 예측함
< Overall of LMCodec >
- SoundStream token 예측을 위해 causal Transformer language model인 AudioLM을 결합한 neural codec
- 결과적으로 매우 낮은 bitrate에서도 기존 codec 수준의 합성 품질을 달성
2. Method
- LMCodec은 encoder, residual quantizer, AudioLM block, decoder의 4가지 component로 구성됨
- Encoder, residual quantizer, decoder의 경우, SoundStream을 따름
- Encoder는 time-domain의 raw speech를 input으로 사용하고 speech를 reconstruction 하는데 필요한 information이 포함된 low-rate feature를 추출
- Residual quantizer는 continuous encoded feature의 discrete representation을 찾는 역할
- Decoder는 discrete encoded feature로부터 input speech signal을 reconstruction 하는 역할 - AudioLM은 quantized discrete representation modeling을 language modeling으로 치환하여, previous audio token이 주어졌을 때 next discrete audio token의 probability distribution을 추정함
- Encoder, residual quantizer, decoder의 경우, SoundStream을 따름

- SoundStream
- LMCodec에서 SoundStream은 high-quality audio token을 생성하기 위해 채택됨
- Encoder
- Length $T$의 raw speech signal $x\in[-1,1]^{T}$가 주어지면, encoder $\mathcal{E}:[-1,1]^{T}\rightarrow \mathbb{R}^{T_{e}\times N_{e}}$는 각각 dimension $N_{e}$를 갖는 length $T_{e}\ll T$의 embedding sequence를 생성함
- 이때 encoder는 $T=16\text{kHz}$의 raw waveform speech를 input으로 하여 frame rate가 $50\text{Hz}$인 $N_{e}=128$ dimensional speech feature를 생성함
- 구조적으로 encoder는 causal 1D convolution을 기반으로 하는 fully convolutional architecture를 따름
- 따라서 algorithmic delay는 overall striding factor에 의해 결정됨 ($T/T_{e}=320$ sample 또는 $20\text{ms}$)
- Residual Vector Quantizer (RVQ)
- Low-bandwidth channel을 통한 continuous speech feature transmission은 RVQ를 통해 수행됨
- 여기서 feature는 distortion을 최소화하면서 discrete representation으로 변환됨 - Encoded feature $\mathbf{e}\in\mathbb{R}^{T_{e}\times N_{e}}$가 주어지면, RVQ $\mathcal{Q}:\mathbb{R}^{T_{e}\times N_{e}}\rightarrow\{0,...,2^{\lceil\log N_{c}\rceil}-1\}^{T_{e}\times N_{q}}$는 $\mathbf{e}$의 binary representation과 해당 inversion을 계산함
- $N_{q}$ : quantizer 수, $N_{c}$ : single quantizer의 codebook size - 논문에서는 $N_{c}=2^{10}$ size의 codebook을 사용하고, RVQ 수를 $N_{q}\in\{3,4,6,12,24\}$로 설정
- Low-bandwidth channel을 통한 continuous speech feature transmission은 RVQ를 통해 수행됨
- Decoder
- Decoder $\mathcal{D}:\mathbb{E}^{T_{e}\times N_{e}} \rightarrow [-1,1]^{T}$는 post-quantized embedding으로부터 original speech signal을 합성함
- 논문에서는 waveform, spectral domain에 대한 loss 뿐만 아니라 adversarial loss로 train 된 CNN-based decoder를 채택
- 구조적으로는 encoder architecture와 유사하고, upsampling을 위해 transposed convolutional layer를 사용함 - 추가적으로 adversarial training을 위해 waveform domain과 STFT domain에 대한 2가지 discriminator를 사용
- Encoder
- AudioLM
- 논문은 SoundStream token의 language modeling을 위해 AudioLM을 활용함
- 특히 bottleneck에 language model을 추가하면 future SoundStream token, VQ layer token distribution에 대한 다양한 모델링이 가능해짐
- 먼저 $N_{\mathcal{C}}, N_{\mathcal{F}}$를 각각 coarse-level, fine-level AudioLM quantizer 수라고 하자
- 그러면 $N_{\mathcal{C}}+N_{\mathcal{F}}=3$부터 $N_{\mathcal{C}}+N_{\mathcal{F}}=24$까지 다양한 $(N_{\mathcal{C}},N_{\mathcal{F}})$ 조합을 구성할 수 있음
- 추가적으로 $c_{k}^{(n)}$은 frame $n$과 VQ layer $k$의 SoundStream token을 의미 - Coarse-level AudioLM
- Coarse-level AudioLM은 past information을 바탕으로 next coarse SoundStream token의 conditional distribution을 모델링하는 것을 목표로 함:
(Eq. 1) $p_{\mathcal{C}}\left(c_{k}^{(n)}\left| \underset{\text{coarse-level current frame}}{\underbrace{c_{k-1}^{(n)},...,c_{1}^{(n)}}}, \underset{\text{past information}}{\underbrace{c_{N_{\mathcal{C}}}^{(n-1)},...,c_{1}^{(1)} }}\right.\right)$
- $k\in\{1,...,N_{\mathcal{C}}\}$ - Future SoundStream token distribution이 주어지면, lossless Entropy Coding을 사용하여 codec을 구축함
- 구체적으로, SoundStream token의 discrete probability distribution은 sender, receiver side 모두에서 추정될 수 있으므로 이를 기반으로 Entropy Codec을 drive 함
- LMCodec에서는 single audio frame 당 $N_{\mathcal{C}}$ token만 transmit 하면 되고, 나머지 $N_{\mathcal{F}}$ token은 receiver side에서만 생성됨
- Coarse-level AudioLM은 past information을 바탕으로 next coarse SoundStream token의 conditional distribution을 모델링하는 것을 목표로 함:
- Fine-level AudioLM
- Coarse-level AudioLM과 비슷하게, fine-level AudioLM은 past information 외에 bottom VQ layer에 대한 information을 바탕으로 top VQ layer를 예측함
- 특히, LMCodec은 다음과 같이 coarse-level token과 pas information을 기반으로 하여 fine-level SoundStream token distribution을 모델링:
(Eq. 2) $p_{\mathcal{F}}\left(c_{k}^{(n)}\left| \underset{\text{fine-level current frame}}{\underbrace{c_{k-1}^{(n)},...,c_{N_{\mathcal{C}}+1}^{(n)}}}, \underset{\text{coarse-level current frame}}{\underbrace{c_{N_{\mathcal{C}}}^{(n)},...,c_{1}^{(n)} }}, \underset{\text{past information}}{\underbrace{c_{N_{\mathcal{C}}+N_{\mathcal{F}}}^{(n-1)},...,c_{1}^{(1)} }}\right.\right)$
- $k\in \{N_{\mathcal{C}+1,...,N_{\mathcal{C}}+N_{\mathcal{F}}}\}$ - Coarse-level token만 transmit 하기 때문에, ground-truth coarse-level SoundStream token에 access 할 수 있다고 가정하여 fine-level token distribution을 모델링함
- 이때 논문은 AudioLM을 causal 하게 구성함으로써 online decoding을 가능하게 함
- Entropy Coding (EC)
- Coarse-level SoundStream token distribution이 주어지면, LMCodec은 lossless data compression technique인 entropy coding을 사용하여 data를 transmit 함
- 논문에서는 RVQ의 각 code를 개별적으로 처리하고 grouping은 적용하지 않음
- 먼저 LMCodec은 raw audio가 주어지면 audio를 SoundStream token으로 encoding 하고 SoundStream token의 probability distribution을 모델링하여 entropy codec을 driving 함
- 여기서 SoundStream token의 discrete probability distribution은 receiver와 sender side 모두에서 추정될 수 있으므로, receiver는 coarse token을 losslessly reconstruct 할 수 있음
- 결과적으로 transmitted coarse-level token에서 fine-level AudioLM을 사용하여 fine-level token을 합성하고 SoundStream decoder를 사용하여 fine-level, coarse-level token 모두에서 audio를 생성함
- Training Strategy
- LMCodec은 two-stage training paradigm을 채택하여, 먼저 encoder, quantizer, decoder를 training 한 다음, 해당 component의 weight를 freeze 하고 AudioLM component를 training 함
- 여기서 coarse-level AudioLM과 fine-level AudioLM을 개별적으로 training함
- Loss Functions
- Standard adversarial loss, feature matching loss, reconstruction loss, quantization loss를 사용하여 SoundStream을 training함
- AudioLM의 경우, vocabulary space에 대한 language modeling을 위해 cross-entropy loss를 활용
- Training Configurations
- Codec module을 구성하기 위해, $\mathrm{T5X}$에서 제공되는 SoundStream, AudioLM의 encoder, decoder, quantizer, generator, discriminator architecture를 활용
- 약 250M parameter를 가짐 - SoundStream은 1M step 동안 LibriVox dataset을 사용해 $16\text{kHz}$의 audio로 training 됨
- Fine-/Coarse-level AudioLM은 0.8 decay rate의 Adafactor optimizer를 사용해 batch size 32, sequence length 1024인 SoundStream token에 대해 1M step 동안 Libri-Light dataset으로 training 됨
- 이때 bitrate는 coarse-level AudioLM의 code로부터 entropy coding을 적용해 계산됨
- Codec module을 구성하기 위해, $\mathrm{T5X}$에서 제공되는 SoundStream, AudioLM의 encoder, decoder, quantizer, generator, discriminator architecture를 활용
3. Experiments
- Settings
- Dataset : LibriSpeech, VCTK
- Comparisons : SoundStream, Opus
- Results
- Subjective Evaluation
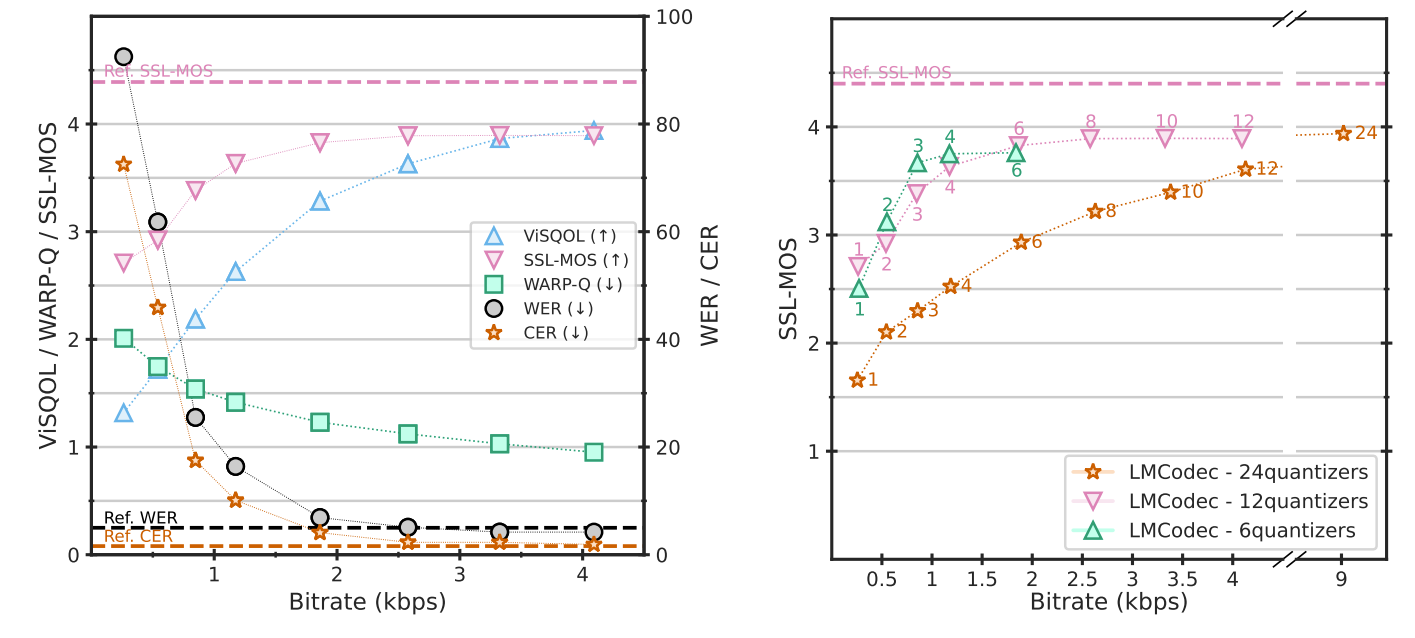
- MUSHRA test 측면에서 4개의 quantizer를 가지는 LMCodec-4/6은 1.1kbps에서 12kpbs Opus 수준의 품질을 보임
- LMCodec-$x/y$ : $N_{\mathcal{C}}=x, N_{\mathcal{C}}+N_{\mathcal{F}}=y$ - 한편으로 2.6kbps에서 8개 quantizer를 사용하는 LMCodec-8/12는 6kbps의 SoundStream과 비슷한 성능을 달성
- MUSHRA test 측면에서 4개의 quantizer를 가지는 LMCodec-4/6은 1.1kbps에서 12kpbs Opus 수준의 품질을 보임

- Discussion
- LibriSpeech에서 future token prediction의 accuracy와 LMCodec의 bitrate performance를 비교해 보면
- Fine-level AudioLM 측면에서, reasonable audio output을 생성하기 위해 반드시 correct code를 생성할 필요는 없는 것으로 나타남
- 한편으로 AudioLM의 code prediction distribution을 시각화해 보면, audio input이 phoneme의 중간인 경우 confident 한 예측이 가능함
- 반면 silence section에 대해서는 future word prediction에 대해 low confident 함

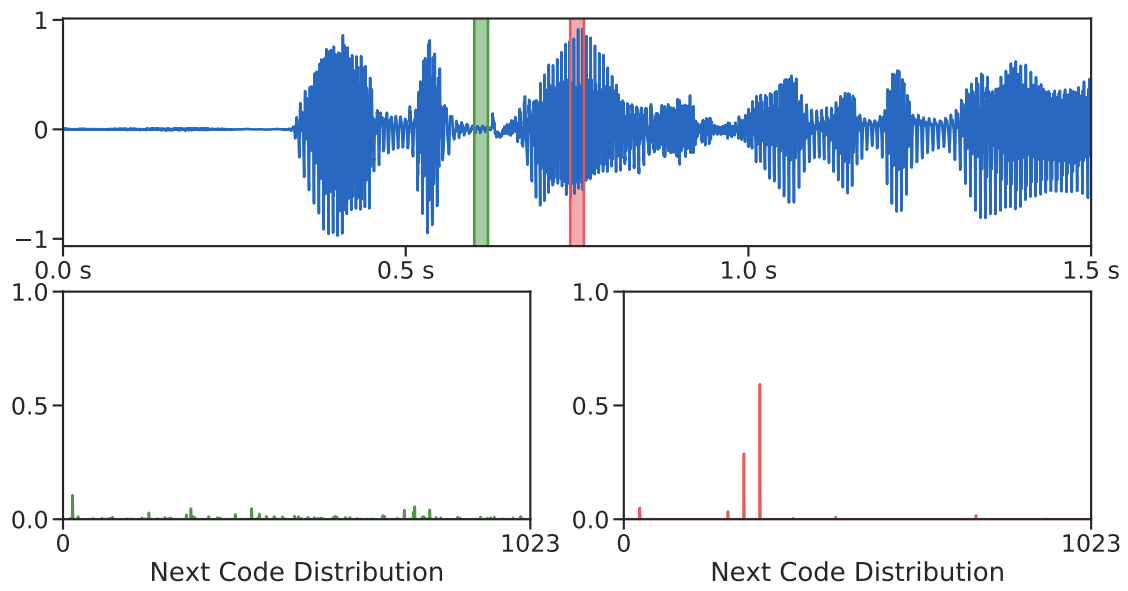
- Voice Activity Detection (VAD)
- Voice activity가 있는 audio region에만 LMCodec을 적용해 보면
- Non-speech signal의 entropy는 speech signal의 entropy보다 높기 때문에 voice만 transmitting 하는 경우 기존과 비슷한 수준의 bitrate를 얻음
- Non-voice에 대해서 zero-bit를 사용하는 경우, Opus와 비슷한 variable bitrate scheme을 활용 가능하므로 매우 낮은 bitrate를 달성 가능함

- Objective Evaluation
- 정량적인 metric 측면에서 성능을 비교해 보면
- LMCodec은 더 적은 수의 quantizer로 더 높은 품질의 audio를 얻을 수 있음
- 즉, 합성된 fine token이 ground-truth와 다르더라도 LMCodec의 language model이 coarse token을 고려해 fine distribution을 잘 모델링할 수 있음을 의미함
반응형
'Paper > Neural Codec' 카테고리의 다른 글
댓글

